Make final UTRs
Philipp Ross
2017-03-08
Last updated: 2018-09-25
Code version: 1e6d9bb
Making final/longest UTRs
There were several methods and data sets used to predict 5’ and 3’ UTRs.
The first method was using the RNA-seq data sets and continuous read coverage. Any continuous coverage found surrounding known transcripts that met a read threshold cutoff of 5 reads or more was added as a UTR to the transcript from which it extended depending on whether it was on the 5’ or 3’ end of the transcript. This was done for each strain inidividually.
The second method to predict 5’ UTRs was done by using a variant of nanoCAGE in order to tag the extreme ends of mRNA molecules and sequence them along with a synthetic oligo used for the pull down of these extreme ends. No 3’ UTRs of transcripts was predicted using this approach although both ends were tagged.
Finally, the 5’ mRNA capture data was used to correct 5’ UTR predictions in all strains IF there was coverage support from the RNA-seq data in that loci where the capture data predicted it to be. If there was no prediction based on the 5’ capture data, then coverage from the 3D7 strain was used to “repair” the 5’ UTRs as well.
These predictions were all combined into lists of “longest possible transcripts” for each strain. Priority was given to predictions:
- 5’ mRNA capture prediction
- 5’ mRNA capture prediction used to repair the coverage prediction
- 3D7 coverage repaired UTRs
- Original RNA-seq UTR predictions
# 3D7
Rscript scripts/create_final_utrs.R
../data/utrs/repaired_cov_utrs/repaired_with_TSO_5UTRs/repaired_with_tso_5UTRs.3d7.filtered.rescued_5utrs.gff
../data/utrs/repaired_cov_utrs/repaired_with_3D7_coverage_5UTRs/repaired_with_3d7_cov_5UTRs.3d7.filtered.rescued_5utrs.gff
../data/utrs/original_utrs/final.5utrs.3d7.3d7_v3_chr.idc.gff
../data/utrs/original_utrs/tso_thr5.gff
../data/utrs/original_utrs/final.3utrs.3d7.3d7_v3_chr.idc.gff
TRUE
../output/final_utrs/final_utrs_3d7.gff
# HB3
Rscript scripts/create_final_utrs.R
../data/utrs/repaired_cov_utrs/repaired_with_TSO_5UTRs/repaired_with_tso_5UTRs.hb3.filtered.rescued_5utrs.gff
../data/utrs/repaired_cov_utrs/repaired_with_3D7_coverage_5UTRs/repaired_with_3d7_cov_5UTRs.hb3.filtered.rescued_5utrs.gff
../data/utrs/original_utrs/final.5utrs.hb3.3d7_v3_chr.idc.gff
../data/utrs/original_utrs/tso_thr5.gff
../data/utrs/original_utrs/final.3utrs.hb3.3d7_v3_chr.idc.gff
TRUE
../output/final_utrs/final_utrs_hb3.gff
#IT
Rscript scripts/create_final_utrs.R
../data/utrs/repaired_cov_utrs/repaired_with_TSO_5UTRs/repaired_with_tso_5UTRs.it.filtered.rescued_5utrs.gff
../data/utrs/repaired_cov_utrs/repaired_with_3D7_coverage_5UTRs/repaired_with_3d7_cov_5UTRs.it.filtered.rescued_5utrs.gff
../data/utrs/original_utrs/final.5utrs.it.3d7_v3_chr.idc.gff
../data/utrs/original_utrs/tso_thr5.gff
../data/utrs/original_utrs/final.3utrs.it.3d7_v3_chr.idc.gff
TRUE
../output/final_utrs/final_utrs_it.gffFinally, we should read in the resulting data:
# function to read in the data
read_utrs <- function(file, input_strain) {
df <- as.data.frame(rtracklayer::import.gff3(file)) %>%
dplyr::select(Parent,type,width)
df$strain <- input_strain
df$Parent <- as.character(df$Parent)
return(df)
}
utrs3d7 <- read_utrs("../output/final_utrs/longest_utrs_3d7_plasmodb_compatible.gff", "3D7")
utrshb3 <- read_utrs("../output/final_utrs/longest_utrs_hb3_plasmodb_compatible.gff", "HB3")
utrsit <- read_utrs("../output/final_utrs/longest_utrs_it_plasmodb_compatible.gff", "IT")
utrs <- rbind(utrs3d7,utrshb3,utrsit)5’ UTRs
What does the distribution of 5’ UTRs look like?
utrs %>%
dplyr::filter(type == "5UTR") %>%
ggplot(aes(x=width)) +
geom_histogram(color="grey90",bins=30) +
facet_grid(.~strain) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 55, hjust = 1))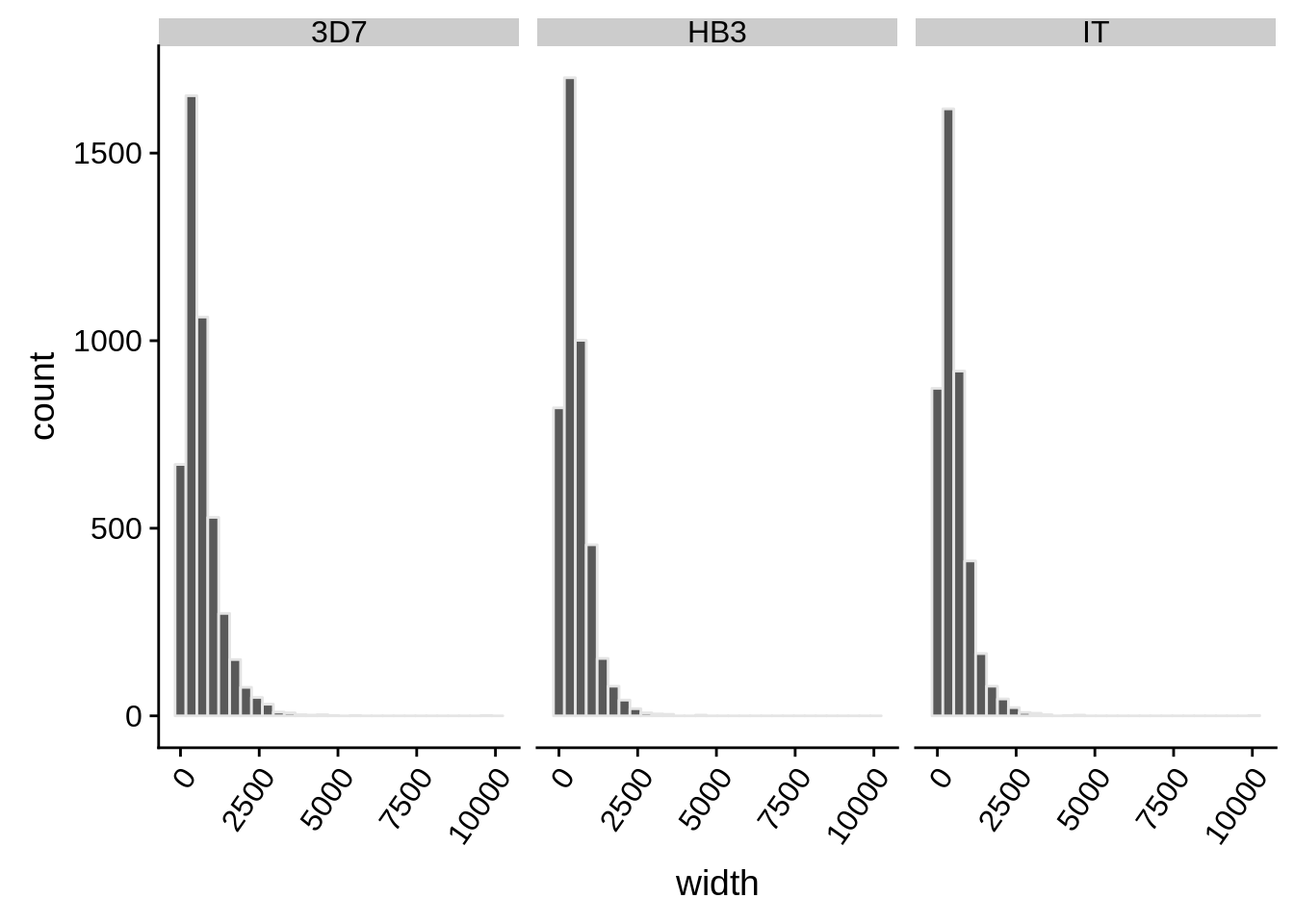
utrs %>%
dplyr::filter(type == "5UTR") %>%
ggplot(aes(x=strain,y=width)) +
geom_boxplot(fill="grey70")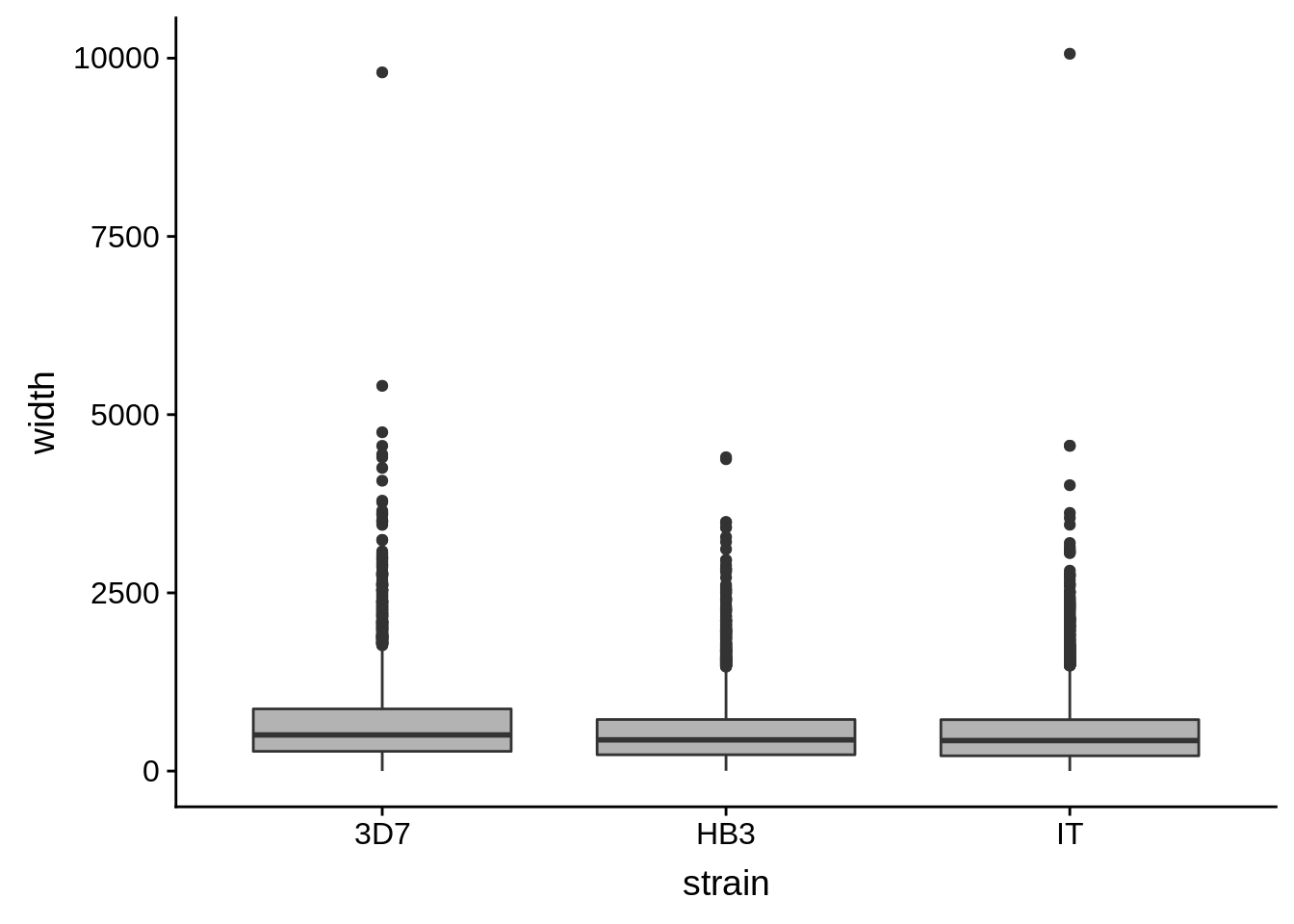
How do summary statistics vary between strains?
utrs %>%
dplyr::filter(type == "5UTR") %>%
dplyr::group_by(strain) %>%
dplyr::summarise(mean=mean(width),median=median(width),sd=sd(width))# A tibble: 3 x 4
strain mean median sd
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 3D7 663. 507 591.
2 HB3 541. 438 458.
3 IT 541. 428 499.3’ UTRs
What does the distribution of 3’ UTRs look like?
utrs %>%
dplyr::filter(type == "3UTR") %>%
ggplot(aes(x=width)) +
geom_histogram(color="grey90",bins=30) +
facet_grid(.~strain) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 55, hjust = 1))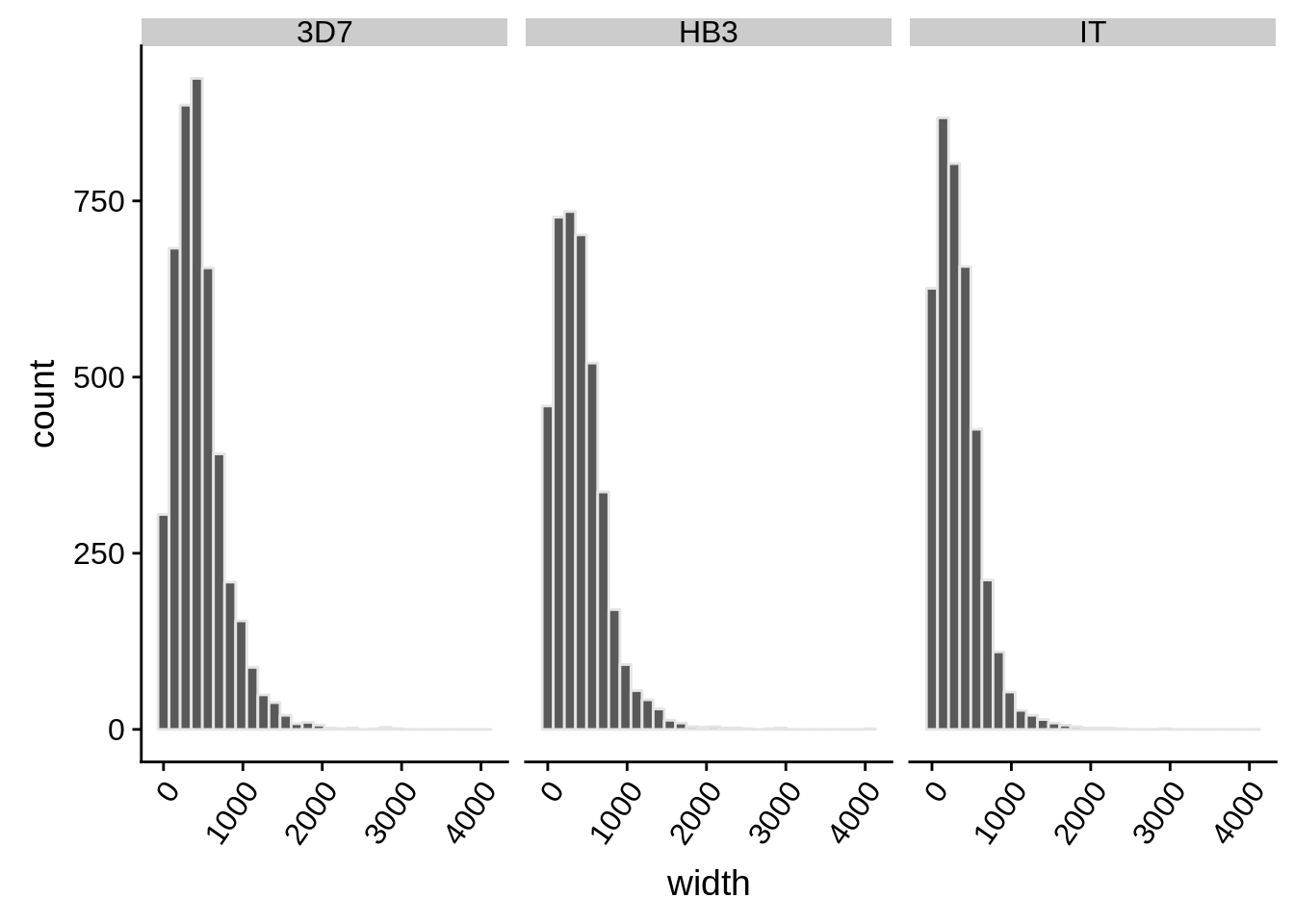
utrs %>%
dplyr::filter(type == "3UTR") %>%
ggplot(aes(x=strain,y=width)) +
geom_boxplot(fill="grey70")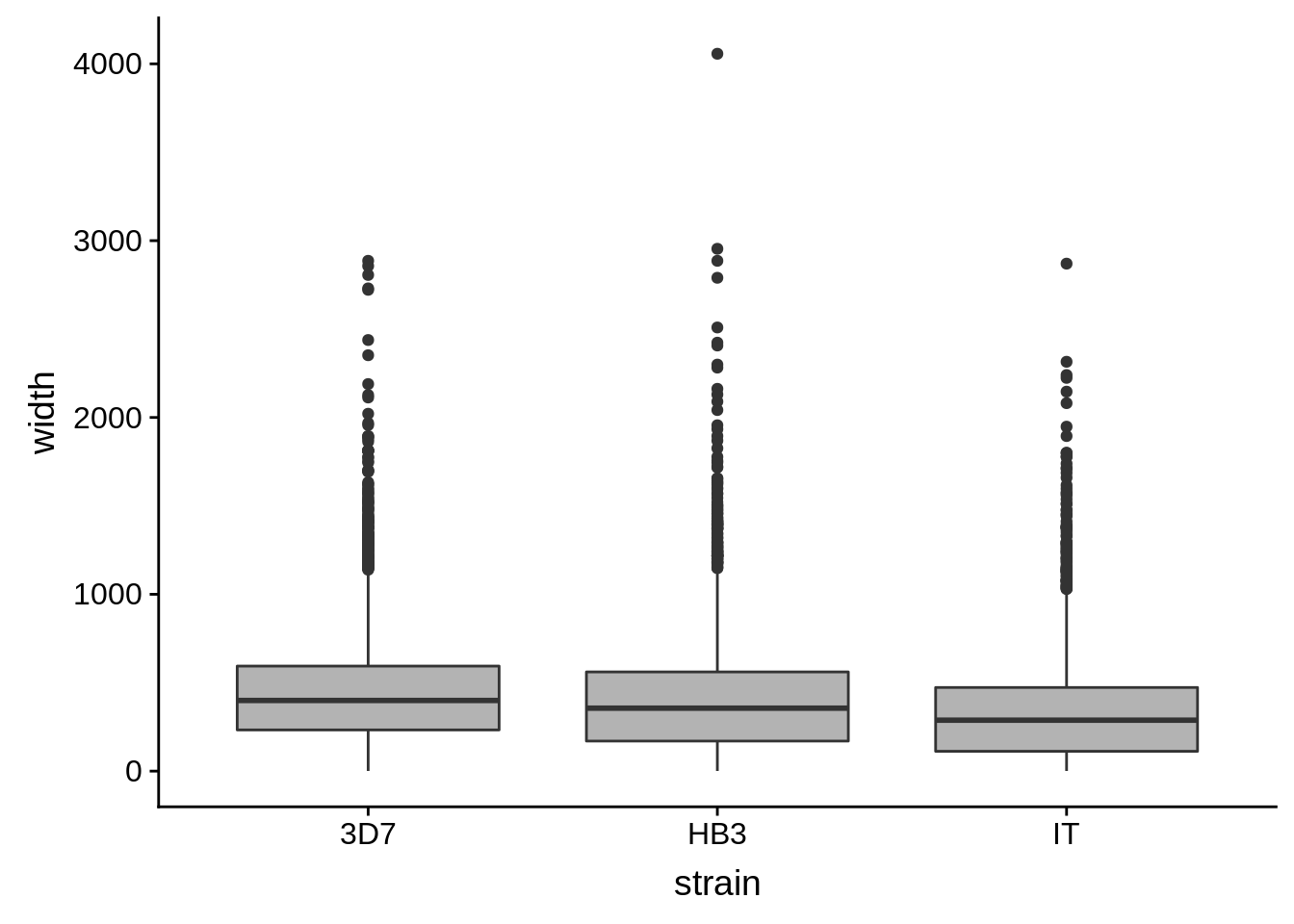
How do summary statistics vary between strains?
utrs %>%
dplyr::filter(type == "3UTR") %>%
dplyr::group_by(strain) %>%
dplyr::summarise(mean=mean(width),median=median(width),sd=sd(width))# A tibble: 3 x 4
strain mean median sd
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 3D7 454. 400. 325.
2 HB3 411. 356 330.
3 IT 335. 288 284.Homopolymer analysis
One thing we were also interested in looking at was why the coverage UTRs some times suffered from “coverage drops”. If we assume that the AT content of the genome isn’t as much of an issue anymore now that we are using PCR-free library preparation and better priming of RNA molecules, then one other issue that could be causing these coverage drops are homopolymer tracts. Another reason we are making this assumption is because the CAGE tags support this conclusion. Where the 5’ UTR often falls short, there is a lack of supporting CAGE tags. If we look upstream, however, we can see CAGE tags AND coverage if we look at the DAFT-seq data.
In the current analysis, I’m forgetting to take into account introns when looking for the presence of long homopolymer tracts within predicted UTRs. Important questions include:
- Do long homopolymer tracts exist within prediced coverage UTRs?
- Are UTRs containing long homopolymer tracts on average shorter than those that don’t?
To address these questions, I extended 5’ UTRs 100 base pairs beyond their predicted coverage-based TSS, counted the length of the longest homopolymer tract for each nucleotide, and looked whether longer homopolymer tracts tend to occur in UTRs that are shorter.
First let’s make 3D7 5UTR sequences for the analysis:
cat ../data/original_utrs/final.5utrs.3d7.3d7_v3_chr.idc.gff |
awk 'BEGIN {{OFS=FS=\"\t\"}} {{split($9,X,\";\"); split(X[1],Y,\"=\"); print $1,$4-1,$5,Y[2],$5-$4+1,$7}}' |
bedtools getfasta -fi ../data/genomes/pf3d7/PlasmoDB-24_Pfalciparum3D7_Genome.fasta -bed - -fo output/homopolymer_analysis/3d7_5utrs.fasta -s -name
bedtools flank -i ../data/original_utrs/final.5utrs.3d7.3d7_v3_chr.idc.gff -g ../data/genomes/pf3d7/PlasmoDB-24_Pfalciparum3D7_Genome.lengths -s -l 100 -r 0 |
awk 'BEGIN {{OFS=FS=\"\t\"}} {{split($9,X,\";\"); split(X[1],Y,\"=\"); print $1,$4-1,$5,Y[2],$5-$4+1,$7}}' |
bedtools getfasta -fi ../data/genomes/pf3d7/PlasmoDB-24_Pfalciparum3D7_Genome.fasta -bed - -fo ../output/homopolymer_analysis/minus_100bp_flank_3d7_5utrs.fasta -s -name
bedtools slop -i ../data/original_utrs/final.5utrs.3d7.3d7_v3_chr.idc.gff -g ../data/genomes/pf3d7/PlasmoDB-24_Pfalciparum3D7_Genome.lengths -s -l 100 -r 0 |
awk 'BEGIN {{OFS=FS=\"\t\"}} {{split($9,X,\";\"); split(X[1],Y,\"=\"); print $1,$4-1,$5,Y[2],$5-$4+1,$7}}' |
bedtools getfasta -fi ../data/genomes/pf3d7/PlasmoDB-24_Pfalciparum3D7_Genome.fasta -bed - -fo ../output/homopolymer_analysis/minus_100bp_slop_3d7_5utrs.fasta -s -nameNow let’s count the number of homopolymers:
Rscript ../code/scripts/final_utrs/count_homopolymers.R -f ../output/homopolymer_analysis/minus_100bp_flank_3d7_5utrs.fasta -l 50 -o ../output/homopolymer_analysis/minus_100bp_flank_3d7_5utrs_counts.tsv
Rscript ../code/scripts/final_utrs/count_homopolymers.R -f ../output/homopolymer_analysis/minus_100bp_slop_3d7_5utrs.fasta -l 50 -o ../output/homopolymer_analysis/minus_100bp_slop_3d7_5utrs_counts.tsv
Rscript ../code/scripts/final_utrs/count_homopolymers.R -f ../output/homopolymer_analysis/3d7_5utrs.fasta -l 50 -o ../output/homopolymer_analysis/3d7_5utrs.fasta_counts.tsvNow import that data:
utrplus <- readr::read_tsv("../output/homopolymer_analysis/minus_100bp_slop_3d7_5utrs_counts.tsv") # UTR plus 100bp upstream
plus<- readr::read_tsv("../output/homopolymer_analysis/minus_100bp_flank_3d7_5utrs_counts.tsv") # only 100 bp upstream of UTR
utrs <- readr::read_tsv("../output/homopolymer_analysis/3d7_5utrs_counts.tsv") # only UTR
originalutrs <- tibble::as_tibble(rtracklayer::import.gff3("../data/utrs/original_utrs/final.5utrs.3d7.3d7_v3_chr.idc.gff"))
originalutrs$Parent <- as.character(originalutrs$Parent)
fixedutrs <- tibble::as_tibble(rtracklayer::import.gff3("../output/final_utrs/final_utrs_3d7.gff")) %>%
dplyr::filter(length_added > 0)
fixedutrs$Parent <- as.character(fixedutrs$Parent)And now plot the data:
tmp <- dplyr::inner_join(originalutrs, utrplus, by = c("Parent" = "gene_id"))
g <- tmp %>%
dplyr::filter(width < 8000) %>%
dplyr::group_by(Parent) %>%
dplyr::summarise(width=unique(width),longest=max(longest)) %>%
ggplot(aes(y=width/longest,x=longest)) + geom_point(alpha=0.5) + stat_smooth(method="lm")
print(g)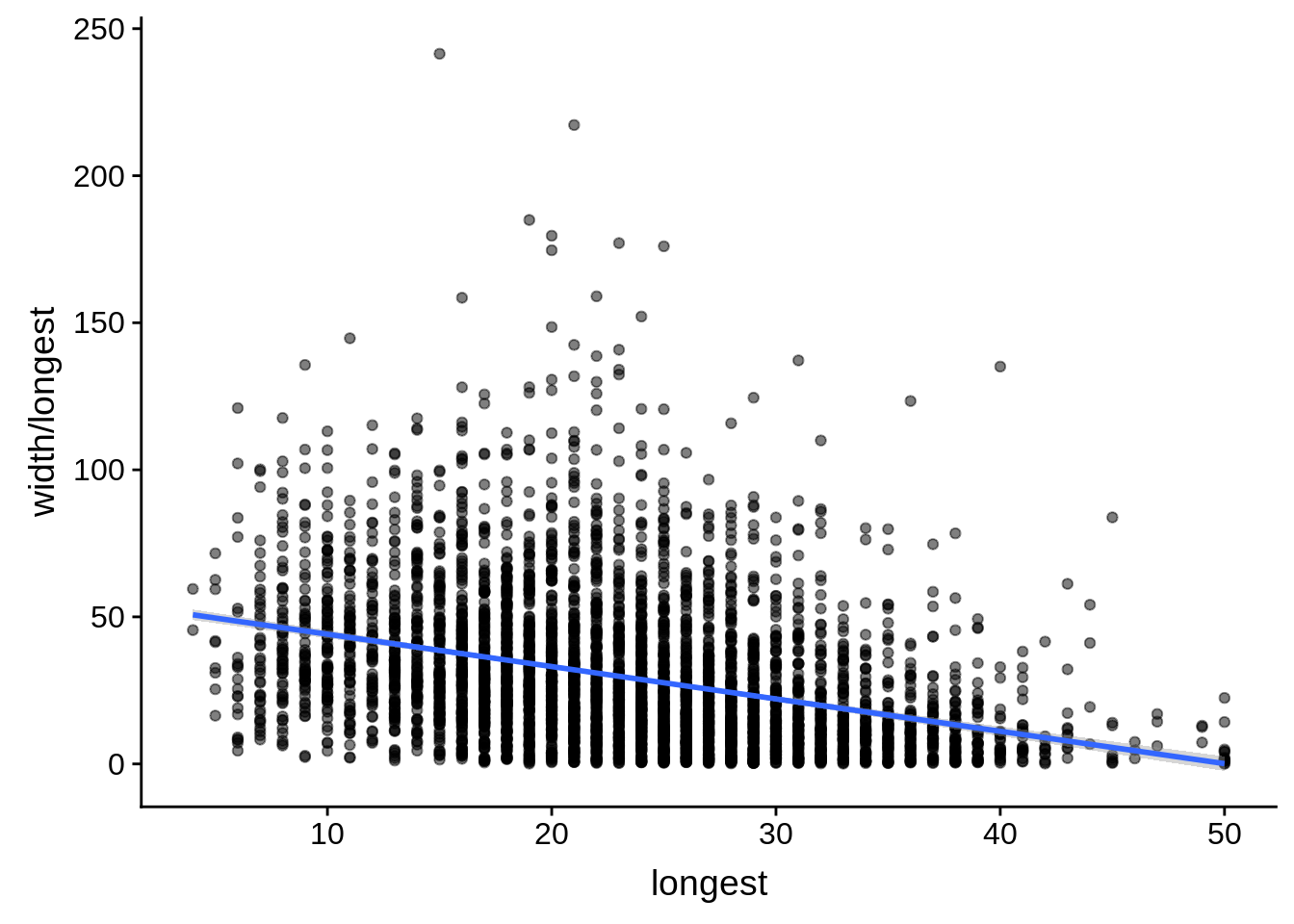
tmp %>%
dplyr::filter(width < 8000) %>%
dplyr::group_by(Parent) %>%
dplyr::summarise(width=unique(width),longest=max(longest)) %>%
do(broom::tidy(cor.test(.$width/.$longest,.$longest)))# A tibble: 1 x 8
estimate statistic p.value parameter conf.low conf.high method
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 -0.346 -24.4 9.37e-124 4385 -0.372 -0.320 Pears…
# ... with 1 more variable: alternative <chr>tmp <- dplyr::inner_join(originalutrs, plus, by = c("Parent" = "gene_id"))
g <- tmp %>%
dplyr::filter(width < 8000) %>%
dplyr::group_by(Parent) %>%
dplyr::summarise(width=unique(width),longest=max(longest)) %>%
ggplot(aes(y=width,x=longest)) + geom_point(alpha=0.5) + stat_smooth(method="lm")
print(g)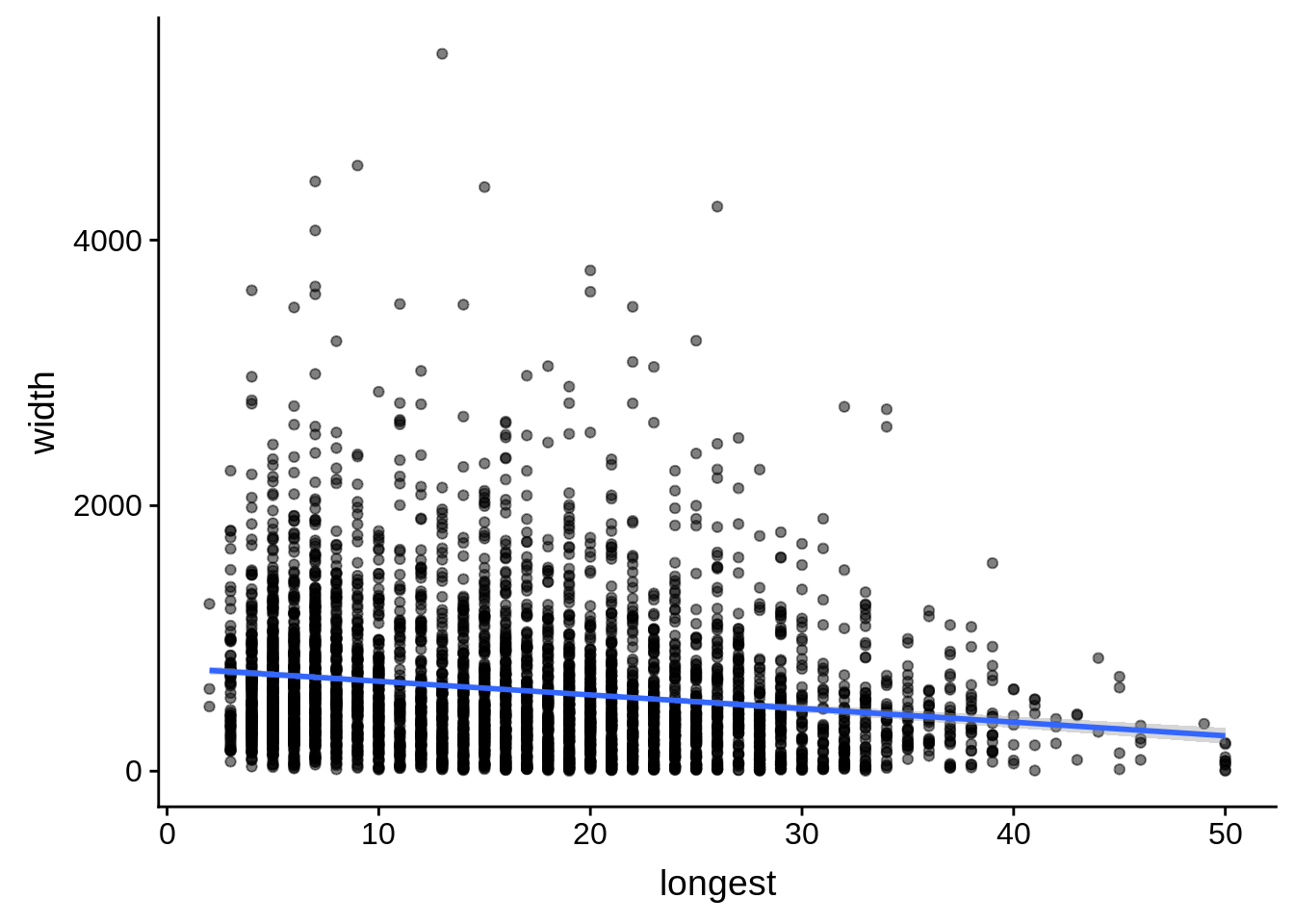
tmp %>%
dplyr::filter(width < 8000) %>%
dplyr::group_by(Parent) %>%
dplyr::summarise(width=unique(width),longest=max(longest)) %>%
do(broom::tidy(cor.test(.$width,.$longest)))# A tibble: 1 x 8
estimate statistic p.value parameter conf.low conf.high method
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 -0.174 -11.7 2.92e-31 4385 -0.203 -0.145 Pears…
# ... with 1 more variable: alternative <chr>tmp <- dplyr::inner_join(originalutrs, utrs, by = c("Parent" = "gene_id"))
g <- tmp %>%
dplyr::filter(width < 8000) %>%
dplyr::group_by(Parent) %>%
dplyr::summarise(width=unique(width),longest=max(longest)) %>%
ggplot(aes(y=width/longest,x=longest)) + geom_point(alpha=0.5) + stat_smooth(method="lm")
print(g)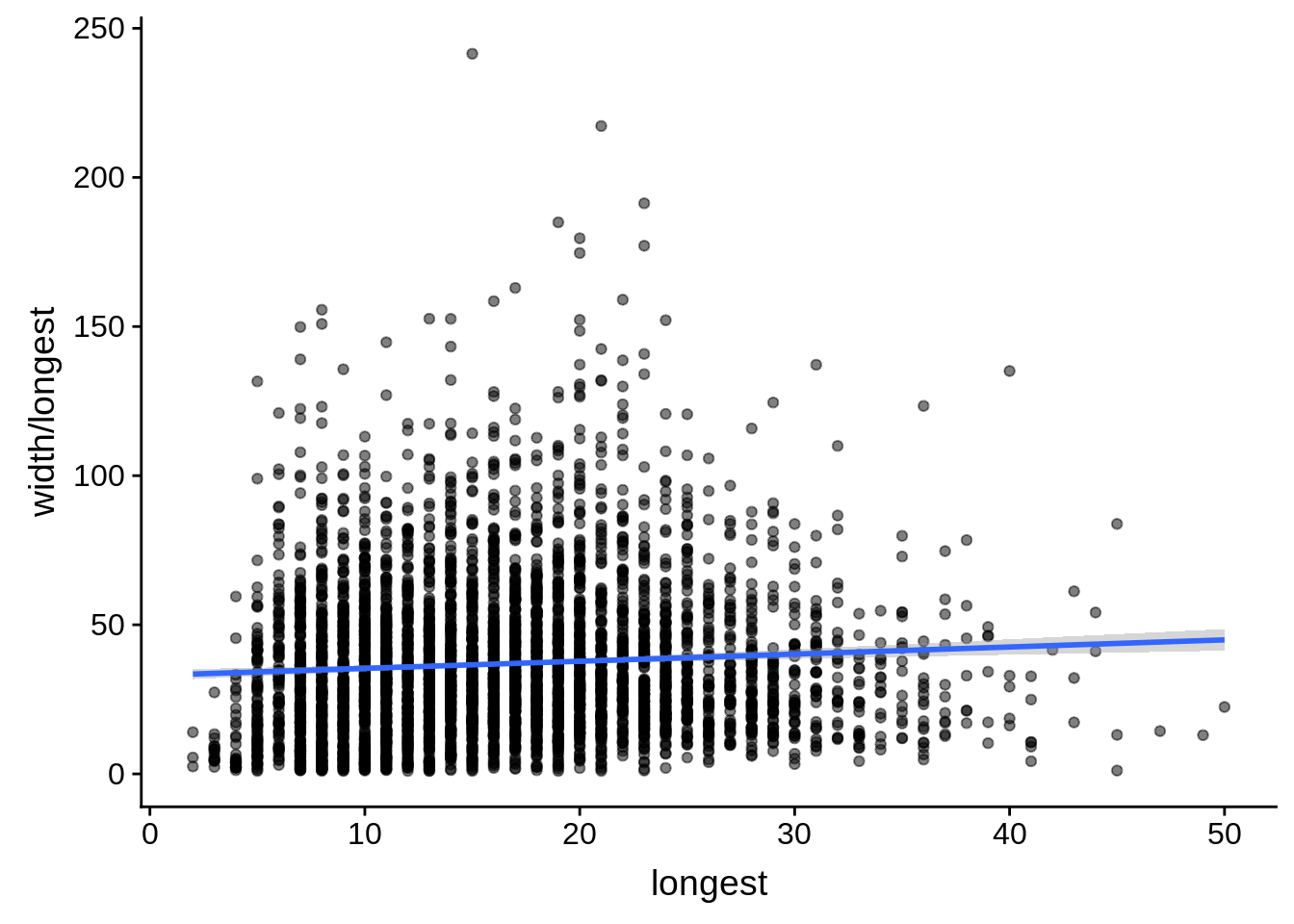
tmp %>%
dplyr::filter(width < 8000) %>%
dplyr::group_by(Parent) %>%
dplyr::summarise(width=unique(width),longest=max(longest)) %>%
do(broom::tidy(cor.test(.$width/.$longest,.$longest)))# A tibble: 1 x 8
estimate statistic p.value parameter conf.low conf.high method
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 0.0672 4.46 8.54e-6 4382 0.0376 0.0966 Pears…
# ... with 1 more variable: alternative <chr>tmp <- dplyr::inner_join(fixedutrs, utrplus, by = c("Parent" = "gene_id"))
g <- tmp %>%
dplyr::filter(width < 8000) %>%
dplyr::group_by(Parent) %>%
dplyr::summarise(width=unique(width),longest=max(longest)) %>%
ggplot(aes(y=width/longest,x=longest)) + geom_point(alpha=0.5) + stat_smooth(method="lm")
print(g)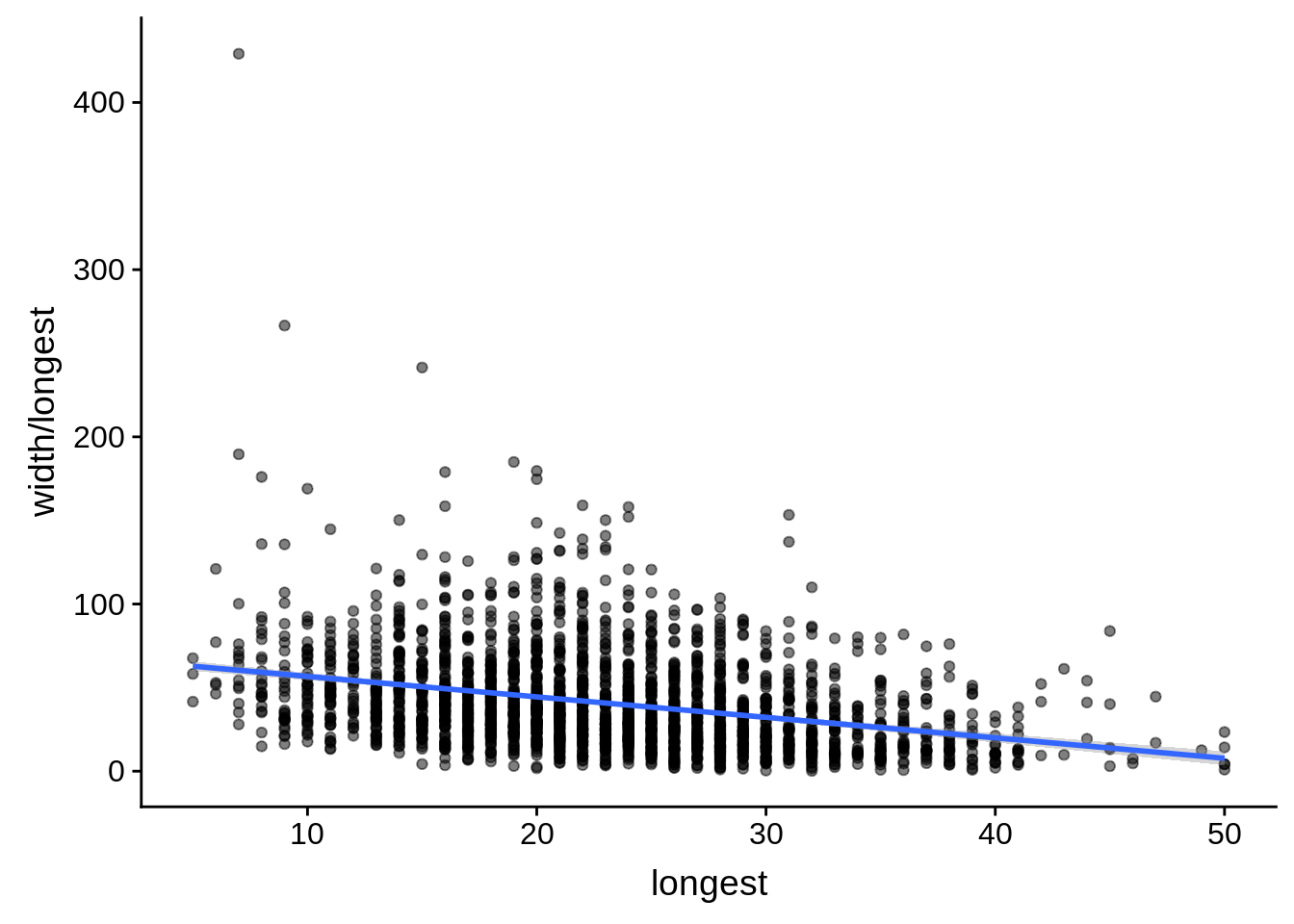
tmp %>%
dplyr::filter(width < 8000) %>%
dplyr::group_by(Parent) %>%
dplyr::summarise(width=unique(width),longest=max(longest)) %>%
do(broom::tidy(cor.test(.$width/.$longest,.$longest)))# A tibble: 1 x 8
estimate statistic p.value parameter conf.low conf.high method
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <chr>
1 -0.320 -16.2 4.10e-56 2299 -0.357 -0.283 Pears…
# ... with 1 more variable: alternative <chr>Session Information
R version 3.5.0 (2018-04-23)
Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu (64-bit)
Running under: Gentoo/Linux
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /usr/local/lib64/R/lib/libRblas.so
LAPACK: /usr/local/lib64/R/lib/libRlapack.so
locale:
[1] LC_CTYPE=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C
[3] LC_TIME=en_US.UTF-8 LC_COLLATE=en_US.UTF-8
[5] LC_MONETARY=en_US.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=en_US.UTF-8
[7] LC_PAPER=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C
[9] LC_ADDRESS=C LC_TELEPHONE=C
[11] LC_MEASUREMENT=en_US.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
attached base packages:
[1] parallel stats4 stats graphics grDevices utils datasets
[8] methods base
other attached packages:
[1] bindrcpp_0.2.2
[2] BSgenome.Pfalciparum.PlasmoDB.v24_1.0
[3] BSgenome_1.48.0
[4] rtracklayer_1.40.6
[5] Biostrings_2.48.0
[6] XVector_0.20.0
[7] GenomicRanges_1.32.6
[8] GenomeInfoDb_1.16.0
[9] org.Pf.plasmo.db_3.6.0
[10] AnnotationDbi_1.42.1
[11] IRanges_2.14.10
[12] S4Vectors_0.18.3
[13] Biobase_2.40.0
[14] BiocGenerics_0.26.0
[15] scales_1.0.0
[16] cowplot_0.9.3
[17] magrittr_1.5
[18] forcats_0.3.0
[19] stringr_1.3.1
[20] dplyr_0.7.6
[21] purrr_0.2.5
[22] readr_1.1.1
[23] tidyr_0.8.1
[24] tibble_1.4.2
[25] ggplot2_3.0.0
[26] tidyverse_1.2.1
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] nlme_3.1-137 bitops_1.0-6
[3] matrixStats_0.54.0 lubridate_1.7.4
[5] bit64_0.9-7 httr_1.3.1
[7] rprojroot_1.3-2 tools_3.5.0
[9] backports_1.1.2 utf8_1.1.4
[11] R6_2.2.2 DBI_1.0.0
[13] lazyeval_0.2.1 colorspace_1.3-2
[15] withr_2.1.2 tidyselect_0.2.4
[17] bit_1.1-14 compiler_3.5.0
[19] git2r_0.23.0 cli_1.0.0
[21] rvest_0.3.2 xml2_1.2.0
[23] DelayedArray_0.6.5 labeling_0.3
[25] digest_0.6.15 Rsamtools_1.32.3
[27] rmarkdown_1.10 R.utils_2.6.0
[29] pkgconfig_2.0.2 htmltools_0.3.6
[31] rlang_0.2.2 readxl_1.1.0
[33] rstudioapi_0.7 RSQLite_2.1.1
[35] bindr_0.1.1 jsonlite_1.5
[37] BiocParallel_1.14.2 R.oo_1.22.0
[39] RCurl_1.95-4.11 GenomeInfoDbData_1.1.0
[41] Matrix_1.2-14 fansi_0.3.0
[43] Rcpp_0.12.18 munsell_0.5.0
[45] R.methodsS3_1.7.1 stringi_1.2.4
[47] yaml_2.2.0 SummarizedExperiment_1.10.1
[49] zlibbioc_1.26.0 plyr_1.8.4
[51] grid_3.5.0 blob_1.1.1
[53] crayon_1.3.4 lattice_0.20-35
[55] haven_1.1.2 hms_0.4.2
[57] knitr_1.20 pillar_1.3.0
[59] reshape2_1.4.3 XML_3.98-1.16
[61] glue_1.3.0 evaluate_0.11
[63] modelr_0.1.2 cellranger_1.1.0
[65] gtable_0.2.0 assertthat_0.2.0
[67] broom_0.5.0 GenomicAlignments_1.16.0
[69] memoise_1.1.0 workflowr_1.1.1 This R Markdown site was created with workflowr