Dependencies
The terms current settings
object, event handler,
event
handler event type, fire a simple
event, queue a task and
trusted
event are defined in [[!HTML51]].
Promise, and
JSON.parse are
defined in [[!ECMASCRIPT]].
EventInit,
DOMException,
AbortError,
InvalidStateError,
InvalidAccessError,
SecurityError,
NetworkError,
event listener,
and steps for
constructing events are defined in [[!DOM]].
The terms service
worker, service worker
registration, installing
worker, waiting worker,
and active
worker, and the types ServiceWorkerRegistration,
ServiceWorkerGlobalScope,
ExtendableEvent,
ExtendableEventInit,
extend
lifetime promises, the Clear
Registration algorithm, and the Handle
Functional Event algorithm are defined in [[!SERVICE-WORKERS]].
The term secure
context is defined in [[!POWERFUL-FEATURES]].
The algorithms utf-8
encode, and utf-8
decode are defined in [[!ENCODING]].
Blob is defined in
[[!FILEAPI]].
Any,
ArrayBuffer,
BufferSource,
NotAllowedError,
and USVString are defined
in [[!WEBIDL]].
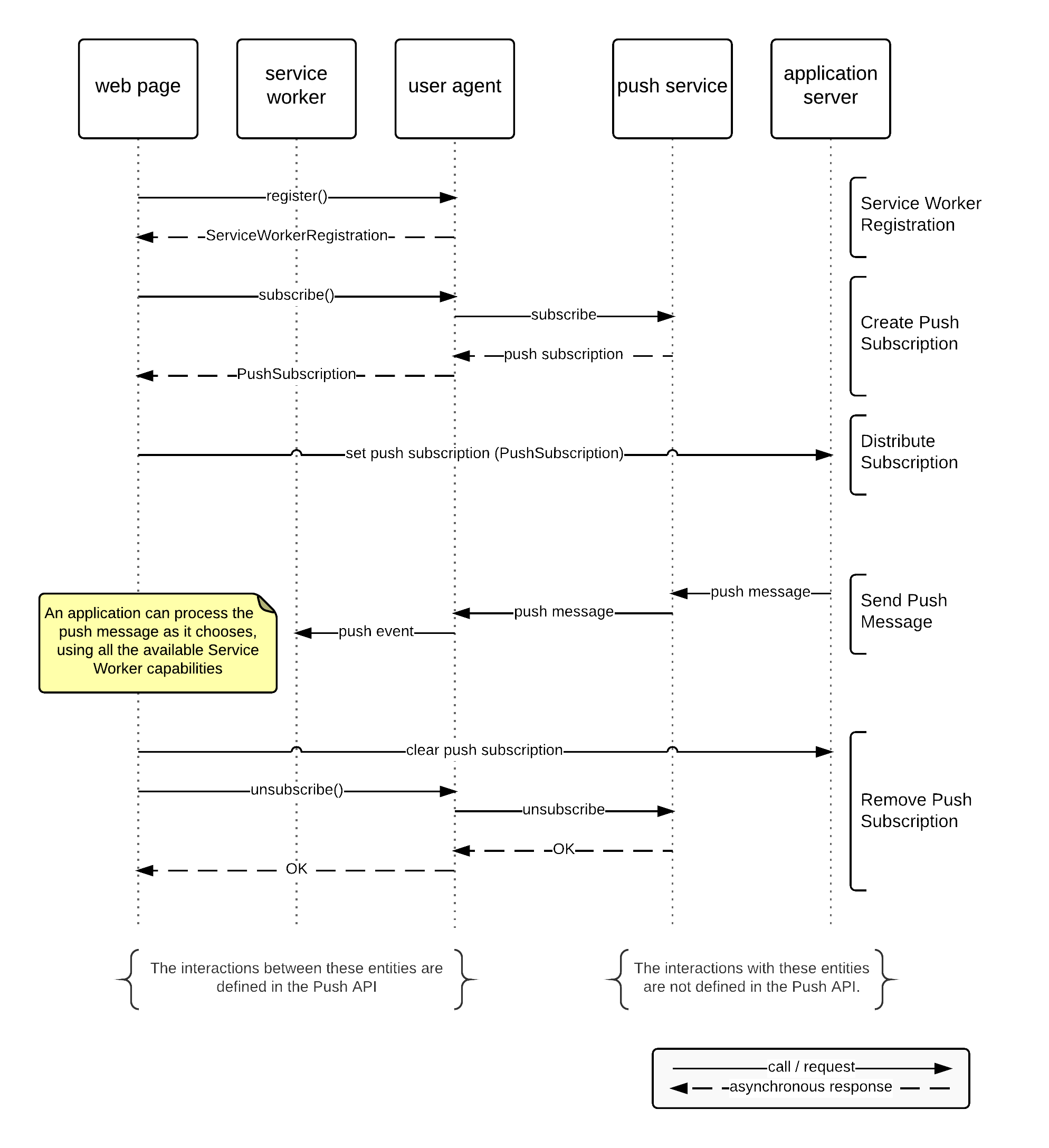
The web push protocol [[!WEBPUSH-PROTOCOL]] describes a protocol that enables
communication between a user agent or application server and a push
service. Alternative protocols could be used in place of this protocol, but this
specification assumes the use of this protocol; alternative protocols are expected to
provide compatible semantics.
Concepts
Webapp
The term webapp refers to a Web application, i.e. an
application implemented using Web technologies, and executing within the context of a Web
user agent, e.g. a Web browser or other Web runtime environment.
The term application server
refers to server-side components of a webapp.
Permission
The term express permission refers to an act by the user, e.g. via user
interface or host device platform features, via which the user approves the use of the
Push API by the webapp.
The Service Worker specification defines a ServiceWorkerRegistration interface
[[!SERVICE-WORKERS]], which this specification extends.
partial interface ServiceWorkerRegistration {
readonly attribute PushManager pushManager;
};
The pushManager
attribute exposes a PushManager, which has an associated service
worker registration represented by the ServiceWorkerRegistration on
which the attribute is exposed.
The PushManager interface defines the operations to access push services.
interface PushManager {
Promise<PushSubscription> subscribe(optional PushSubscriptionOptionsInit options);
Promise<PushSubscription?> getSubscription();
Promise<PushPermissionState> permissionState(optional PushSubscriptionOptionsInit options);
};
The subscribe
method when invoked MUST run the following steps:
- Let promise be a new
Promise.
- Return promise and continue the following steps asynchronously.
- If the current settings object is not a secure context, reject
promise with a
DOMException whose name is
"SecurityError" and terminate these steps.
- Let allOptions be the value of the
options argument, if
provided, or a PushSubscriptionOptions dictionary with default values.
- If allOptions includes a non-null value for the
applicationServerKey attribute, check that the value is valid (i.e.,
ensure that it describes a valid point on the P-256 curve). If the
applicationServerKey value is invalid, reject promise with
an InvalidAccessError and terminate these steps.
- Let registration be the
PushManager's associated
service worker registration.
- If registration has no active worker, run the following substeps:
- If registration has no installing worker and no waiting
worker, reject promise with a
DOMException whose
name is "InvalidStateError" and terminate these steps.
- Wait for the installing worker or waiting worker of
registration to become its active worker.
- If registration fails to activate either worker, reject
promise with a
DOMException whose name is
"InvalidStateError" and terminate these steps.
- Once registration has an active worker, proceed with the steps
below.
- Ask the user whether they allow the webapp to receive push messages,
unless a prearranged trust relationship applies or the user has already granted or denied
permission explicitly for this webapp.
- If not granted, reject promise with a
DOMException whose
name is "NotAllowedError" and terminate these steps.
- If the Service Worker is already subscribed, run the following substeps:
- Retrieve the push subscription associated with the Service Worker.
- If there is an error, reject promise with a
DOMException whose name is "AbortError" and
terminate these steps.
- Let subscription be the retrieved subscription.
- Compare allOptions with the
options attribute of
subscription. If any attribute on allOptions contains a different
value to that stored for subscription, then reject promise with
an InvalidStateError and terminate these steps. The contents of
BufferSource values are compared for equality rather than
references.
- When the request has been completed, resolve promise with
subscription.
- Make a request to the push service to create a new push subscription for the
Service Worker.
- If there is an error, reject promise with a
DOMException
whose name is "AbortError" and terminate these steps.
- Let subscription be a new subscription.
- Set the
options attribute of subscription to be a copy of
allOptions.
- Generate a new P-256 ECDH key pair. Store the private key in an internal slot on
subscription; this value MUST NOT be made available to applications. The public
key is also stored in an internal slot and can be retrieved by calling the
getKey method of the PushSubscription with an argument of
p256dh.
- Generate a new authentication secret, which is a sequence of octets as defined in
[[!WEBPUSH-ENCRYPTION]]. Store the authentication secret in an internal slot on
subscription. This key can be retrieved by calling the
getKey
method of the PushSubscription with an argument of
auth.
- When the request has been completed, resolve promise with a
PushSubscription providing the details of the new push
subscription.
The getSubscription
method when invoked MUST run the following steps:
- Let promise be a new
Promise.
- Return promise and continue the following steps asynchronously.
- If the Service Worker is not subscribed, resolve promise with null.
- Retrieve the push subscription associated with the Service Worker.
- If there is an error, reject promise with a
DOMException
whose name is "AbortError" and terminate these steps.
- When the request has been completed, resolve promise with a
PushSubscription providing the details of the retrieved push
subscription.
The
permissionState method when invoked MUST run the following steps:
- Let promise be a new
Promise.
- Return promise and continue the following steps asynchronously.
- Retrieve the push permission status (
PushPermissionState) of the
requesting webapp.
- If there is an error, reject promise with no arguments and terminate these
steps.
- When the request has been completed, resolve promise with
PushPermissionState providing the push permission status.
Permission to use the push service can be persistent, that is, it does not need to be
reconfirmed for subsequent subscriptions if a valid permission exists.
If there is a need to ask for permission, it needs to be done by invoking the
subscribe method.
A PushSubscriptionOptionsInit represents additional options associated with a
push subscription. The user agent MAY consider these options when
requesting express permission from the user. When an option is considered, the
user agent SHOULD enforce it on incoming push messages.
These options are optional, and user agents MAY choose to support only a subset of
them. A user agent MUST NOT expose options that it does not support.
Once set, options for a push subscription cannot change. A pre-existing push
subscription can be unsubscribed to create a push
subscription with new options.
dictionary PushSubscriptionOptionsInit {
boolean userVisibleOnly = false;
BufferSource? applicationServerKey = null;
};
interface PushSubscriptionOptions {
readonly attribute boolean userVisibleOnly;
[SameObject] readonly attribute ArrayBuffer? applicationServerKey;
};
The userVisibleOnly option,
when set to true, indicates that the push subscription will only be
used for push messages whose effect is made visible to the user, for example by
displaying a Web Notification. [[NOTIFICATIONS]]
The applicationServerKey
option includes an elliptic curve public key for an application server. This is the key
that the application server will use to authenticate itself when sending push messages to
this subscription as defined in [[!WEBPUSH-VAPID]]; the push service will reject any push
message unless the corresponding private key is used to generate an authentication token.
If present, the value of applicationServerKey MUST include a point on
the P-256 elliptic curve [[!DSS]], encoded in the uncompressed form described in
[[!X9.62]] Annex A (that is, 65 octets, starting with an 0x04 octet). The
applicationServerKey MUST be a different value to the one used for
message encryption [[WEBPUSH-ENCRYPTION]].
A PushSubscription object represents a push subscription.
interface PushSubscription {
readonly attribute USVString endpoint;
[SameObject] readonly attribute PushSubscriptionOptions options;
ArrayBuffer? getKey(PushEncryptionKeyName name);
Promise<boolean> unsubscribe();
serializer;
};
When getting the endpoint
attribute, the user agent MUST return the push endpoint associated with the
push subscription.
The getKey method retrieves keying material that
can be used for encrypting and authenticating messages. When getKey is
invoked the following process is followed:
- Find the internal slot corresponding to the key named by the
name
argument.
- If a slot was not found, return
null.
- Initialize a variable key with a newly instantiated
ArrayBuffer
instance.
- If the internal slot contains an asymmetric key pair, set the contents of
key to the serialized value of the public key from the key pair. This uses the
serialization format described in the specification that defines the name. For example,
[[!WEBPUSH-ENCRYPTION]] specifies that the
p256dh public key is encoded
using the uncompressed format defined in [[X9.62]] Annex A (that is, a 65 octet sequence
that starts with a 0x04 octet).
- Otherwise, if the internal slot contains a symmetric key, set the contents of
key to a copy of the value from the internal slot. For example, the
auth parameter contains an octet sequence used by the user agent to
authenticate messages sent by an application server.
- Return key.
Keys named p256dh and auth MUST be supported, and
their values MUST correspond to those necessary for the user agent to decrypt received push
messages in accordance with [[!WEBPUSH-ENCRYPTION]].
The unsubscribe method when
invoked MUST run the following steps:
- Let promise be a new
Promise.
- Return promise and continue the following steps asynchronously.
- If the push subscription has already been deactivated, resolve
promise with
false and terminate these steps.
- Make a request to the push service to deactivate the push
subscription.
- If it was not possible to access the push service, reject promise
with a "
NetworkError" exception and terminate these steps.
- When the request has been completed, resolve promise with
true.
The serializer for a PushSubscription invokes the following steps:
- Let map be an empty map.
- Add an entry to map whose key name is
endpoint and whose value
is the result of converting the endpoint attribute of the
PushSubscription to a serialized value. The user agent MUST use
a serialization method that does not contain input-dependent branchs (that is, one that is
constant time). Note that a URL - as ASCII text - will not ordinarily require special
treatment.
- Let keys be an empty map.
- For each identifier i corresponding to keys in internal slots on the
PushSubscription, ordered by the name of the key:
- If the internal slot corresponds to an asymmetric key pair, let b be the
encoded value of the public key corresponding to the key name i, using the
encoding defined for the key name (see
getKey).
- Otherwise, let b be the value as returned by
getKey.
- Let s be the URL-safe base64 encoding without padding [[!RFC4648]] of
b as a
USVString. The user agent MUST use a
serialization method that does not branch based on the value of b.
- Add an entry to keys whose key name is the name of i and
whose value is s.
- Add an entry to map whose key name is
keys and whose value is
keys.
- Return map.
Note that the options to a PushSubscription are not serialized.
Encryption keys used for push message encryption are provided to a webapp
through the getKey method or the serializer of
PushSubscription. Each key is named using a value from the
PushEncryptionKeyName enumeration.
enum PushEncryptionKeyName {
"p256dh",
"auth"
};
The p256dh value is
used to retrieve the P-256 ECDH Diffie-Hellman public key described in
[[!WEBPUSH-ENCRYPTION]].
The auth value is used to
retrieve the authentication secret described in [[!WEBPUSH-ENCRYPTION]].
typedef any JSON;
[Exposed=ServiceWorker]
interface PushMessageData {
ArrayBuffer arrayBuffer();
Blob blob();
JSON json();
USVString text();
};
PushMessageData objects have an associated bytes (a byte sequence) set on
creation, which is null if there was no data in the push message.
The arrayBuffer()
method, when invoked, MUST return an ArrayBuffer whose contents are
bytes. Exceptions thrown during the creation of the
ArrayBuffer object are re-thrown.
The blob() method, when
invoked, MUST return a Blob whose contents are bytes and
type is not provided.
The json() method, when
invoked, MUST return the result of invoking the initial value of
JSON.parse with the result of running utf-8 decode on
bytes as argument. Re-throw any exceptions thrown by
JSON.parse.
The text() method, when
invoked, MUST return the result of running utf-8 decode on bytes.
To extract a byte sequence from object, run these steps:
- Let bytes be an empty byte sequence.
- Switch on object's type:
-
BufferSource
-
Set bytes to a copy of object's contents.
-
USVString
-
Set bytes to the result of running utf-8 encode on
object.
- Return bytes.
Events
The Service Worker specification defines a ServiceWorkerGlobalScope interface
[[!SERVICE-WORKERS]], which this specification extends.
partial interface ServiceWorkerGlobalScope {
attribute EventHandler onpush;
attribute EventHandler onpushsubscriptionchange;
};
The onpush attribute is
an event handler whose corresponding event handler event type is
push.
The onpushsubscriptionchange
attribute is an event handler whose corresponding event handler event type is
pushsubscriptionchange.
The push event
The PushEvent interface represents a received push message.
typedef (BufferSource or USVString) PushMessageDataInit;
dictionary PushEventInit : ExtendableEventInit {
PushMessageDataInit data;
};
[Constructor(DOMString type, optional PushEventInit eventInitDict), Exposed=ServiceWorker]
interface PushEvent : ExtendableEvent {
readonly attribute PushMessageData? data;
};
Upon receiving a push message from the push service, the user agent
MUST run the following steps:
- Let registration be the service worker registration corresponding
to the push message.
- If registration is not found, abort these steps.
- Let subscription be the active push subscription for
registration.
- Initialize pushdata to a value of
null.
- If the push message contains a payload, perform the following steps:
- Decrypt the push message using the private key from the key pair
associated with subscription and the process described in
[[!WEBPUSH-ENCRYPTION]]. This produces the plain text of the message.
- If the push message could not be decrypted for any reason, perform the
following steps:
- Acknowledge the receipt of the push message according to
[[!WEBPUSH-PROTOCOL]]. Though the message was not successfully received and
processed, this prevents the push service from attempting to retransmit the
message; a badly encrypted message is not recoverable.
- Discard the push message.
- Terminate this process.
A push event MUST NOT be fired for a push message that was
not successfully decrypted using the key pair associated with the push
subscription.
- Let pushdata be the decrypted plain text of the push message.
- Invoke the Handle Functional Event algorithm with a service worker
registration of registration and callbackSteps set to the
following steps:
- Set global to the global object that was provided as an argument.
- Create a trusted event, e, that uses the
PushEvent interface, with the event type push, which
does not bubble, is not cancelable, and has no default action.
- If the push message contains valid data - that is, if the message can be
successfully decoded and decrypted - set the
data attribute of
e to a new PushMessageData instance with bytes
set to the binary push message data.
- Dispatch e to global.
- Run the following steps in parallel:
- Wait for all of the promises in the extend lifetime promises of
e to resolve.
- If all the promises resolve successfully, acknowledge the receipt of the
push message according to [[!WEBPUSH-PROTOCOL]] and abort these steps.
-
If the same push message has been delivered to a service worker
registration multiple times unsuccessfully, acknowledge the receipt of
the push message according to [[!WEBPUSH-PROTOCOL]].
Acknowledging the push message causes the push service to stop
delivering the message and to report success to the application
server. This prevents the same push message from being retried by
the push service indefinitely.
Acknowledging also means that an application server could incorrectly
receive a delivery receipt indicating successful delivery of the push
message. Therefore, multiple rejections SHOULD be permitted before
acknowledging; allowing at least three attempts is recommended.
When a constructor of the PushEvent interface, or of an interface that inherits
from the PushEvent interface, is invoked, the usual steps for constructing
events are extended to include the following steps:
- If eventInitDict's
data member is not present, set the
data attribute of the event to null and terminate these steps.
- Set b to the result of extracting a
byte sequence from the "
data" member of eventInitDict.
- Set the
data attribute of the event to a new PushMessageData
instance with bytes set to b.
The pushsubscriptionchange event
The pushsubscriptionchange event indicates that a push subscription
has been invalidated, or will soon be invalidated. For example, the push service
MAY set an expiration time. A Service Worker SHOULD attempt to resubscribe while
handling this event, in order to continue receiving push messages.
When new push subscription information becomes available, the user agent
MUST run the following steps:
- Let registration be the service worker registration corresponding
to the push message.
- If registration is not found, abort these steps.
- Invoke the Handle Functional Event algorithm with a service worker
registration of registration and callbackSteps set to the
following steps:
- Set global to the global object that was provided as an argument.
- Create a trusted event, e, that uses the
ExtendableEvent interface, with the event type
pushsubscriptionchange, which does not bubble, is not cancelable, and
has no default action.
- Dispatch e to global.
- If the previous push subscription is still active, perform the following
steps in parallel:
- Set oldSubscription to the previous push subscription.
- Wait for all of the promises in the extend lifetime promises of
e to either resolve or reject.
- Unsubscribe oldSubscription.
This algorithm ensures that the Service Worker is able to react to any
non-destructive change in a push subscription, such as an automatic refresh,
without causing any active push subscription to be terminated prematurely. A
Service Worker can request a new push subscription during this process and
ensure that no push messages are lost.
Permission Enumeration
enum PushPermissionState {
"granted",
"denied",
"prompt"
};
|
Enumeration
|
Description
|
granted
|
The webapp has permission to use the Push API.
|
denied
|
The webapp has been denied permission to use the Push API.
|
prompt
|
The webapp needs to ask for permission in order to use the Push API.
|
Acknowledgements
The editors would like to express their gratitude to the Mozilla and Telefónica Digital
teams implementing the Firefox OS Push message solution and specially to Doug Turner,
Nikhil Marathe, Fernando R. Sela, Guillermo López, Antonio Amaya, José Manuel Cantera and
Albert Crespell, for their technical guidance, implementation work and support.