Spikes demo
Zhengrong Xing, Peter Carbonetto and Matthew Stephens
Last updated: 2018-08-23
workflowr checks: (Click a bullet for more information)-
✔ R Markdown file: up-to-date
Great! Since the R Markdown file has been committed to the Git repository, you know the exact version of the code that produced these results.
-
✔ Environment: empty
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
-
✔ Seed:
set.seed(1)The command
set.seed(1)was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible. -
✔ Session information: recorded
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
-
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility. The version displayed above was the version of the Git repository at the time these results were generated.✔ Repository version: 822ab98
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can usewflow_publishorwflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.Ignored files: Ignored: docs/figure/ Ignored: dsc/code/R/ Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/CPAnalysis.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/DownDyadHi.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/DownDyadLo.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/FAIPT.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/FCPSynthesis.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/FMIPT.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/FWPSynthesis.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/FWT2_PO.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/FWT_PBS.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/FWT_PO.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/FWT_TI.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/IAIPT.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/IMIPT.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/IWT2_PO.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/IWT_PBS.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/IWT_PO.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/IWT_TI.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/LMIRefineSeq.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/MedRefineSeq.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/UpDyadHi.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/UpDyadLo.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/WPAnalysis.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/dct_ii.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/dct_iii.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/dct_iv.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/dst_ii.mexmac Ignored: dsc/code/Wavelab850/MEXSource/dst_iii.mexmac Unstaged changes: Modified: code/misc.R
Expand here to see past versions:
| File | Version | Author | Date | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rmd | 822ab98 | Peter Carbonetto | 2018-08-23 | wflow_publish(“spikesdemo.Rmd”) |
This script illustrates key features of the smash method on a small, simulated data set.
Set up environment
We begin by loading the ashr, smashr, scales, ggplot2 and cowplot packages, as well as some additional functions used in the code below.
library(ashr)
library(smashr)
library(scales)
library(ggplot2)Warning: package 'ggplot2' was built under R version 3.4.4suppressMessages(library(cowplot))Warning: package 'cowplot' was built under R version 3.4.4source("../code/misc.R")Define the “spikes” mean function
Function spike.f defines the mean signal.
n <- 1024
t <- 1:n/n
spike.f <-
function (x) (0.75 * exp(-500 * (x - 0.23)^2) +
1.5 * exp(-2000 * (x - 0.33)^2) +
3 * exp(-8000 * (x - 0.47)^2) +
2.25 * exp(-16000 * (x - 0.69)^2) +
0.5 * exp(-32000 * (x - 0.83)^2))
mu.sp <- spike.f(t)
mu.sp <- (1 + mu.sp)/5Simulate data
Add text here.
pos <- c(0.1,0.13,0.15,0.23,0.25,0.4,0.44,0.65,0.76,0.78,0.81)
hgt <- 2.88/5 * c(4,-5,3,-4,5,-4.2,2.1,4.3,-3.1,2.1,-4.2)
sig.cb <- rep(0,length(t))
for (j in 1:length(pos))
sig.cb <- sig.cb + (1 + sign(t - pos[j])) * (hgt[j]/2)
sig.cb[sig.cb < 0] <- 0
sig.cb <- 0.1 + (sig.cb - min(sig.cb))/max(sig.cb)
rsnr <- sqrt(3)
sig.cb <- sig.cb/mean(sig.cb) * sd(mu.sp)/rsnr^2
x.sim <- rnorm(n,mu.sp,sig.cb)Plot the simulated data set.
par(cex.axis = 0.8,cex.sub = 1,cex.lab = 1)
plot(mu.sp,type = 'l',ylim = c(-0.05,1),xlab = "position",
ylab = "",lwd = 1.7,xaxp = c(0,1024,4),yaxp = c(0,1,4))
lines(mu.sp + 2*sig.cb,col = "darkorange",lty = 5,lwd = 1.8)
lines(mu.sp - 2*sig.cb,col = "darkorange",lty = 5,lwd = 1.8)
points(x.sim,cex = 0.7,pch = 16,col = "darkblue")
Run SMASH and TI thresholding
Apply smash and translation invariant (TI) thresholding to the “spikes” data. Here, we run the TI thresholding twice—once when the standard deviation (s.d.) function is provided, and once when it is estimated using the MAD algorithm.
sig.est <- sqrt(2/(3 * (n - 2)) *
sum((1/2 * x.sim[1:(n-2)] - x.sim[2:(n-1)] + x.sim[3:n])^2/2))
mu.smash <- smash(x.sim,family = "DaubLeAsymm",filter.number = 8)
mu.ti <- ti.thresh(x.sim,method = "rmad",family = "DaubLeAsymm",
filter.number = 8)
mu.ti.homo <- ti.thresh(x.sim,sigma = sig.est,family = "DaubLeAsymm",
filter.number = 8)Get the wavelet coefficients and their variances.
wc.sim <- titable(x.sim)$difftable
wc.var.sim <- titable(sig.cb^2)$sumtable
wc.true <- titable(mu.sp)$difftableGet shrunken estimates of the wavelet coefficients.
wc.sim.shrunk <- vector("list",10)
wc.pres <- vector("list",10)
for(j in 0:(log2(n) - 1)){
wc.sim.shrunk[[j+1]] <-
ash(wc.sim[j+2,],sqrt(wc.var.sim[j+2,]),prior = "nullbiased",
pointmass = TRUE,mixsd = NULL,mixcompdist = "normal",
gridmult = 2,df = NULL)$result
wc.pres[[j+1]] <- 1/sqrt(wc.var.sim[j+2,])
}Summarize results
Plot the distribution of observed wavelet coefficients.
par(cex.axis = 0.8,cex.lab = 0.8)
hist(wc.sim[4,],breaks = 2,xlab = "observed wavelet coefficients",
xlim = c(-25,25),ylim = c(0,600),col = "darkblue",xaxp = c(-25,25,10),
yaxp = c(0,600,6),main = "")
hist(wc.sim[10,],breaks = 40,add = TRUE,col = "darkorange")
Plot the observed wavelet coefficients (at scales 1 and 7 only) vs. the “shrunken” wavelet coefficients estimated by adaptive shrinkage.
par(cex.axis = 0.8,cex.lab = 0.8)
plot(c(),c(),xlab = "observed wavelet coefficients",
ylab = "shrunken wavelet coefficients",
xlim = c(-2.5,2.5),ylim = c(-2.5,2.5))
abline(0,1,lty = 1,col = "gray",lwd = 1)
points(wc.sim[10,],wc.sim.shrunk[[9]]$PosteriorMean,pch = 20,cex = 0.6,
col = "darkorange")
points(wc.sim[4,],wc.sim.shrunk[[3]]$PosteriorMean,pch = 20,cex = 0.6,
col = "darkblue")
Plot the observed wavelet coefficients (at scale 7 only) vs. the “shrunken” wavelet coefficients estimated by adaptive shrinkage, and how how the amount of shrinkage depends on the standard error (s.e.) in the observations.
wc.sig.3 <- 1/wc.pres[[3]]
p <- ggplot(data.frame(observed = wc.sim[4,],
shrunken = wc.sim.shrunk[[3]]$PosteriorMean,
se = wc.sig.3),
aes(x = observed,y = shrunken,col = se)) +
geom_point() +
xlim(c(-1,1)) +
ylim(c(-1,1)) +
scale_color_gradientn(colors = c("deepskyblue","darkblue")) +
theme_cowplot()
print(p)Warning: Removed 3 rows containing missing values (geom_point).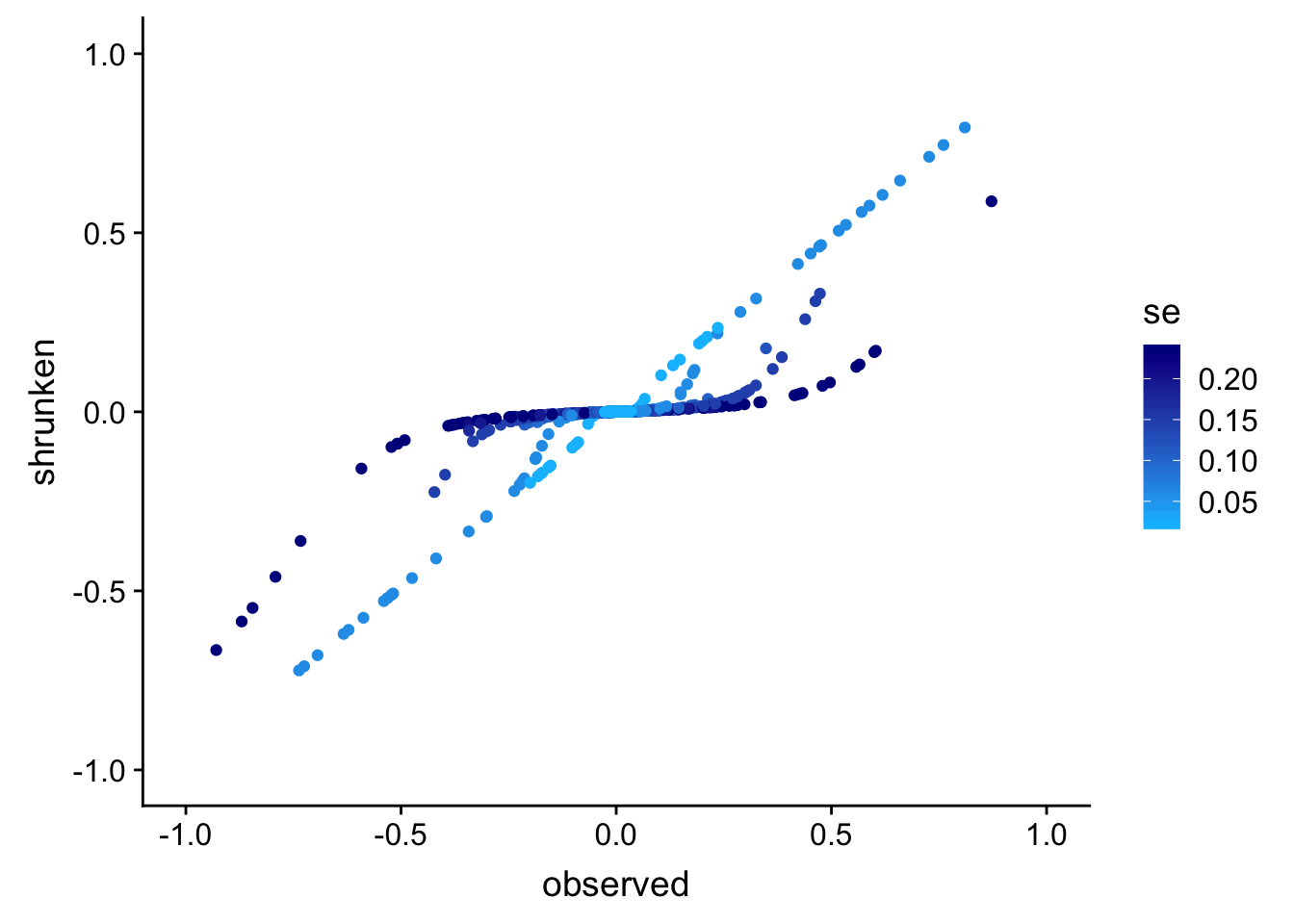
Plot the ground-truth signal (mean function) and the signals recovered by the TI thresholding and smash methods.
par(cex.axis = 0.8)
plot(mu.sp,type = "l",col = "black",lwd = 2,xlab = "position",ylab = "",
ylim = c(-0.05,1),xaxp = c(0,1024,4),yaxp = c(0,1,4))
lines(mu.ti,col = "dodgerblue",lwd = 1.5)
lines(mu.smash,col = "orangered",lwd = 1.5)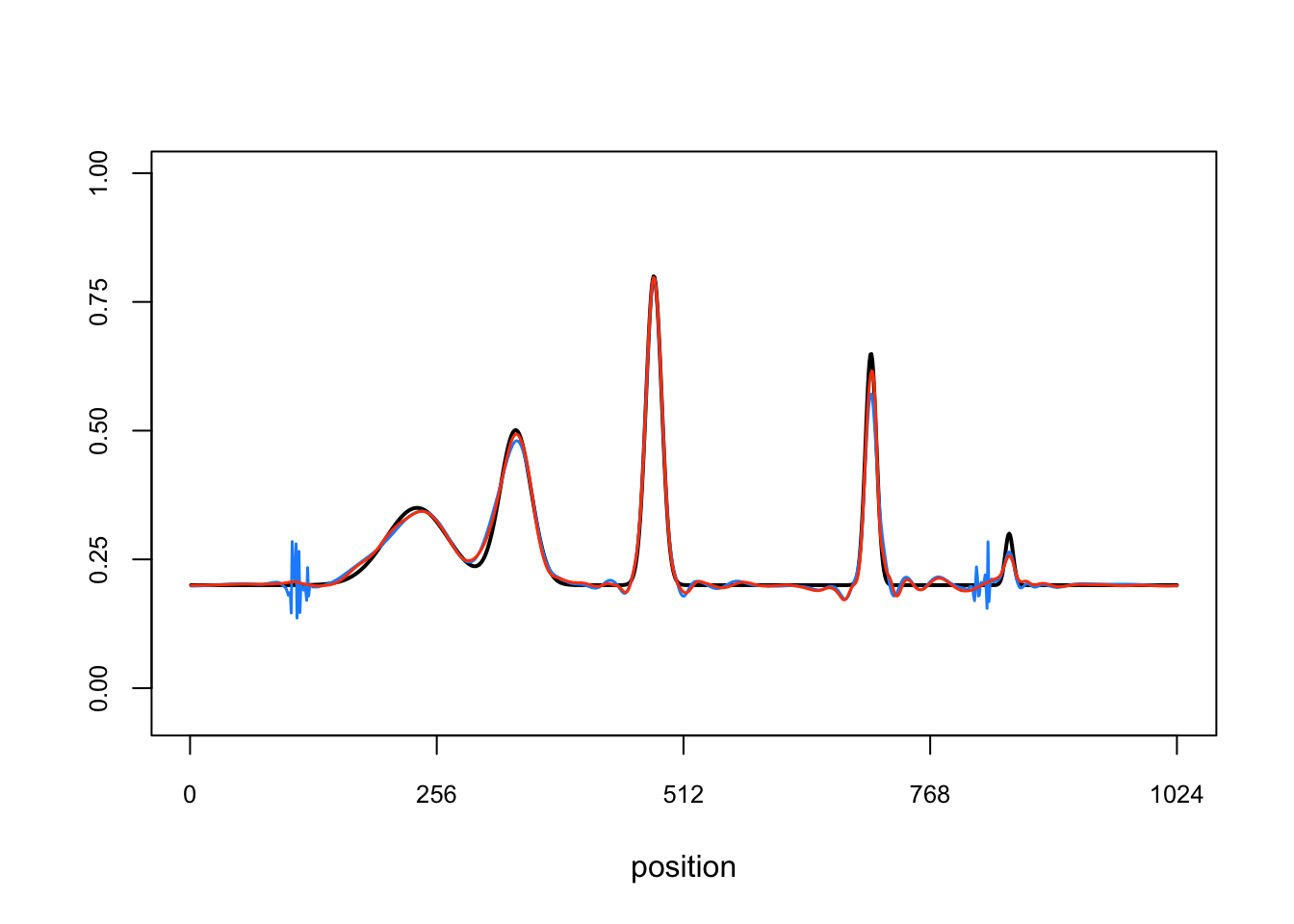
cat("Demo is over.\n")Demo is over.Session information
sessionInfo()R version 3.4.3 (2017-11-30)
Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin15.6.0 (64-bit)
Running under: macOS High Sierra 10.13.6
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/3.4/Resources/lib/libRblas.0.dylib
LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/3.4/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib
locale:
[1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] cowplot_0.9.3 ggplot2_3.0.0 scales_0.5.0 smashr_1.2-0 ashr_2.2-9
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] wavethresh_4.6.8 tidyselect_0.2.4 purrr_0.2.5
[4] lattice_0.20-35 Rmosek_8.0.69 colorspace_1.4-0
[7] htmltools_0.3.6 yaml_2.1.19 rlang_0.2.1
[10] R.oo_1.21.0 pillar_1.2.1 glue_1.2.0
[13] withr_2.1.2 R.utils_2.6.0 REBayes_1.3
[16] bindrcpp_0.2.2 foreach_1.4.4 plyr_1.8.4
[19] bindr_0.1.1 stringr_1.3.0 munsell_0.4.3
[22] gtable_0.2.0 workflowr_1.1.1 R.methodsS3_1.7.1
[25] caTools_1.17.1 codetools_0.2-15 evaluate_0.10.1
[28] labeling_0.3 knitr_1.20 pscl_1.5.2
[31] doParallel_1.0.11 parallel_3.4.3 Rcpp_0.12.17
[34] backports_1.1.2 truncnorm_1.0-8 digest_0.6.15
[37] stringi_1.1.7 dplyr_0.7.5 grid_3.4.3
[40] rprojroot_1.3-2 tools_3.4.3 bitops_1.0-6
[43] magrittr_1.5 lazyeval_0.2.1 tibble_1.4.2
[46] whisker_0.3-2 pkgconfig_2.0.1 MASS_7.3-48
[49] Matrix_1.2-12 SQUAREM_2017.10-1 data.table_1.11.4
[52] mixSQP_0.1-6 assertthat_0.2.0 rmarkdown_1.9
[55] iterators_1.0.9 R6_2.2.2 git2r_0.21.0
[58] compiler_3.4.3 This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr 1.1.1