2015-09-09 15:38:58
Open Science Practices Have Made my Work Better
Overview
- Development of Optic Flow Processing
- What is optic flow?
- How does optic flow sensitivity develop?
- How do brain systems for processing optic flow develop?
- What shapes the patterns of brain development?
- How Open, Transparent, Reproducible Research Practices Have Improved my Work
- Open workflows
- Data sharing
Open, Transparent, Reproducible Practices
- Estimating the reproducibility of psychological science. (Collaboration 2015).
Promoting an open research culture. (Nosek et al. 2015)
- Publishing replication failures: some lessons from history. (Deevybee 2015)
- The slower, harder ways to increase reproducibility. (Frank 2015)
What is Optic Flow?
- Structured pattern of visual motion generated by observer movement
What is Optic Flow?
Types of Optic Flow
- Radial (expansion/contraction), rotation, linear/laminar/translational, shear
How Does Optic Flow Sensitivity Develop?
- Sensitivity at birth, (Jouen et al. 2000)
- Infants
- Brain responses stronger to fast, translational flow, (Hou et al. 2009; R. O. Gilmore et al. 2007)
- Behavioral responses stronger to fast translational flow, (Kiorpes and Movshon 2004)
- Primate universal pattern? Not adult-like until late adolescence?
- Adults
- Brain responses stronger to radial flow, (R. O. Gilmore et al. 2007; Fesi, Thomas, and Gilmore 2014).
Gaps
- Brain responses in childhood
- Adults' behavioral responses
- What influences developmental shifts?
- Why fast speeds and linear flows?
How Do Children's Brains Respond to Flow?
- If infant-like: stronger responses to fast, linear flows
- If adult-like: stronger responses to slow, radial flows
Child Responses to Flow
Methods
- Time-varying optic flow patterns
- Steady-state visual evoked potentials (SSVEPs)
- Event-related EEG technique
- Focus on phase-locked, low-order harmonics
- n=29 4-8 year-olds
(Gilmore, Thomas, & Fesi, under review)
Example Displays
2 deg/s translation
https://databrary.org/slot/6493/-/asset/11635/download?inline=true
4 deg/s rotation
https://databrary.org/slot/6493/-/asset/11649/download?inline=true
8 deg/s radial
https://nyu.databrary.org/slot/6493/-/asset/11645/download?inline=true
Displays
- Modulate coherence/signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), 100%/0%
- Modulation frequency 1.2 Hz (1F1), dots update rate 24 Hz (1F2)
- Cross pattern and speed
Data analysis
- Fourier analysis (frequency domain)
- generates complex domain (real, imaginary) components
- time-varying signals have amplitude, phase
- Codepen Demo
- Use mixed effects MANOVA to capture phase, amplitude
- Pattern (radial, rotation, linear) and Speed (2, 4, 8 deg/s) as fixed effects
- Individual means as random factors
- Analyze channels independently
1F1 Channel-Wise Results

1F1 Channels p < .0005

Complex Domain Plot of 1F1 Channels

1F1 Results Summary
- Highly responsive channels over right lateral cortex
- Radial & rotation >> translation
- Amplitude and phase differences
2F1 Channel-Wise Results

3F1 Channel-Wise Results

3F1 Channels p < .0005

Complex Domain Plot of 3F1 Channels

3F1 Results Summary
- Highly responsive channels over medial cortex.
- Speed, but not pattern tuned, 2 < 4 < 8 deg/s.
- Amplitude and phase differences.
1F2 Channel-Wise Results

1F2 Channels p < .0005

Results Summary
- Anatomical separation of responses
- speed (medial)
- vs. pattern (lateral)
- Radial & rotation != translation, phase and amplitude
- Speed tuning
Comparing Adults 1F1

To Children's

Adults' 3F1

To Children's

Adults' 1F2

To Children's

Developmental Effects
- Children adult-like in some respects
- Lateral "pattern" responses @ 1F1
- Medial "speed" responses @ 3F1 and 1F2
- Activate smaller # of channels
- Unilateral
- 'Internal' replication
Adults' Behavioral Responses
- Predictions
- Higher sensitivity to slow, radial patterns
Methods
- Time-varying optic flow
- Radial, linear
- 2, 8 deg/s
- 5, 10, 15, 20% coherence
- Side by side displays
- Signal/noise
- Choose side with signal
- 2AFC, 10 s response period
- Linear mixed effects modeling (lmer in R)
(Adamiak, Thomas, Patel & Gilmore, 2015)
https://databrary.org/volume/73, http://f1000research.com/posters/1098278
Results p(correct)

Results RT
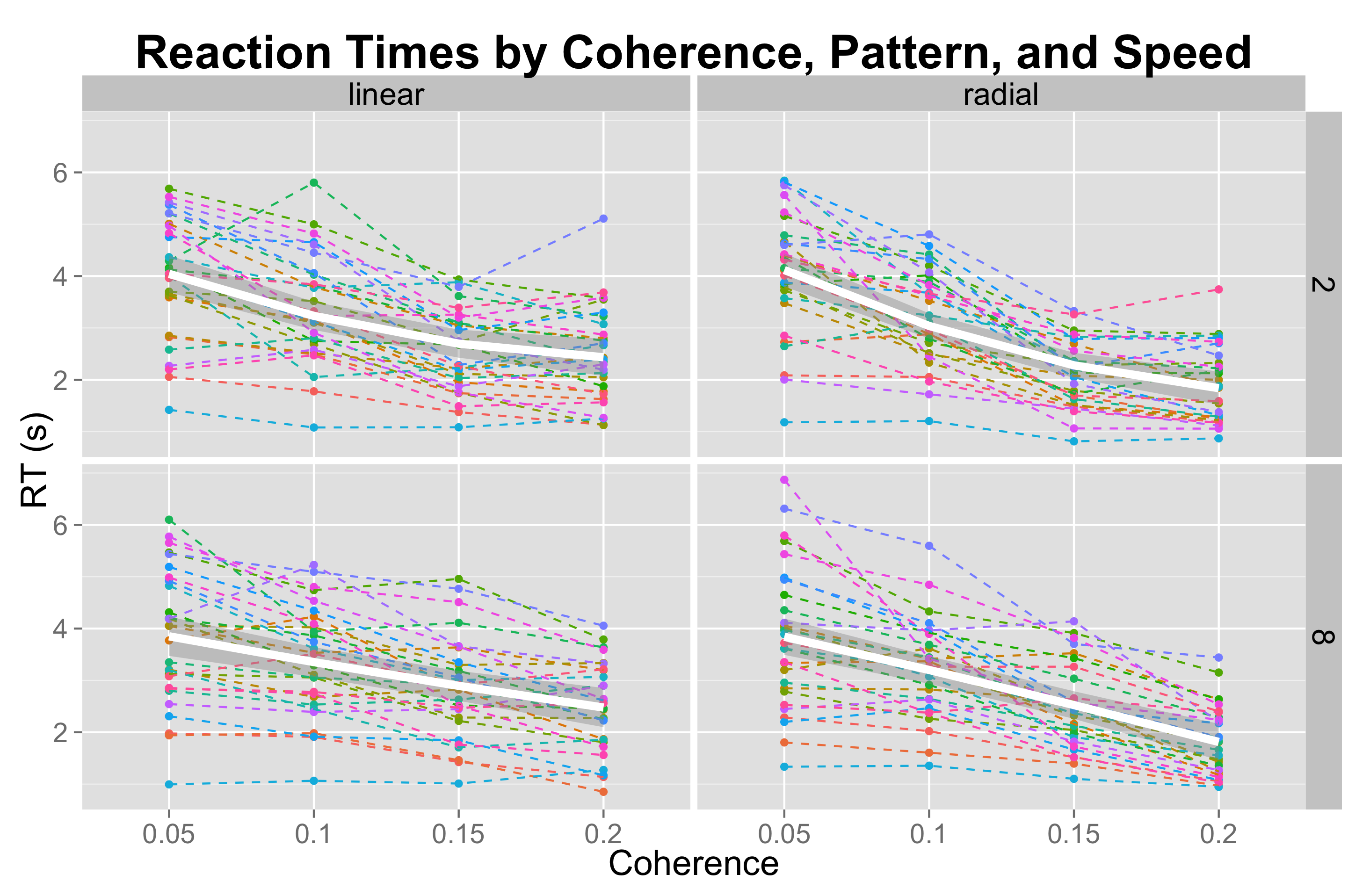
Adult Behavioral Summary
- Adults faster and more accurate to detect slow, radial flow.
What influences developmental shifts?
- Predictions
- Fast, laminar flows common in natural experiences of infants
- Eye/head movements, head instability
- (Florian Raudies and Gilmore 2014; F. Raudies et al. 2012)
- Conjectures
- Geometry of environment?
- Head/body posture changes?
- Carrying vs. independent locomotion?
- Cultural differences in home environment, relatives, carrying practices?
- Changes across developmental milestones?
Methods
- Simulation
- How does "maturation" change optic flow?
- Does environmental geometry change optic flow?
- Measure natural scene statistics of optic flow
- Videos from head-mounted cameras
- Infants from India, Indiana
- Extract flow; what are speed, pattern distributions?
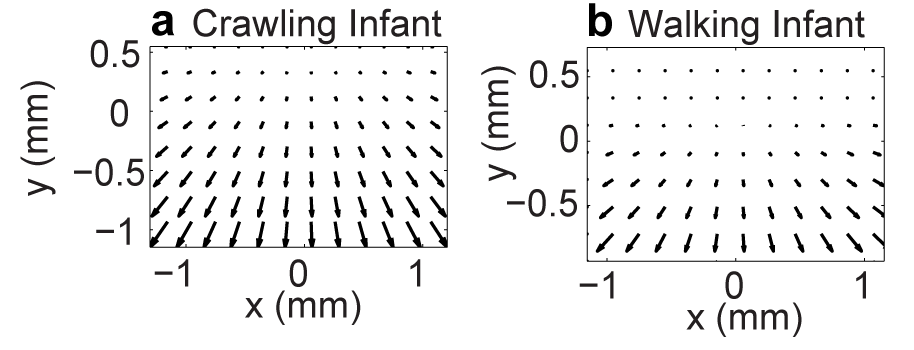
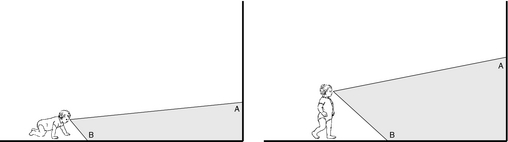
Simulating Optic Flow
Parameters For Simulation
| Parameter | Crawling Infant | Walking Infant |
|---|---|---|
| Eye height | 0.30 m | 0.60 m |
| Locomotor speed | 0.33 m/s | 0.61 m/s |
| Head tilt | 20 deg | 9 deg |
Parameters for Simulation
| Geometric Feature | Distance |
|---|---|
| Side wall | +/- 2 m |
| Side wall height | 2.5 m |
| Distance of ground plane | 32 m |
| Field of view width | 60 deg |
| Field of view height | 45 deg |
Simulating Flow Fields
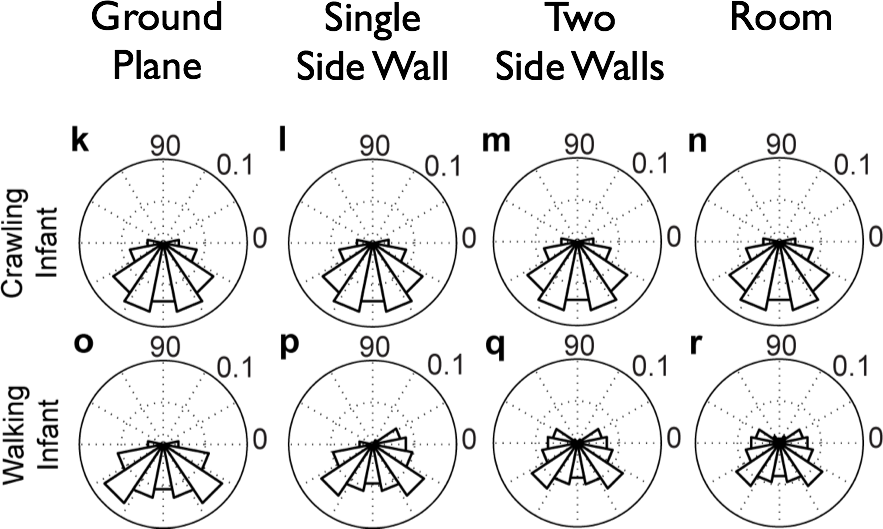
Flow Direction Distributions by Geometry & Posture
Flow Speeds By Geometry and Posture
Mean Simulated Flow Speeds By Posture and Geometry
| Type of Locomotion | Ground Plane | Room | Side Wall | Two Walls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crawling | 14.41 | 14.42 | 14.43 | 14.62 |
| Walking | 9.38 | 8.56 | 7.39 | 9.18 |
Empirical Measurements of Optic Flow
- First-person videos from head-mounted cameras
- 20 infants, 41 days to 13.2 mos
- Chennai, India & Bloomington, Indiana
- Data: http://databrary.org/volume/81
Cultural Differences in Segment Durations
Segment Durations
Normalized Durations as \(p\)(total-time)
Natural Scene Statistics for Optic Flow
- Selected 10 5 s segments/participant, both moving and stationary
- Estimated frame by frame flow fields
- Details in Raudies & Gilmore 2014
Speed Distributions
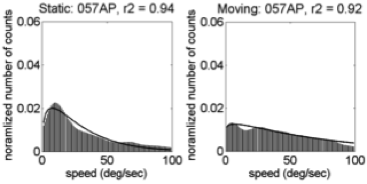
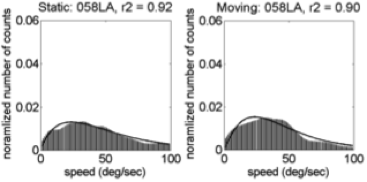
Comparing Shapes of (Trimmed) Speed Distributions
- Fit \(\gamma\) distribution to trimmed (0,100) speed histograms
\(f(x;k,\theta) = \alpha\frac{x^{k-1}e^{-\frac{x}{\theta}}}{\theta^k\Gamma(k)}\)
\(\alpha\), amplitude; \(\kappa\), shape; and \(\theta\), scale parameters.Illustrative Speed Histograms – 6 weeks
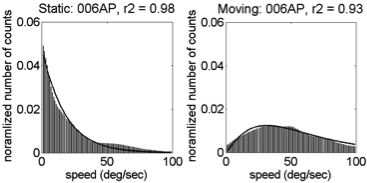
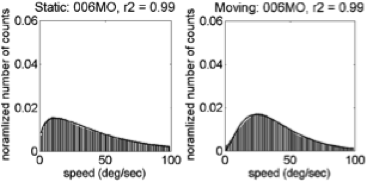
Illustrative Speed Histograms – 34 weeks
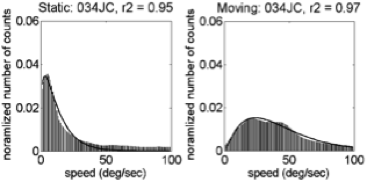
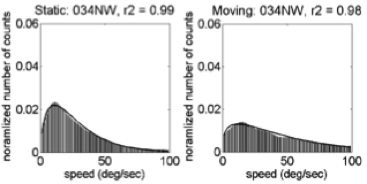
Illustrative Speed Histograms – 58 weeks
Fitted \(\kappa\) Parameters
Fitted \(\alpha\) Parameters
Fitted \(\theta\) Parameters
Summary: Empirical Flow Speed Effects
- Fast speeds (> 100 deg/s) common
- Moving ≠ Stationary
- Broad distribution: \(\kappa\), \(\alpha\)(moving) > \(\kappa\), \(\alpha\)(stationary)
- U.S. ~ India
Empirical Pattern Distributions
- Correlation with 'canonical' flow patterns
- radial
- rotational
- translational
Pattern Correlation Results
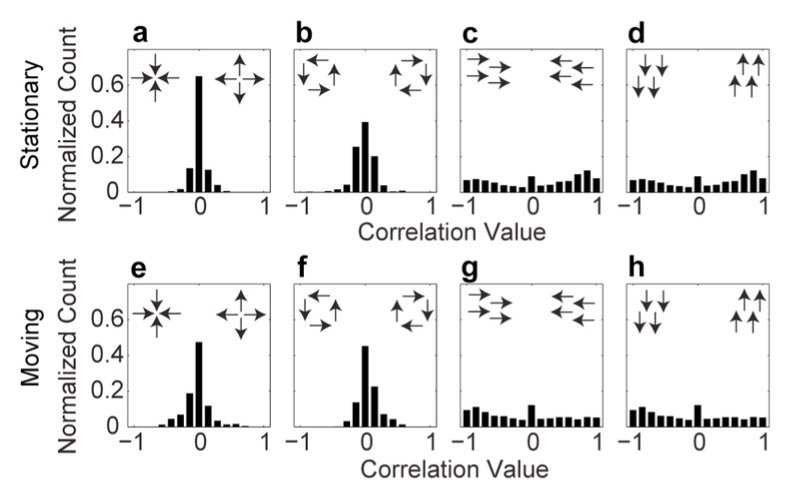
Pattern Correlation Results by Country
Moving Laminar ≠ Stationary Laminar in 13/22 infants.
Conclusions: Simulation
- Posture influences optic flow speeds & patterns
- Crawling: faster speeds, more translational flow
- Proximity to ground and pitch of head
- Geometry matters relatively little
Conclusions: Empirical Data
- Time stationary >> time in motion
- Time stationary declines with age (India)
- Fast speeds, broad speed distributions
- Individual differences in moving vs. stationary speed distributions
- Laminar flow >> radial or rotational flow, especially when stationary
- Replicates and extends Raudies & Gilmore '12, '14
Summmary of Findings
- Children's brain responses to optic flow are adult-like in many respects
- Adults' are most sensitive to slow, radial flow patterns.
- Infants commonly experience fast, laminar flows.
- Statistics of visual input may shape developmental transition from fast laminar to slow radial flow.
Stack
- RStudio, https://www.rstudio.com/
- R Markdown, http://rmarkdown.rstudio.com/
- GitHub, http://github.com/gilmore-lab/, http://github.com/psu-psychology/cognitive-area
- Databrary, https://nyu.databrary.org/volume/81
- Access to identifiable data (e.g. videos) restricted
- Access agreement + institutional authorization
- Datayvu, http://datavyu.org
- Matlab
References
Collaboration, Open Science. 2015. “Estimating the Reproducibility of Psychological Science.” Science 349 (6251): aac4716. doi:10.1126/science.aac4716.
Deevybee. 2015. “BishopBlog: Publishing Replication Failures: Some Lessons from History.” BishopBlog. http://deevybee.blogspot.com/2015/07/publishing-replication-failures-some.html.
Fesi, Jeremy D., Amanda L. Thomas, and Rick O. Gilmore. 2014. “Cortical Responses to Optic Flow and Motion Contrast Across Patterns and Speeds.” Vision Research 100 (July): 56–71. doi:10.1016/j.visres.2014.04.004.
Frank, Michael. 2015. “Babies Learning Language: The Slower, Harder Ways to Increase Reproducibility.” Babies Learning Language. http://babieslearninglanguage.blogspot.com/2015/08/the-slower-harder-ways-to-increase.html.
Gilmore, Rick O., C. Hou, M.W. Pettet, and A.M. Norcia. 2007. “Development of Cortical Responses to Optic Flow.” Visual Neuroscience 24 (06): 845–56. doi:10.1017/S0952523807070769.
Hou, C., R.O. Gilmore, M.W. Pettet, and A.M. Norcia. 2009. “Spatio-Temporal Tuning of Coherent Motion Evoked Responses in 4–6 Month Old Infants and Adults.” Vision Research 49 (20): 2509–17. doi:10.1016/j.visres.2009.08.007.
Jouen, François, Jean-Claude Lepecq, Olivier Gapenne, and Bennett I Bertenthal. 2000. “Optic Flow Sensitivity in Neonates.” Infant Behavior and Development 23 (3–4): 271–84. doi:10.1016/S0163-6383(01)00044-3.
Kiorpes, Lynne, and J. Anthony Movshon. 2004. “Development of Sensitivity to Visual Motion in Macaque Monkeys.” Visual Neuroscience 21 (6): 851–59. doi:10.1017/S0952523804216054.
Nosek, B. A., G. Alter, G. C. Banks, D. Borsboom, S. D. Bowman, S. J. Breckler, S. Buck, et al. 2015. “Promoting an Open Research Culture.” Science 348 (6242): 1422–25. doi:10.1126/science.aab2374.
Raudies, F., R.O. Gilmore, K.S. Kretch, J.M. Franchak, and K.E. Adolph. 2012. “Understanding the Development of Motion Processing by Characterizing Optic Flow Experienced by Infants and Their Mothers.” In 2012 IEEE International Conference on Development and Learning and Epigenetic Robotics (ICDL), 1–6. doi:10.1109/DevLrn.2012.6400584.
Raudies, Florian, and Rick O. Gilmore. 2014. “Visual Motion Priors Differ for Infants and Mothers.” Neural Computation 26 (11): 2652–68. doi:10.1162/NECO_a_00645.