Comparing loadings update algorithms
Jason Willwerscheid
7/19/2018
Last updated: 2018-07-20
workflowr checks: (Click a bullet for more information)-
✔ R Markdown file: up-to-date
Great! Since the R Markdown file has been committed to the Git repository, you know the exact version of the code that produced these results.
-
✔ Environment: empty
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
-
✔ Seed:
set.seed(20180714)The command
set.seed(20180714)was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible. -
✔ Session information: recorded
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
-
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility. The version displayed above was the version of the Git repository at the time these results were generated.✔ Repository version: c23f41c
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can usewflow_publishorwflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.Ignored files: Ignored: .DS_Store Ignored: .Rhistory Ignored: .Rproj.user/ Ignored: docs/.DS_Store Ignored: docs/figure/.DS_Store
Expand here to see past versions:
Intro
Here I implement the algorithm described in a previous note and compare results with FLASH.
Code
Click “Code” to view the implementation.
# INITIALIZATION FUNCTIONS ------------------------------------------
add_new_altfl <- function(data, fl, seed=1) {
set.seed(seed)
altfl <- list()
altfl$tau <- fl$tau
altfl$Rk <- flashr:::flash_get_R(data, fl)
n <- nrow(fl$tau)
p <- ncol(fl$tau)
altfl$wl <- rep(0.1, n)
altfl$wf <- rep(0.1, p)
altfl$mul <- rnorm(n)
altfl$muf <- rnorm(p)
altfl$s2l <- rep(1, n)
altfl$s2f <- rep(1, p)
altfl$al <- altfl$af <- 1
altfl$pi0l <- altfl$pi0f <- 0.9
altfl$KL <- sum(unlist(fl$KL_l) + unlist(fl$KL_f))
return(altfl)
}
fl_to_altfl <- function(data, fl, k) {
altfl <- list()
altfl$tau <- fl$tau
altfl$Rk <- flashr:::flash_get_R(data, fl)
altfl$al <- fl$gl[[k]]$a
altfl$pi0l <- fl$gl[[k]]$pi0
altfl$af <- fl$gf[[k]]$a
altfl$pi0f <- fl$gf[[k]]$pi0
s2 = 1/(fl$EF2[, k] %*% t(fl$tau))
s = sqrt(s2)
Rk = flashr:::flash_get_Rk(data, fl, k)
x = fl$EF[, k] %*% t(Rk * fl$tau) * s2
w = 1 - fl$gl[[k]]$pi0
a = fl$gl[[k]]$a
altfl$wl <- ebnm:::wpost_normal(x, s, w, a)
altfl$mul <- ebnm:::pmean_cond_normal(x, s, a)
altfl$s2l <- ebnm:::pvar_cond_normal(s, a)
s2 = 1/(fl$EL2[, k] %*% fl$tau)
s = sqrt(s2)
Rk = flashr:::flash_get_Rk(data, fl, k)
x = fl$EL[, k] %*% (Rk * fl$tau) * s2
w = 1 - fl$gf[[k]]$pi0
a = fl$gf[[k]]$a
altfl$wf <- ebnm:::wpost_normal(x, s, w, a)
altfl$muf <- ebnm:::pmean_cond_normal(x, s, a)
altfl$s2f <- ebnm:::pvar_cond_normal(s, a)
altfl$KL <- sum(unlist(fl$KL_l)[-k] + unlist(fl$KL_f)[-k])
return(altfl)
}
altfl_to_fl <- function(altfl, fl, k) {
fl$EL[, k] <- compute_EX(altfl$wl, altfl$mul)
fl$EL2[, k] <- compute_EX2(altfl$wl, altfl$mul, altfl$s2l)
fl$EF[, k] <- compute_EX(altfl$wf, altfl$muf)
fl$EF2[, k] <- compute_EX2(altfl$wf, altfl$muf, altfl$s2f)
fl$gl[[k]] <- list(pi0 = altfl$pi0l, a = altfl$al)
fl$gf[[k]] <- list(pi0 = altfl$pi0f, a = altfl$af)
fl$ebnm_fn_l <- fl$ebnm_fn_f <- "alt"
fl$ebnm_param_l <- fl$ebnm_param_f <- list()
fl$tau <- altfl$tau
return(fl)
}
# OBJECTIVE FUNCTION ------------------------------------------------
compute_obj <- function(altfl) {
with(altfl, {
EL <- compute_EX(wl, mul)
EL2 <- compute_EX2(wl, mul, s2l)
EF <- compute_EX(wf, muf)
EF2 <- compute_EX2(wf, muf, s2f)
obj <- rep(0, 8)
obj[1] <- sum(0.5 * log(tau / (2 * pi)))
obj[2] <- sum(-0.5 * (tau * (Rk^2 - 2 * Rk * outer(EL, EF) + outer(EL2, EF2))))
tmp <- (1 - wl) * (log(pi0l) - log(1 - wl))
obj[3] <- sum(tmp[!is.nan(tmp)])
tmp <- wl * (log(1 - pi0l) - log(wl))
obj[4] <- sum(tmp[!is.nan(tmp)])
obj[5] <- sum(0.5 * wl * (log(al) + log(s2l) + 1 - al * (mul^2 + s2l)))
tmp <- (1 - wf) * (log(pi0f) - log(1 - wf))
obj[6] <- sum(tmp[!is.nan(tmp)])
tmp <- wf * (log(1 - pi0f) - log(wf))
obj[7] <- sum(tmp[!is.nan(tmp)])
obj[8] <- sum(0.5 * wf * (log(af) + log(s2f) + 1 - af * (muf^2 + s2f)))
return(sum(obj) + KL)
})
}
compute_EX <- function(w, mu) {
return(as.vector(w * mu))
}
compute_EX2 <- function(w, mu, sigma2) {
return(as.vector(w * (mu^2 + sigma2)))
}
# UPDATE FUNCTIONS --------------------------------------------------
update_a <- function(w, EX2) {
return(sum(w) / sum(EX2))
}
update_pi0 <- function(w) {
return(sum(1 - w) / length(w))
}
update_mul <- function(a, tau, Rk, EF, EF2) {
n <- nrow(tau)
p <- ncol(tau)
numer <- rowSums(tau * Rk * matrix(EF, nrow=n, ncol=p, byrow=TRUE))
denom <- a + rowSums(tau * matrix(EF2, nrow=n, ncol=p, byrow=TRUE))
return(numer / denom)
}
update_muf <- function(a, tau, Rk, EL, EL2) {
n <- nrow(tau)
p <- ncol(tau)
numer <- colSums(tau * Rk * matrix(EL, nrow=n, ncol=p, byrow=FALSE))
denom <- a + colSums(tau * matrix(EL2, nrow=n, ncol=p, byrow=FALSE))
return(numer / denom)
}
update_s2l <- function(a, tau, EF2) {
n <- nrow(tau)
p <- ncol(tau)
return(1 / (a + rowSums(tau * matrix(EF2, nrow=n, ncol=p, byrow=TRUE))))
}
update_s2f <- function(a, tau, EL2) {
n <- nrow(tau)
p <- ncol(tau)
return(1 / (a + colSums(tau * matrix(EL2, nrow=n, ncol=p, byrow=FALSE))))
}
update_wl <- function(a, pi0, mu, sigma2, tau, Rk, EF, EF2) {
C1 <- log(1 - pi0) - log(pi0)
C2 <- 0.5 * (log(a) + log(sigma2) - a * (mu^2 + sigma2) + 1)
C3 <- rowSums(tau * (Rk * outer(mu, EF) - 0.5 * outer(mu^2 + sigma2, EF2)))
C <- C1 + C2 + C3
return(1 / (1 + exp(-C)))
}
update_wf <- function(a, pi0, mu, sigma2, tau, Rk, EL, EL2) {
C1 <- log(1 - pi0) - log(pi0)
C2 <- 0.5 * (log(a) + log(sigma2) - a * (mu^2 + sigma2) + 1)
C3 <- colSums(tau * (Rk * outer(EL, mu) - 0.5 * outer(EL2, mu^2 + sigma2)))
C <- C1 + C2 + C3
return(1 / (1 + exp(-C)))
}
# ALGORITHM ---------------------------------------------------------
update_tau <- function(altfl) {
within(altfl, {
EL <- compute_EX(wl, mul)
EL2 <- compute_EX2(wl, mul, s2l)
EF <- compute_EX(wf, muf)
EF2 <- compute_EX2(wf, muf, s2f)
R2 <- Rk^2 - 2 * Rk * outer(EL, EF) + outer(EL2, EF2)
tau <- matrix(1 / colMeans(R2), nrow=nrow(tau), ncol=ncol(tau),
byrow=TRUE)
})
}
update_loadings_post <- function(altfl) {
within(altfl, {
EF <- compute_EX(wf, muf)
EF2 <- compute_EX2(wf, muf, s2f)
mul <- update_mul(al, tau, Rk, EF, EF2)
s2l <- update_s2l(al, tau, EF2)
wl <- update_wl(al, pi0l, mul, s2l, tau, Rk, EF, EF2)
})
}
update_loadings_prior <- function(altfl) {
within(altfl, {
EL2 <- compute_EX2(wl, mul, s2l)
al <- update_a(wl, EL2)
pi0l <- update_pi0(wl)
})
}
update_factor_post <- function(altfl) {
within(altfl, {
EL <- compute_EX(wl, mul)
EL2 <- compute_EX2(wl, mul, s2l)
muf <- update_muf(af, tau, Rk, EL, EL2)
s2f <- update_s2f(af, tau, EL2)
wf <- update_wf(af, pi0f, muf, s2f, tau, Rk, EL, EL2)
})
}
update_factor_prior <- function(altfl) {
within(altfl, {
EF2 <- compute_EX2(wf, muf, s2f)
af <- update_a(wf, EF2)
pi0f <- update_pi0(wf)
})
}
do_one_update <- function(altfl) {
obj <- rep(0, 5)
altfl <- update_tau(altfl)
obj[1] <- compute_obj(altfl)
altfl <- update_loadings_post(altfl)
obj[2] <- compute_obj(altfl)
altfl <- update_loadings_prior(altfl)
obj[3] <- compute_obj(altfl)
altfl <- update_factor_post(altfl)
obj[4] <- compute_obj(altfl)
altfl <- update_factor_prior(altfl)
obj[5] <- compute_obj(altfl)
return(list(altfl = altfl, obj = obj))
}
optimize_alt_fl <- function(altfl, tol = .01, verbose = FALSE) {
obj <- compute_obj(altfl)
diff <- Inf
while (diff > tol) {
tmp <- do_one_update(altfl)
new_obj <- tmp$obj[length(tmp$obj)]
diff <- new_obj - obj
obj <- new_obj
if (verbose) {
message(paste("Objective:", obj))
}
altfl <- tmp$altfl
}
return(altfl)
}Fit
Using the same dataset as in previous investigations, I fit a FLASH object with four factors (recall that it’s the fourth factor that has been causing problems during loadings updates):
load("./data/before_bad.Rdata")
# devtools::install_github("stephenslab/flashr")
devtools::load_all("/Users/willwerscheid/GitHub/flashr")Loading flashr# devtools::install_github("stephenslab/flashr")
devtools::load_all("/Users/willwerscheid/GitHub/ebnm")Loading ebnmfl <- flash_add_greedy(data, Kmax=4, verbose=FALSE)fitting factor/loading 1fitting factor/loading 2fitting factor/loading 3fitting factor/loading 4The objective as computed by FLASH is:
flash_get_objective(data, fl)[1] -1297135I now convert the fourth factor to an “altfl” object. The objective as computed by the alternate method is:
altfl <- fl_to_altfl(data, fl, 4)
compute_obj(altfl)[1] -1287925Next, I optimize the altfl object:
altfl <- optimize_alt_fl(altfl, verbose=TRUE)Objective: -1266527.52893897Objective: -1259591.41880171Objective: -1256717.73280192Objective: -1256092.73281445Objective: -1255909.73574933Objective: -1255818.46915015Objective: -1255766.3647692Objective: -1255735.3950312Objective: -1255716.97331457Objective: -1255705.43249546Objective: -1255697.71996832Objective: -1255692.31493727Objective: -1255688.43367143Objective: -1255685.61158832Objective: -1255683.53045841Objective: -1255681.97109968Objective: -1255680.78688195Objective: -1255679.87854253Objective: -1255679.17674322Objective: -1255678.63159121Objective: -1255678.20636055Objective: -1255677.87357066Objective: -1255677.61241567Objective: -1255677.40700628Objective: -1255677.24512755Objective: -1255677.11733974Objective: -1255677.01631629Objective: -1255676.93635016Objective: -1255676.87298197Objective: -1255676.82271789Objective: -1255676.78281419Objective: -1255676.75111177Objective: -1255676.72590854Objective: -1255676.7058606Objective: -1255676.68990533Objective: -1255676.67720158Objective: -1255676.66708273Objective: -1255676.65902003Finally, I put the altfl object back into the fourth factor of the flash object.
fl2 <- altfl_to_fl(altfl, fl, 4)Comparison
The fits are very different. For priors on both factors and loadings, the altfl fit favors less sparsity (smaller spikes, i.e., smaller pi0) and more shrinkage (narrower slabs, i.e., greater a).
list(loadings = fl$gl[[4]], alt_loadings = fl2$gl[[4]])$loadings
$loadings$pi0
[1] 0.72317
$loadings$a
[1] 0.04110932
$alt_loadings
$alt_loadings$pi0
[1] 0.6009072
$alt_loadings$a
[1] 0.09951342list(factors = fl$gf[[4]], alt_factors = fl2$gf[[4]])$factors
$factors$pi0
[1] 0.3616584
$factors$a
[1] 29.84806
$alt_factors
$alt_factors$pi0
[1] 0.1264111
$alt_factors$a
[1] 46.48745A scatterplot comparing the fitted fourth factor/loading appears as follows:
fitted <- flash_get_fitted_values(fl)
fitted2 <- flash_get_fitted_values(fl2)
minval <- min(c(fitted, fitted2))
maxval <- max(c(fitted, fitted2))
plot(fitted, fitted2, pch='.',
xlab="FLASH fit", ylab="Alternate fit",
xlim=c(minval, maxval), ylim=c(minval, maxval),
main="Fitted values")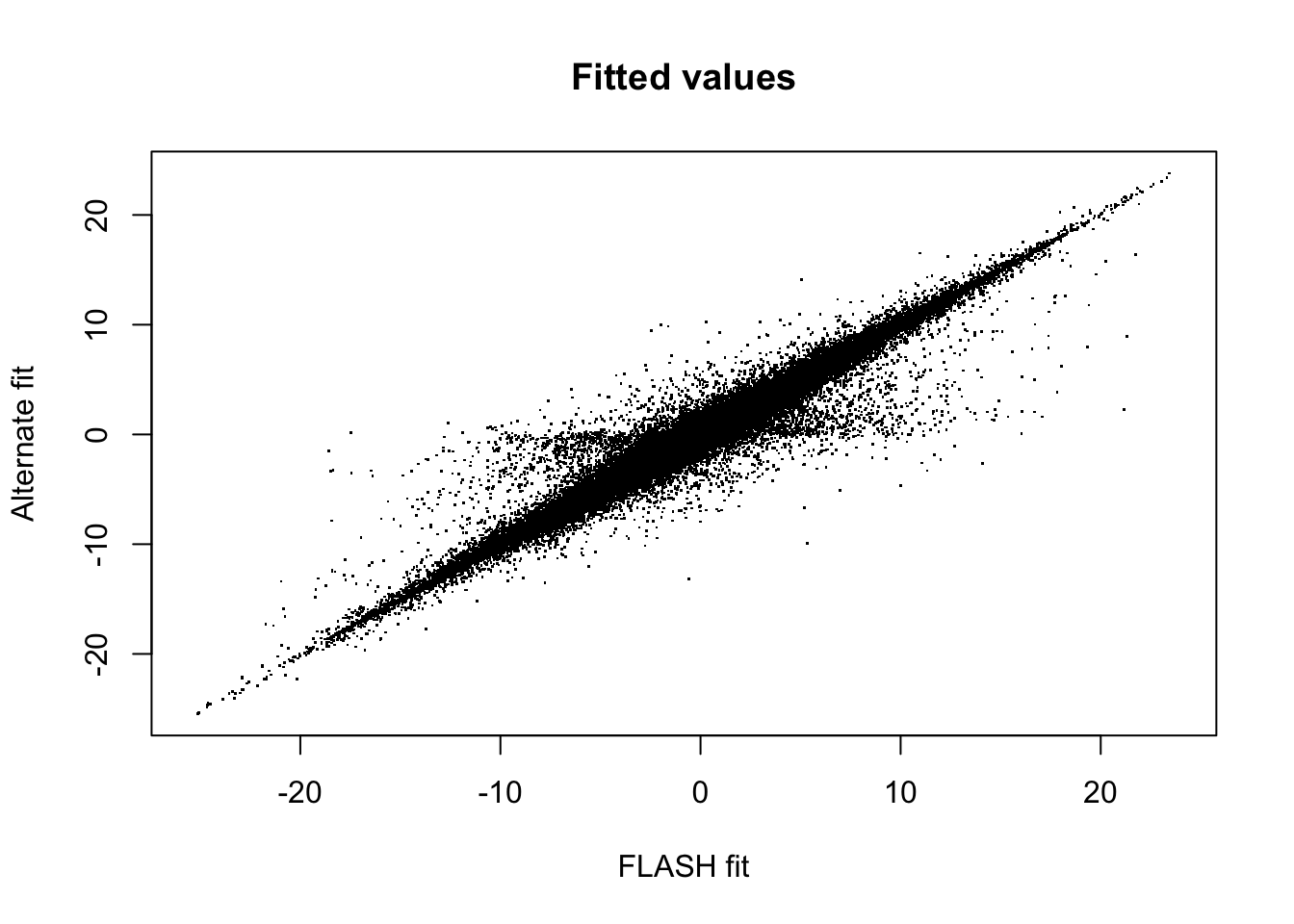
Expand here to see past versions of comp_fitted-1.png:
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2cbe7dd | Jason Willwerscheid | 2018-07-19 |
To see what’s going on, I fit the estimated loadings against the estimated prior on the loadings. For the FLASH fit:
plot(density(fl$EL[, 4]), xlim=c(-15, 15), ylim=c(0, 0.1),
main="FLASH loadings")
grid <- seq(-15, 15, by=.05)
y <- (1 - fl$gl[[4]]$pi0) * dnorm(grid, 0, 1/sqrt(fl$gl[[4]]$a))
lines(grid, y, lty=2)
legend("topright", legend = c("fitted", "prior"), lty = c(1, 2))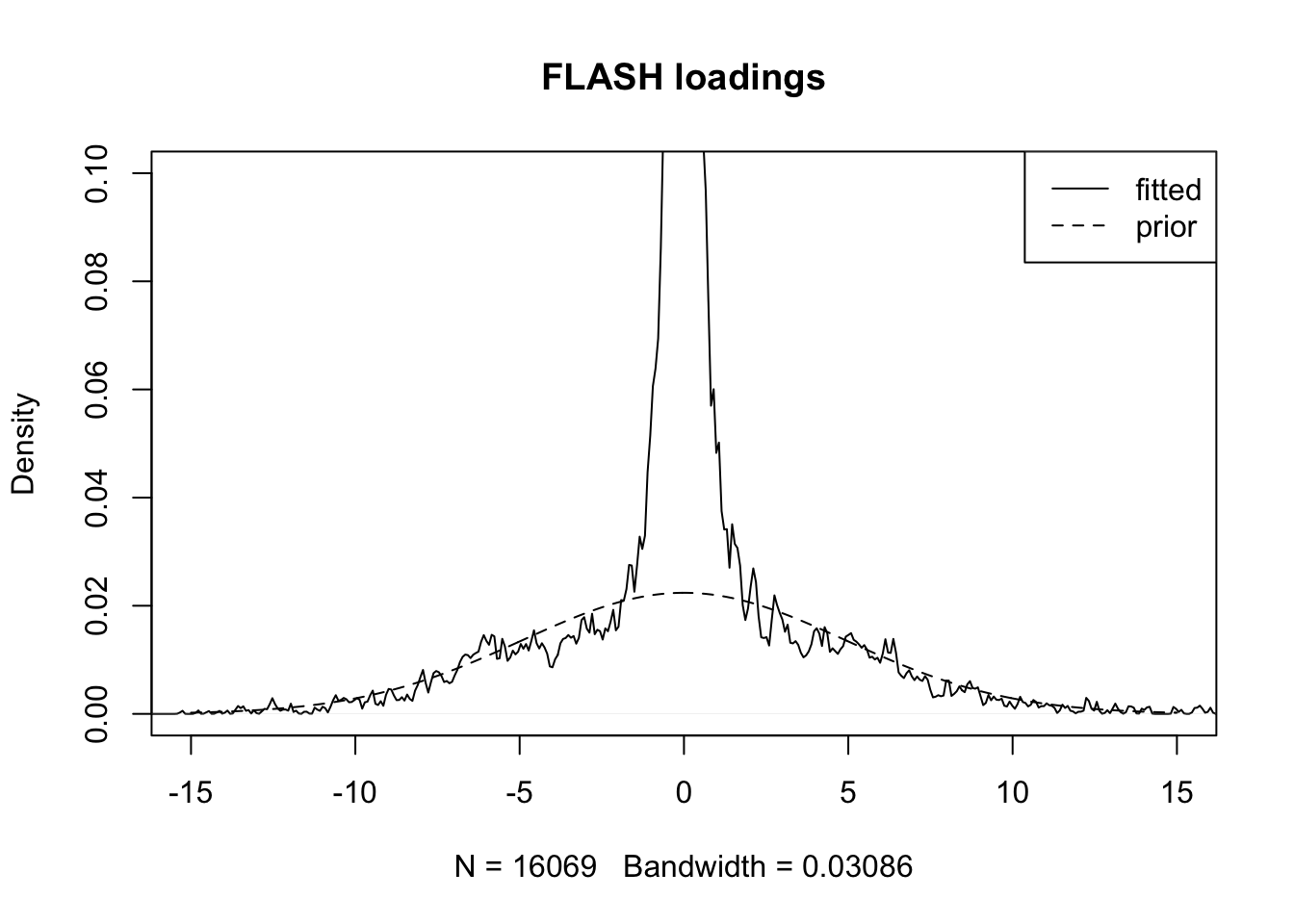
Expand here to see past versions of density1-1.png:
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2cbe7dd | Jason Willwerscheid | 2018-07-19 |
For the alternate approach:
plot(density(fl2$EL[, 4]), xlim=c(-15, 15), ylim=c(0, 0.1),
main="Alternate approach")
grid <- seq(-15, 15, by=.05)
y <- (1 - fl2$gl[[4]]$pi0) * dnorm(grid, 0, 1/sqrt(fl2$gl[[4]]$a))
lines(grid, y, lty=2)
legend("topright", legend = c("fitted", "prior"), lty = c(1, 2))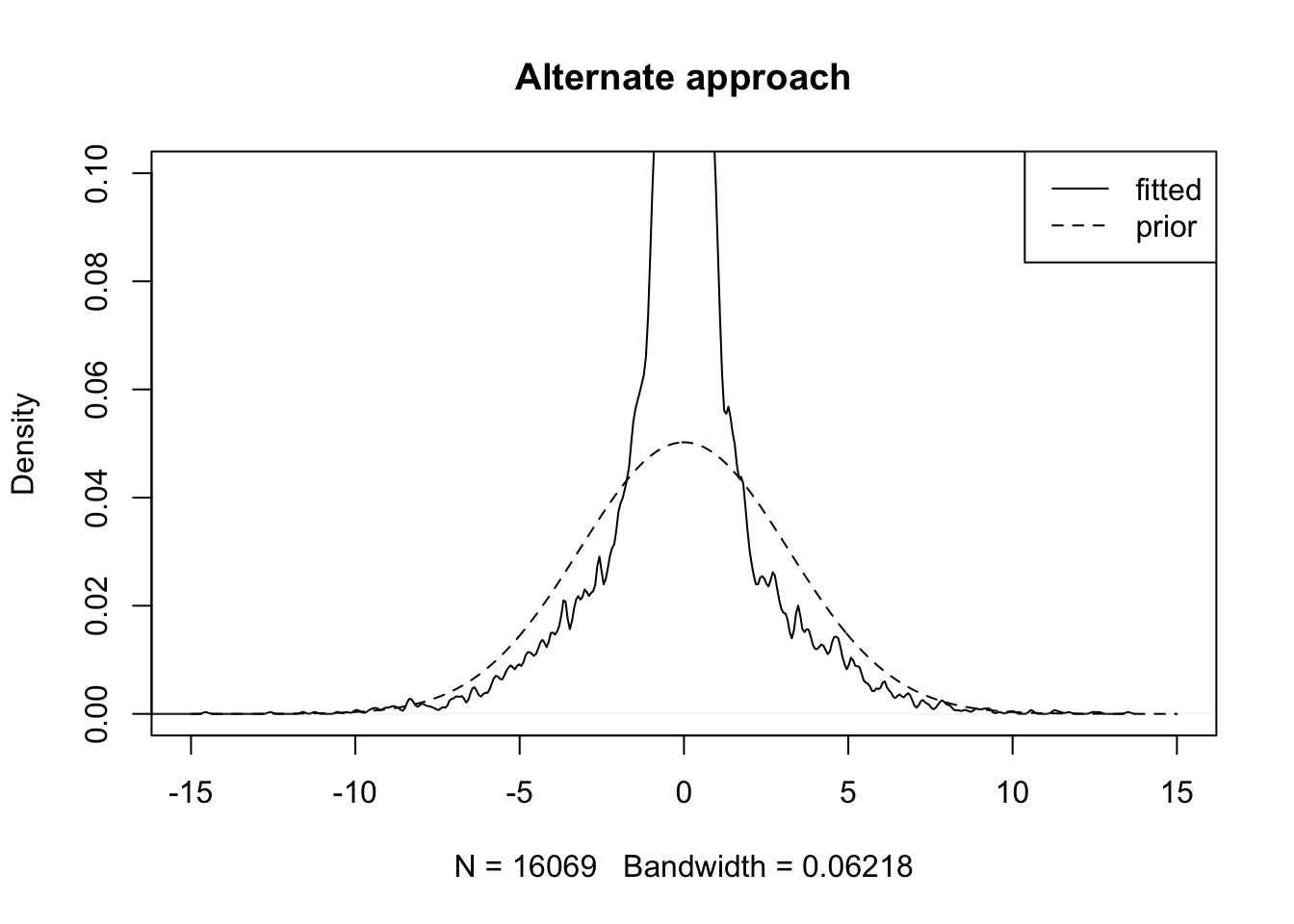
Expand here to see past versions of density2-1.png:
| Version | Author | Date |
|---|---|---|
| 2cbe7dd | Jason Willwerscheid | 2018-07-19 |
This doesn’t seem right!
Session information
sessionInfo()R version 3.4.3 (2017-11-30)
Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin15.6.0 (64-bit)
Running under: macOS Sierra 10.12.6
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/3.4/Resources/lib/libRblas.0.dylib
LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/3.4/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib
locale:
[1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] ebnm_0.1-13 flashr_0.5-12
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] Rcpp_0.12.17 pillar_1.2.1 plyr_1.8.4
[4] compiler_3.4.3 git2r_0.21.0 workflowr_1.0.1
[7] R.methodsS3_1.7.1 R.utils_2.6.0 iterators_1.0.9
[10] tools_3.4.3 testthat_2.0.0 digest_0.6.15
[13] tibble_1.4.2 evaluate_0.10.1 memoise_1.1.0
[16] gtable_0.2.0 lattice_0.20-35 rlang_0.2.0
[19] Matrix_1.2-12 foreach_1.4.4 commonmark_1.4
[22] yaml_2.1.17 parallel_3.4.3 withr_2.1.1.9000
[25] stringr_1.3.0 roxygen2_6.0.1.9000 xml2_1.2.0
[28] knitr_1.20 devtools_1.13.4 rprojroot_1.3-2
[31] grid_3.4.3 R6_2.2.2 rmarkdown_1.8
[34] ggplot2_2.2.1 ashr_2.2-10 magrittr_1.5
[37] whisker_0.3-2 backports_1.1.2 scales_0.5.0
[40] codetools_0.2-15 htmltools_0.3.6 MASS_7.3-48
[43] assertthat_0.2.0 softImpute_1.4 colorspace_1.3-2
[46] stringi_1.1.6 lazyeval_0.2.1 munsell_0.4.3
[49] doParallel_1.0.11 pscl_1.5.2 truncnorm_1.0-8
[52] SQUAREM_2017.10-1 R.oo_1.21.0 This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr 1.0.1