Poisson nugget effect(modified)
Dongyue Xie
May 7, 2018
Last updated: 2018-05-07
workflowr checks: (Click a bullet for more information)-
✔ R Markdown file: up-to-date
Great! Since the R Markdown file has been committed to the Git repository, you know the exact version of the code that produced these results.
-
✔ Environment: empty
Great job! The global environment was empty. Objects defined in the global environment can affect the analysis in your R Markdown file in unknown ways. For reproduciblity it’s best to always run the code in an empty environment.
-
✔ Seed:
set.seed(20180501)The command
set.seed(20180501)was run prior to running the code in the R Markdown file. Setting a seed ensures that any results that rely on randomness, e.g. subsampling or permutations, are reproducible. -
✔ Session information: recorded
Great job! Recording the operating system, R version, and package versions is critical for reproducibility.
-
Great! You are using Git for version control. Tracking code development and connecting the code version to the results is critical for reproducibility. The version displayed above was the version of the Git repository at the time these results were generated.✔ Repository version: b082c1b
Note that you need to be careful to ensure that all relevant files for the analysis have been committed to Git prior to generating the results (you can usewflow_publishorwflow_git_commit). workflowr only checks the R Markdown file, but you know if there are other scripts or data files that it depends on. Below is the status of the Git repository when the results were generated:
Note that any generated files, e.g. HTML, png, CSS, etc., are not included in this status report because it is ok for generated content to have uncommitted changes.Ignored files: Ignored: .Rhistory Ignored: .Rproj.user/ Ignored: log/ Untracked files: Untracked: analysis/overdis.Rmd
Expand here to see past versions:
| File | Version | Author | Date | Message |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rmd | b082c1b | Dongyue | 2018-05-07 | correct mu_t+E(u_t) |
Note: 1. Switch to \(m_t=\exp(\hat\mu_t+\hat u_t)\) at each iteration. 2. Change the functions to be circular(kept polynomial curve for comparisons).
Algorithm
Let \(X_t\) be a Poisson observation, \(t=1,2,\dots,T\).
- Input \(\sigma\) and initialize \(m_t^{(0)}=\frac{\Sigma_{t=1}^T X_t}{T}\), \(Y_t^{(0)}=\log(m_t^{(0)})+\frac{X_t-m_t^{(0)}}{m_t^{(0)}}\) and \(s_t^{2(0)}=\frac{1}{m_t^{(0)}}\) for \(t=1,2,\dots,T\).
- For \(i=1,2,...\), iterate until convergence:
- Fit \(Y_t=\tilde\mu_t+N(0,s_t^2)\) using
smash.gausand obtain \(\hat{\tilde\mu}_t\). - Update \(m_t^{(i)}=\exp(\hat{\tilde\mu}_t)\), \(Y_t^{(i)}=\log(m_t^{(i)})+\frac{X_t-m_t^{(i)}}{m_t^{(i)}}\), and \(s_t^{2(i)}=\frac{1}{m_t^{(i)}}\)
- Fit \(Y_t^{(i)}=\mu_t+N(0,\sigma^2+s_t^{2(i)})\) using
smash.gausand output \(\hat{\mu}_t\).
Convergence criteria: \(||\tilde\mu^{(i)}-\tilde\mu^{(i-1)}||_2\leq \epsilon\).
#' smash generaliation function
#' A modified version. Instead of input \sigma^2+s_t^2 and estiamte \mu_t, we simply input s_t^2 and after convergence, input both to estimate the final \mu_t.
#' This function is for $Y_t=\mu_t+N(0,s_t^2)+N(0,\sigma^2)$ with known $s_t^2$ and $\sigma^2$.
#' @param x: a vector of observations
#' @param sigma: standard deviations, scalar.
#' @param family: choice of wavelet basis to be used, as in wavethresh.
#' @param niter: number of iterations for IRLS
#' @param tol: tolerance of the criterion to stop the iterations
smash.gen=function(x,sigma,family='DaubExPhase',niter=30,tol=1e-2){
mu=c()
s=c()
y=c()
munorm=c()
mu=rbind(mu,rep(mean(x),length(x)))
s=rbind(s,rep(1/mu[1],length(x)))
y=rbind(y,log(mean(x))+(x-mean(x))/mean(x))
for(i in 1:niter){
vars=ifelse(s[i,]<0,1e-8,s[i,])
mu.hat=smash.gaus(y[i,],sigma=sqrt(vars))#mu.hat is \mu_t+E(u_t|y)
mu=rbind(mu,mu.hat)
munorm[i]=norm(mu.hat-mu[i,],'2')
if(munorm[i]<tol){
break
}
#update m and s_t
mt=exp(mu.hat)
s=rbind(s,1/mt)
y=rbind(y,log(mt)+(x-mt)/mt)
}
mu.hat=smash.gaus(y[i,],sigma = sqrt(sigma^2+ifelse(s[i,]<0,1e-8,s[i,])))
return(list(mu.hat=mu.hat,mu=mu,s=s,y=y,munorm=munorm))
}#' Simulation study comparing smash and smashgen
simu_study=function(m,sigma,seed=1234,
niter=30,family='DaubExPhase',tol=1e-2,
reflect=FALSE){
set.seed(seed)
lamda=exp(m+rnorm(length(m),0,sigma))
x=rpois(length(m),lamda)
#fit data
smash.out=smash.poiss(x,reflect=reflect)
smash.gen.out=smash.gen(x,sigma=sigma,niter=niter,family = family,tol=tol)
return(list(smash.out=smash.out,smash.gen.out=exp(smash.gen.out$mu.hat),smash.gen.est=smash.gen.out,x=x,loglik=smash.gen.out$loglik))
}Simulation 1: Constant trend Poisson nugget
\(\sigma=0.01\)
library(smashr)
m=rep(3,256)
simu.out=simu_study(m,0.01)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright", # places a legend at the appropriate place
c("truth","smash-gen"), # puts text in the legend
lty=c(1,1), # gives the legend appropriate symbols (lines)
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))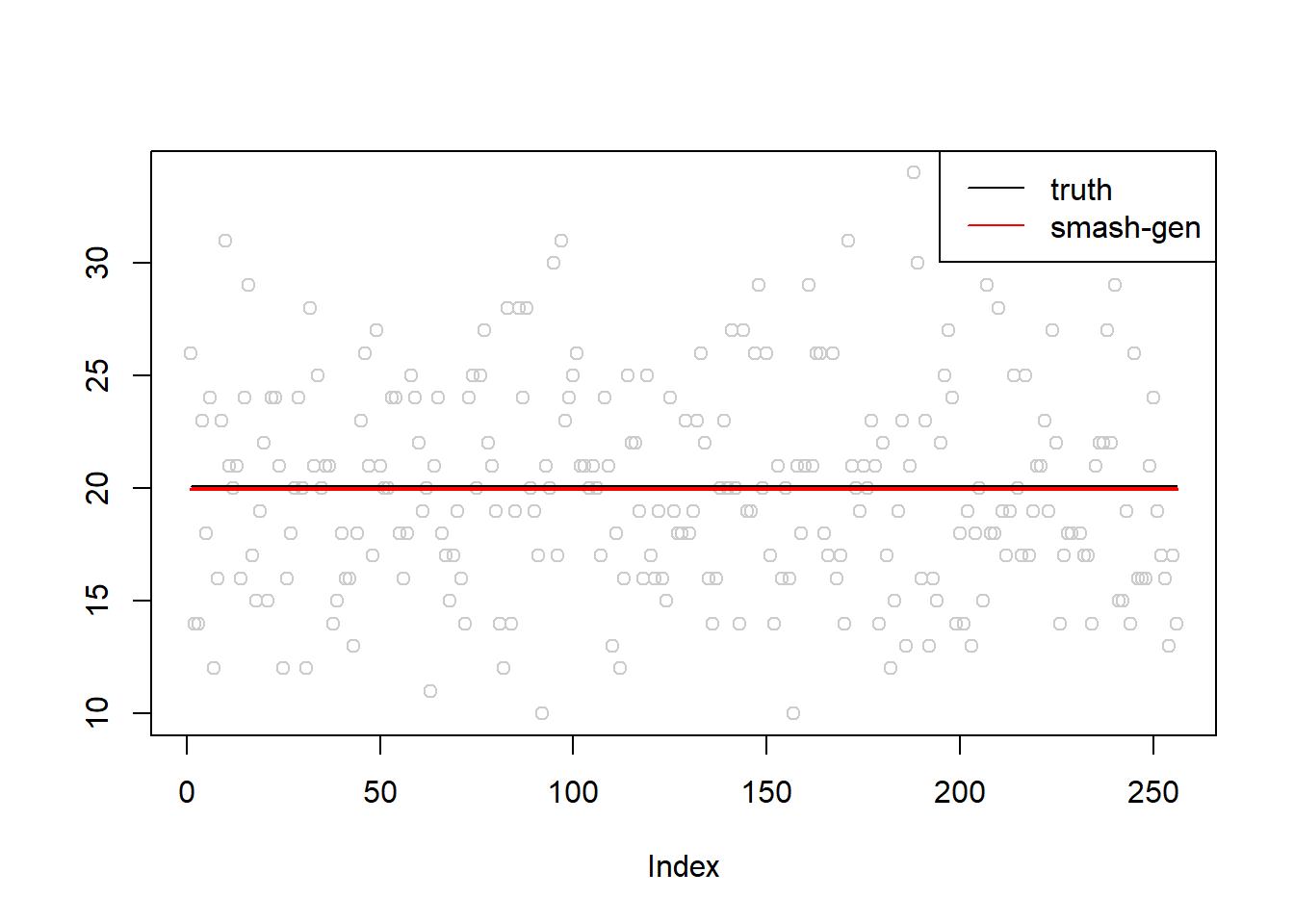
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))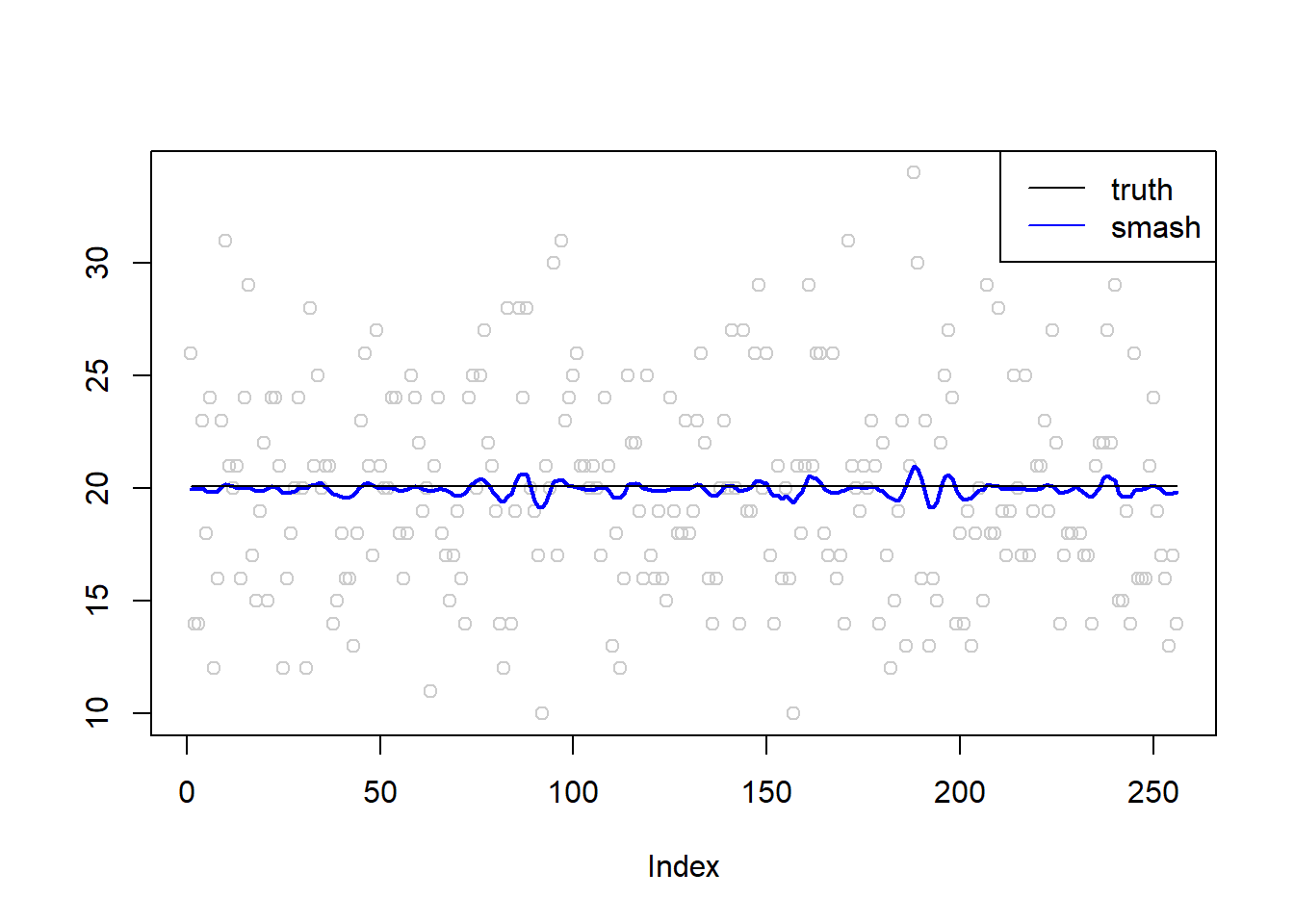
\(\sigma=0.1\)
simu.out=simu_study(m,0.1)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))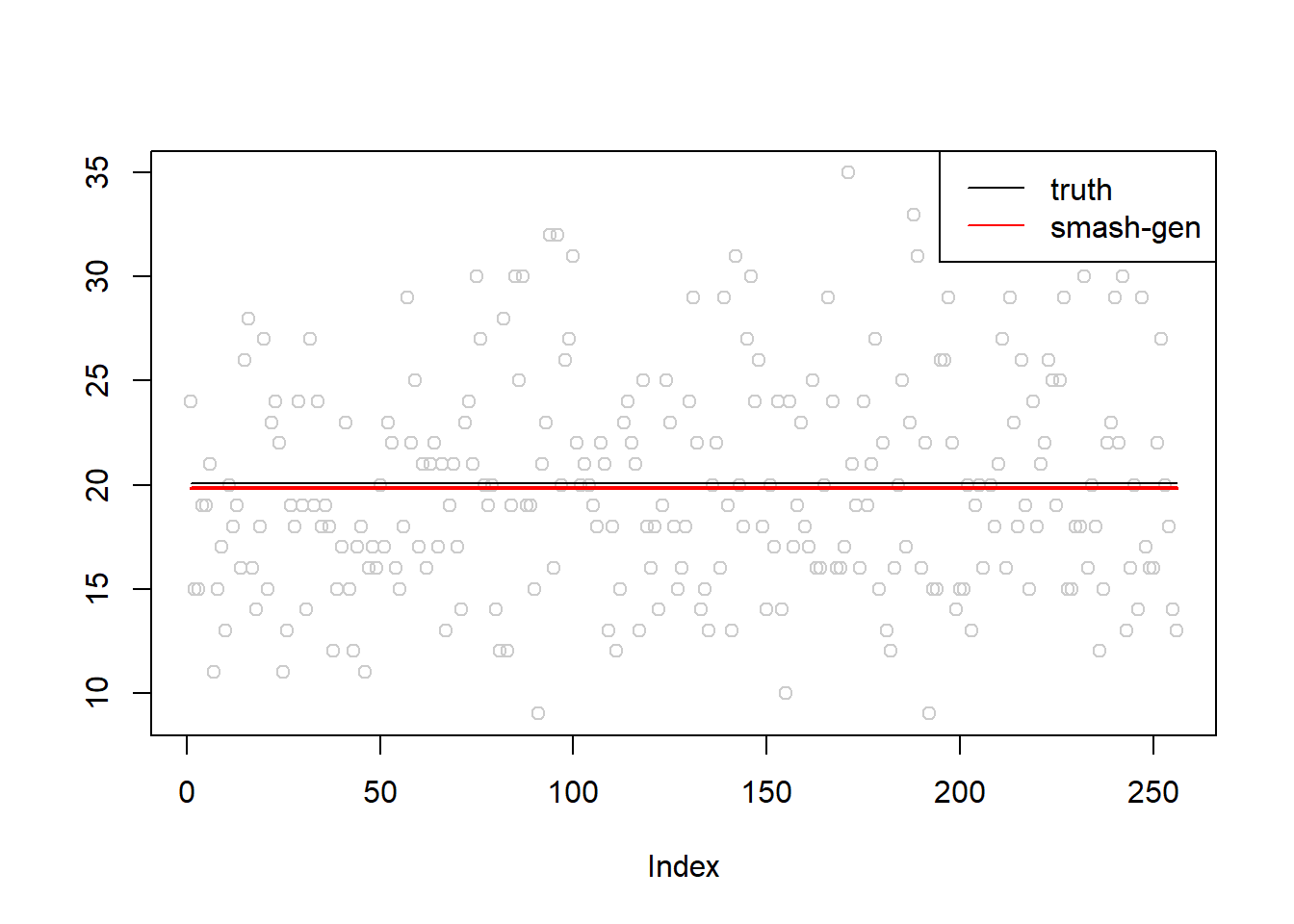
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))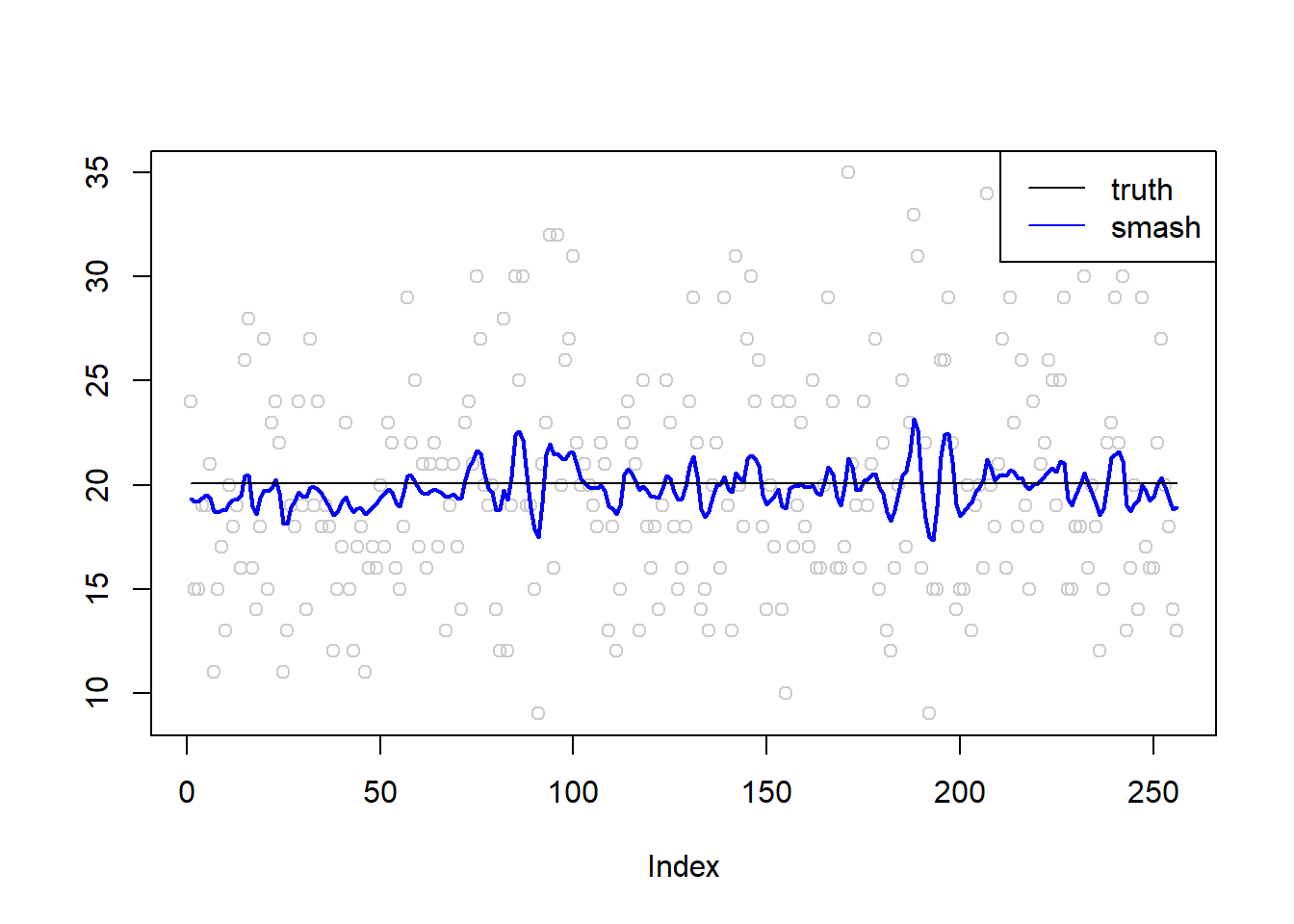
\(\sigma=0.5\)
simu.out=simu_study(m,0.5)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m),col='gray80')
legend("topright",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))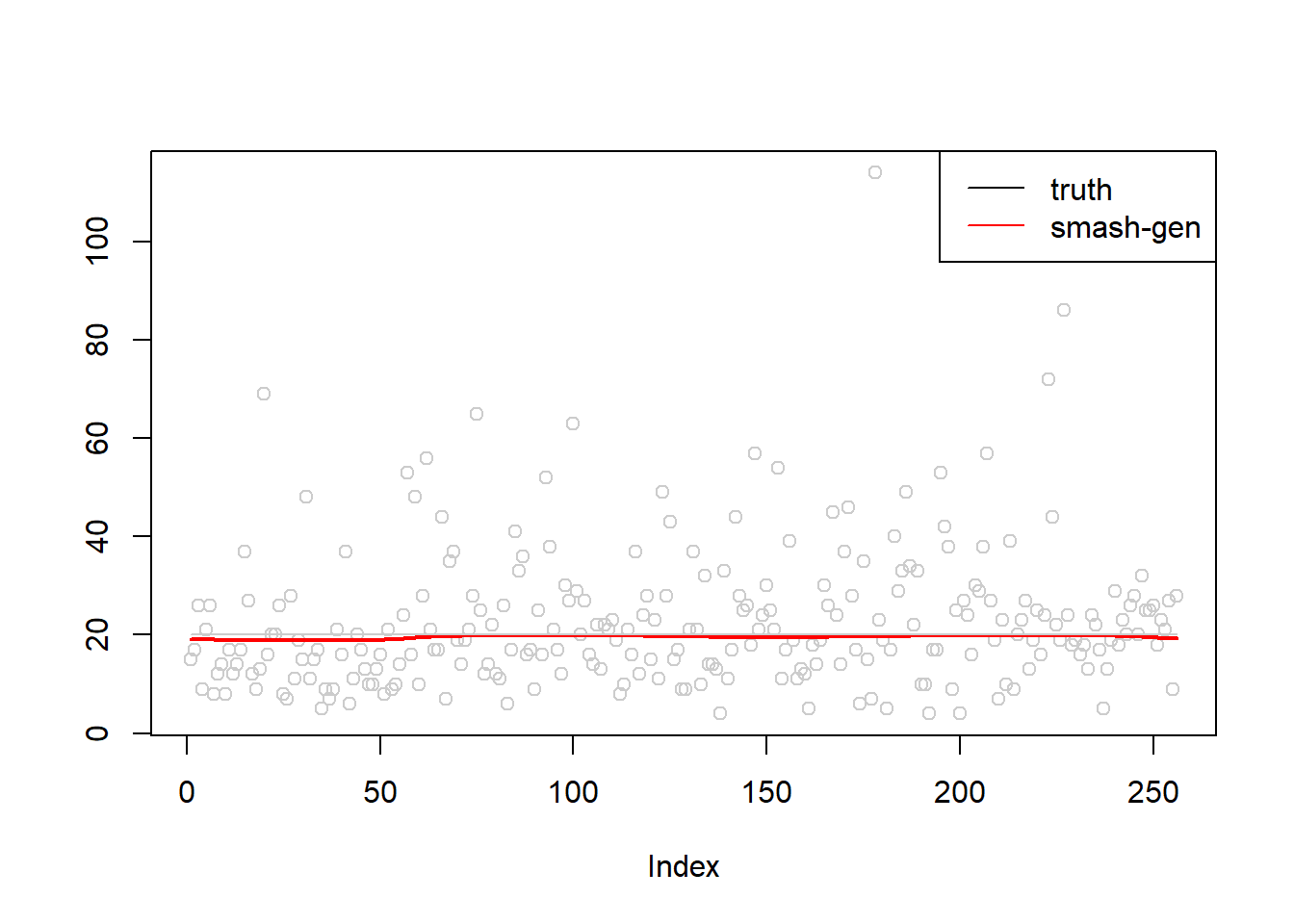
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m),col='gray80')
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))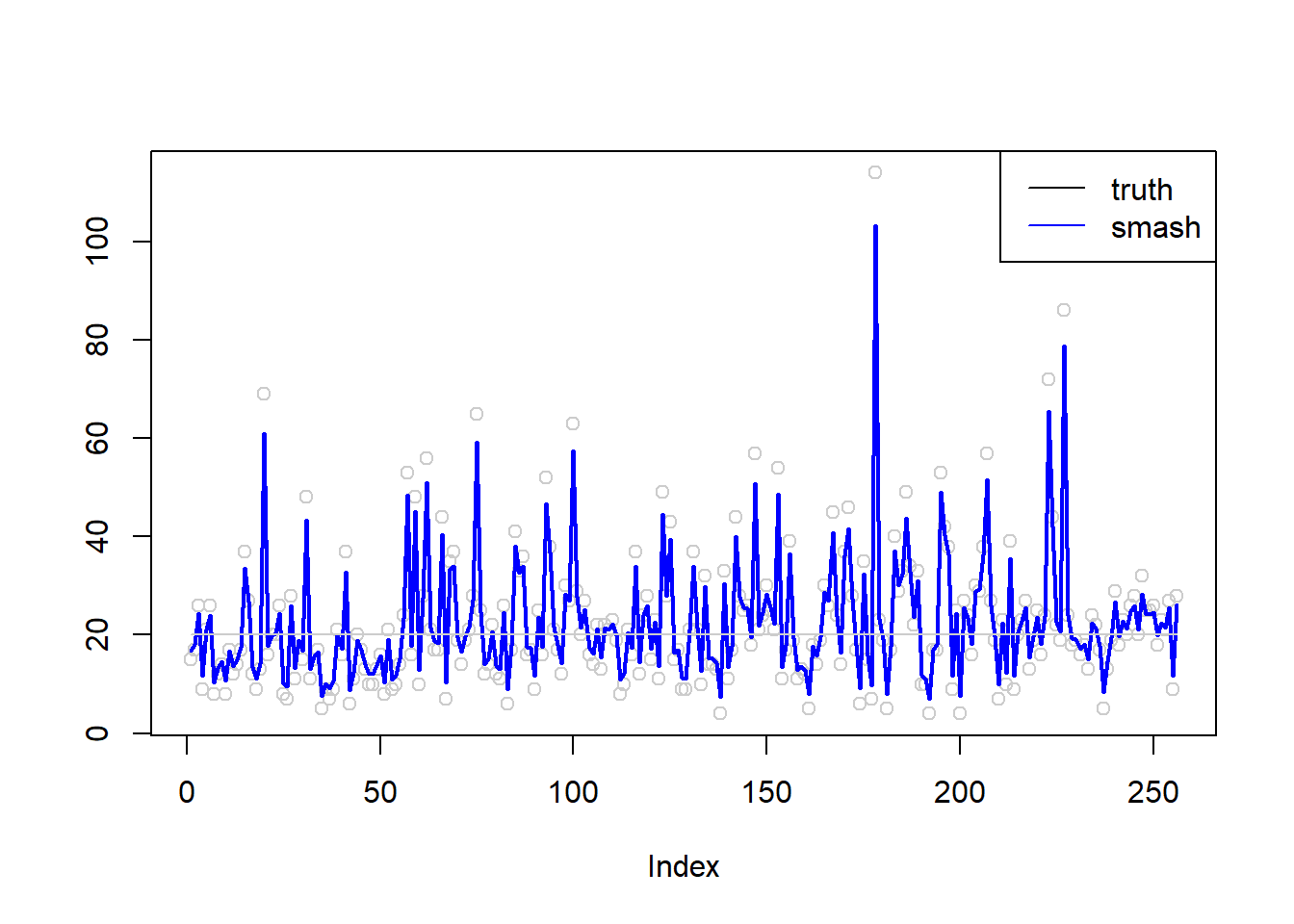
\(\sigma=1\)
simu.out=simu_study(m,1)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m),col='black')
legend("topleft",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))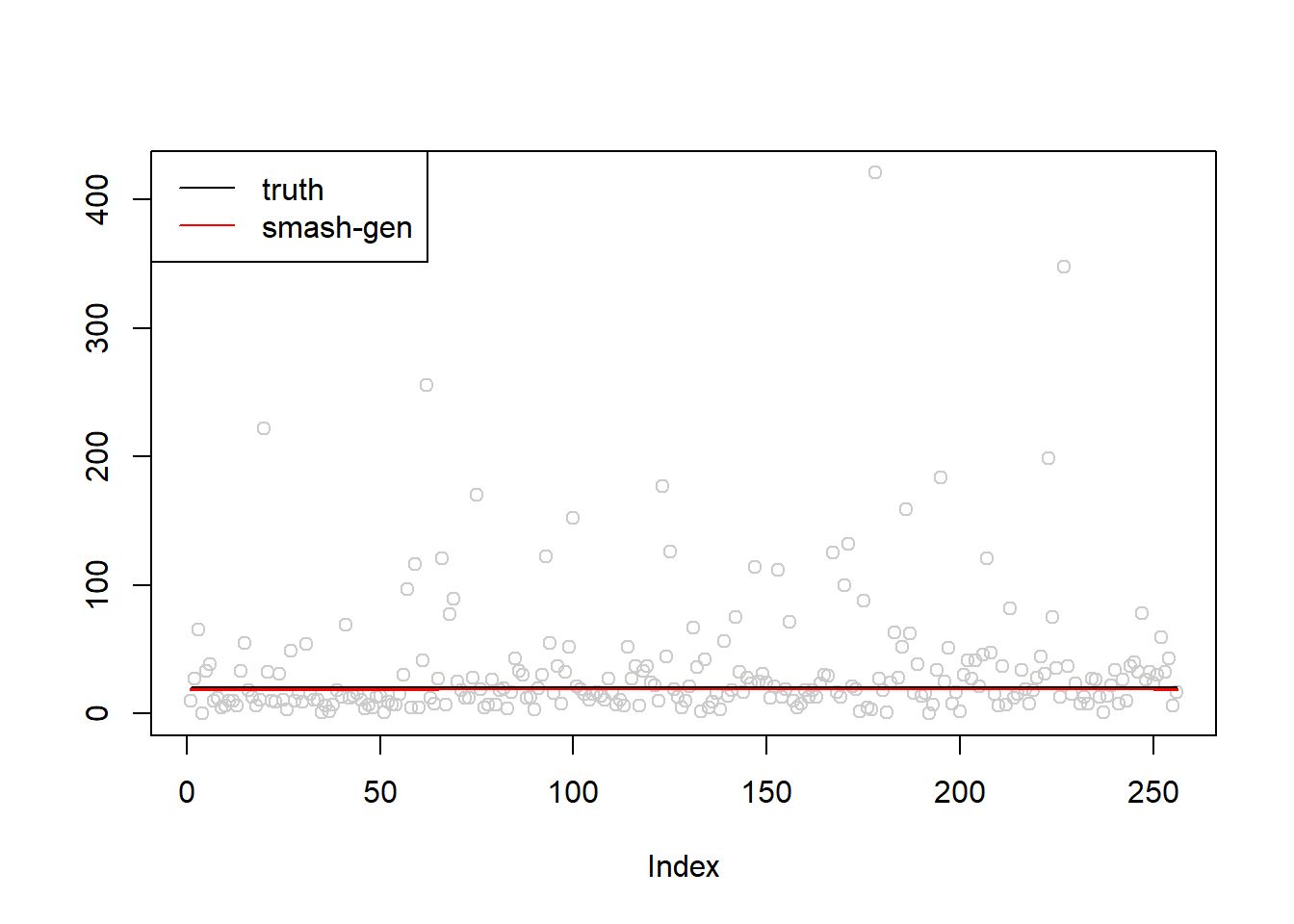
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m),col='black')
legend("topleft",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))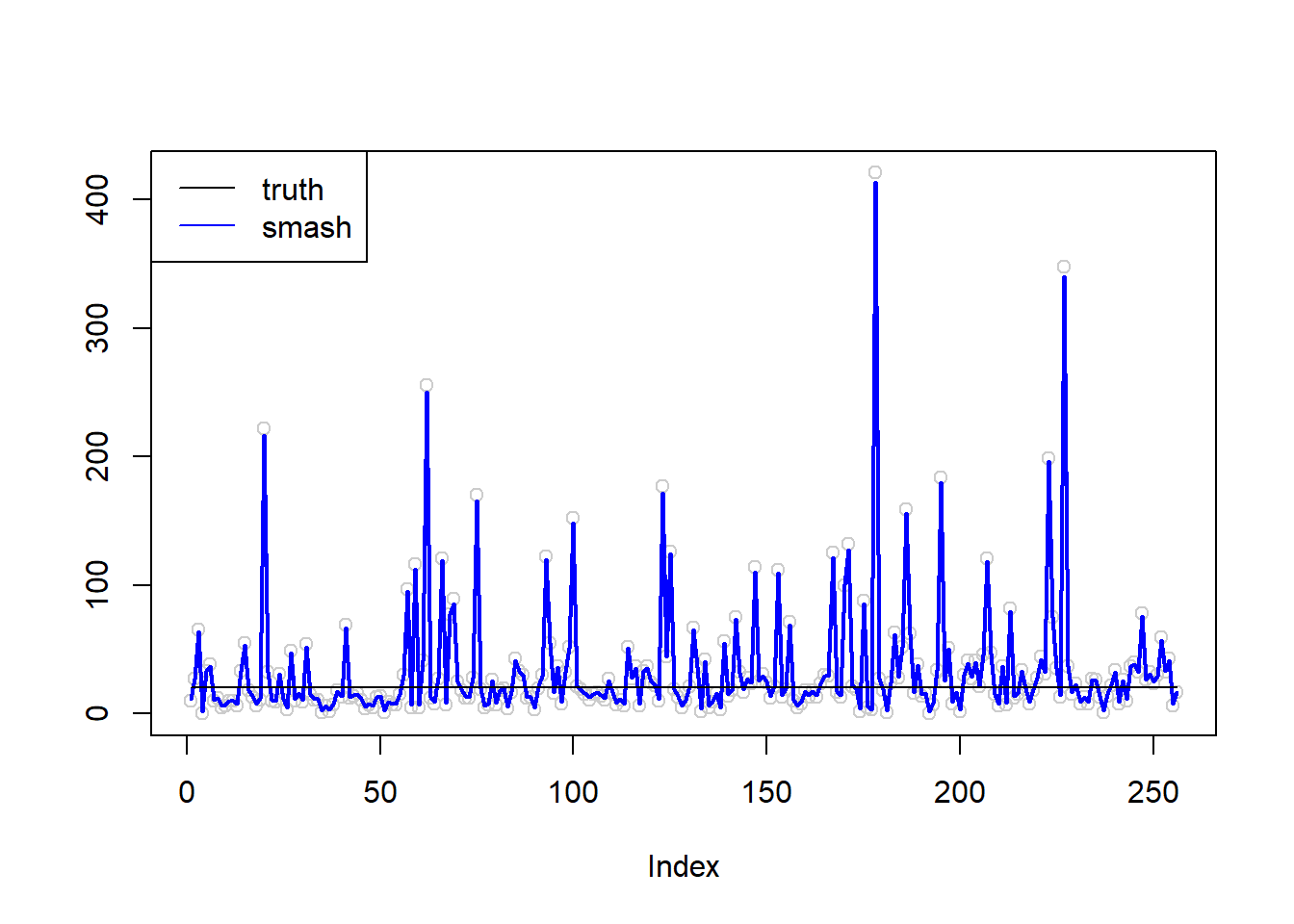
Simulation 2: Step trend
\(\sigma=0.01\)
m=c(rep(3,128), rep(5, 128), rep(6, 128), rep(3, 128))
simu.out=simu_study(m,0.01)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))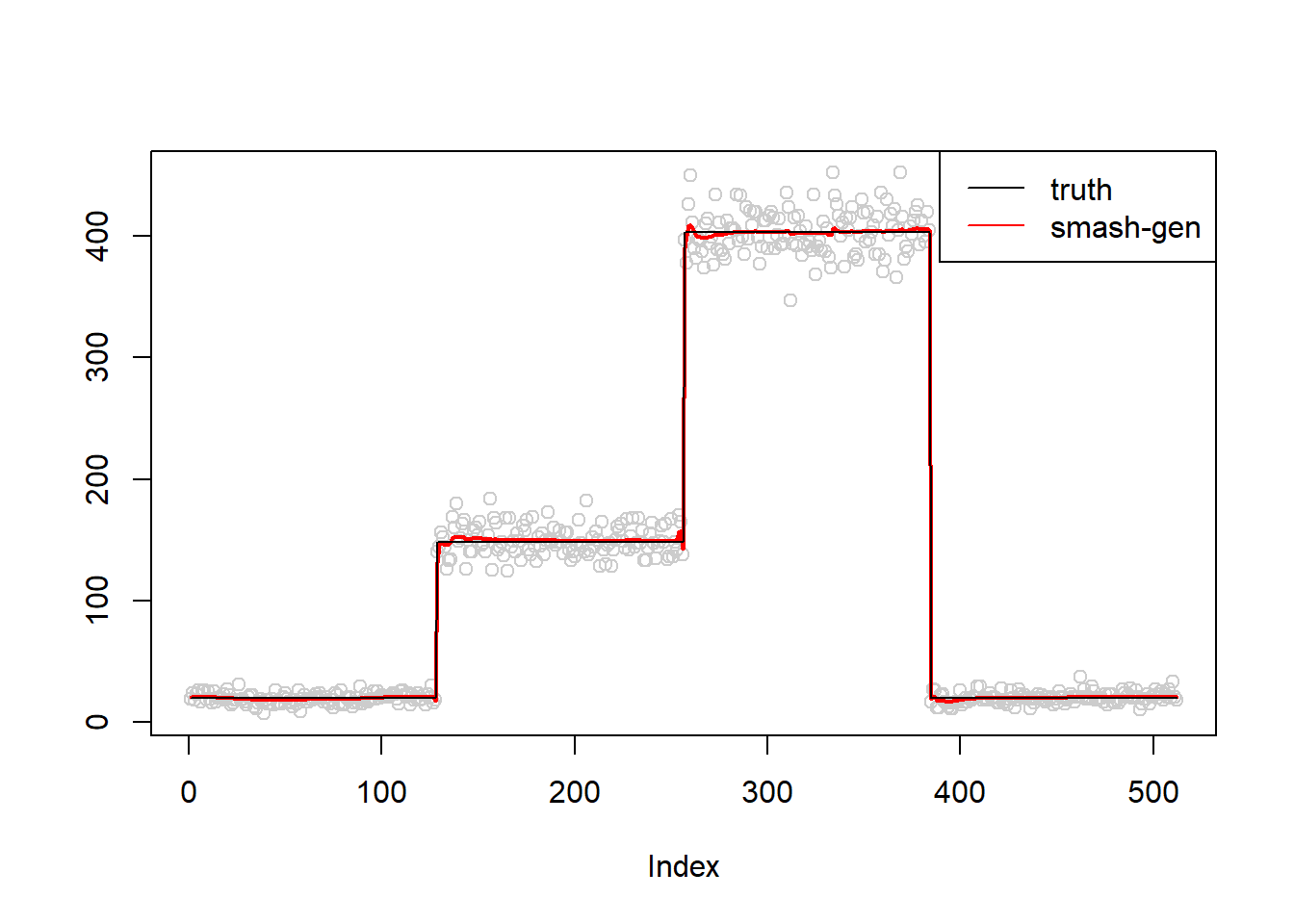
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))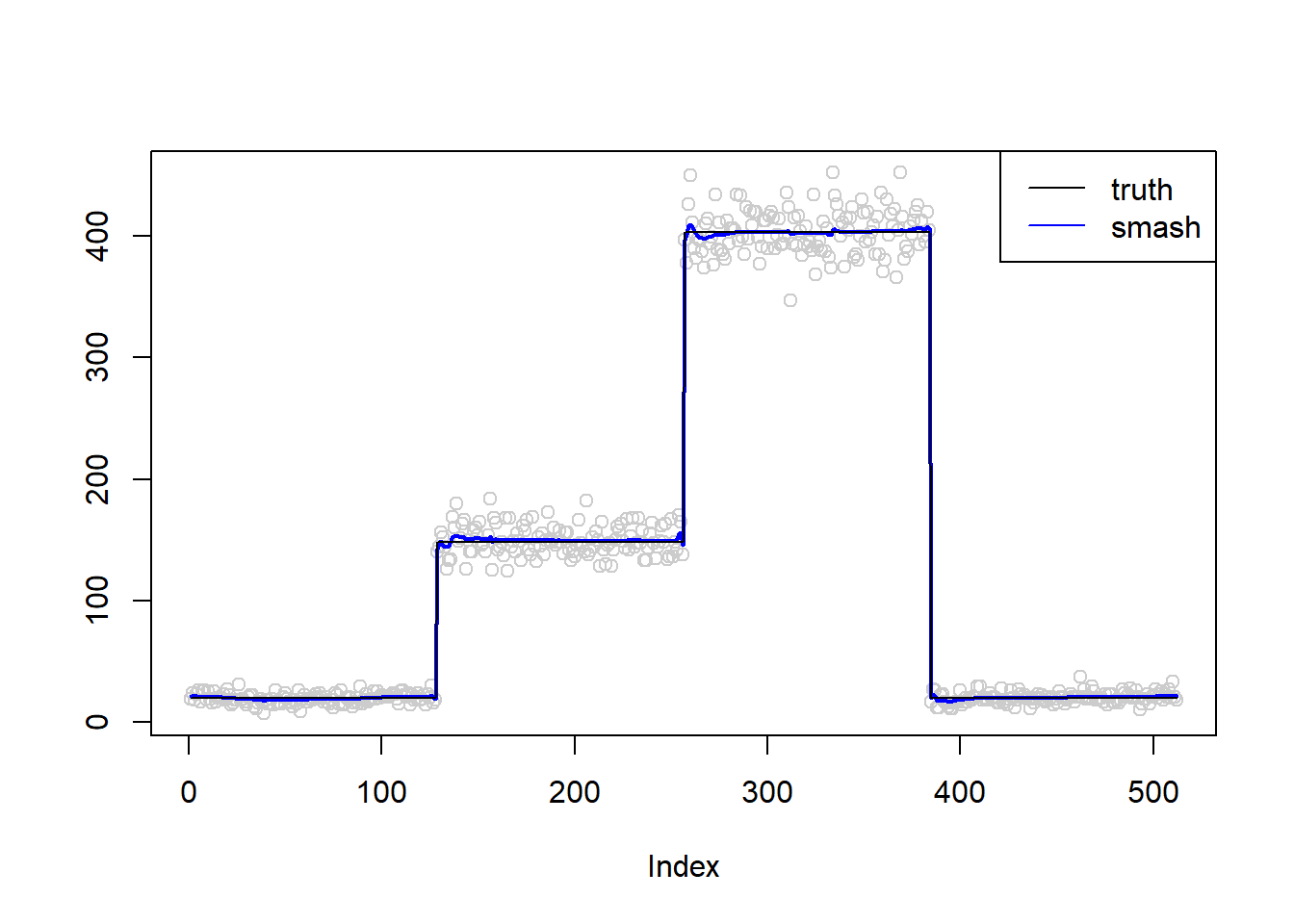
\(\sigma=0.1\)
simu.out=simu_study(m,0.1)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))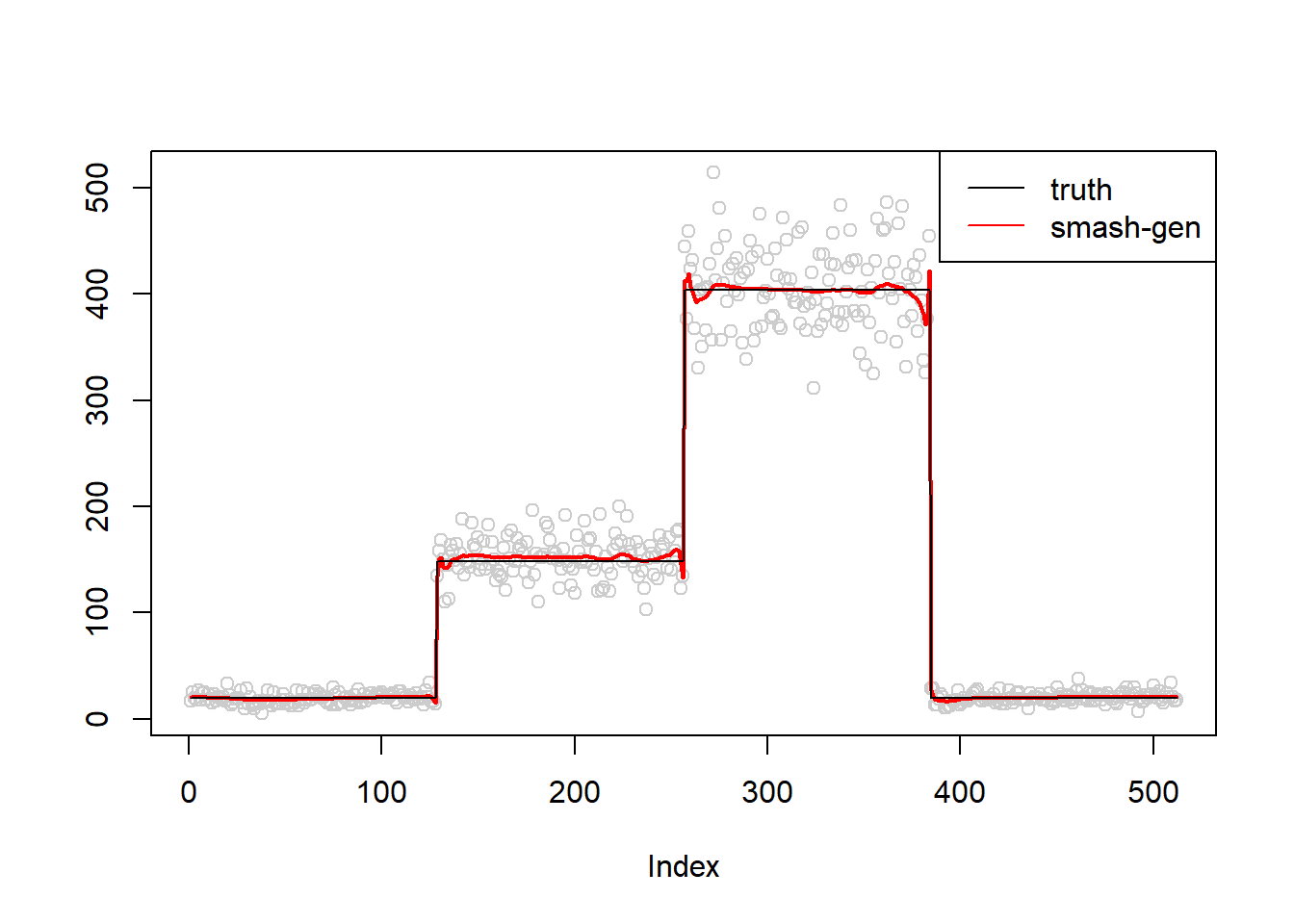
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))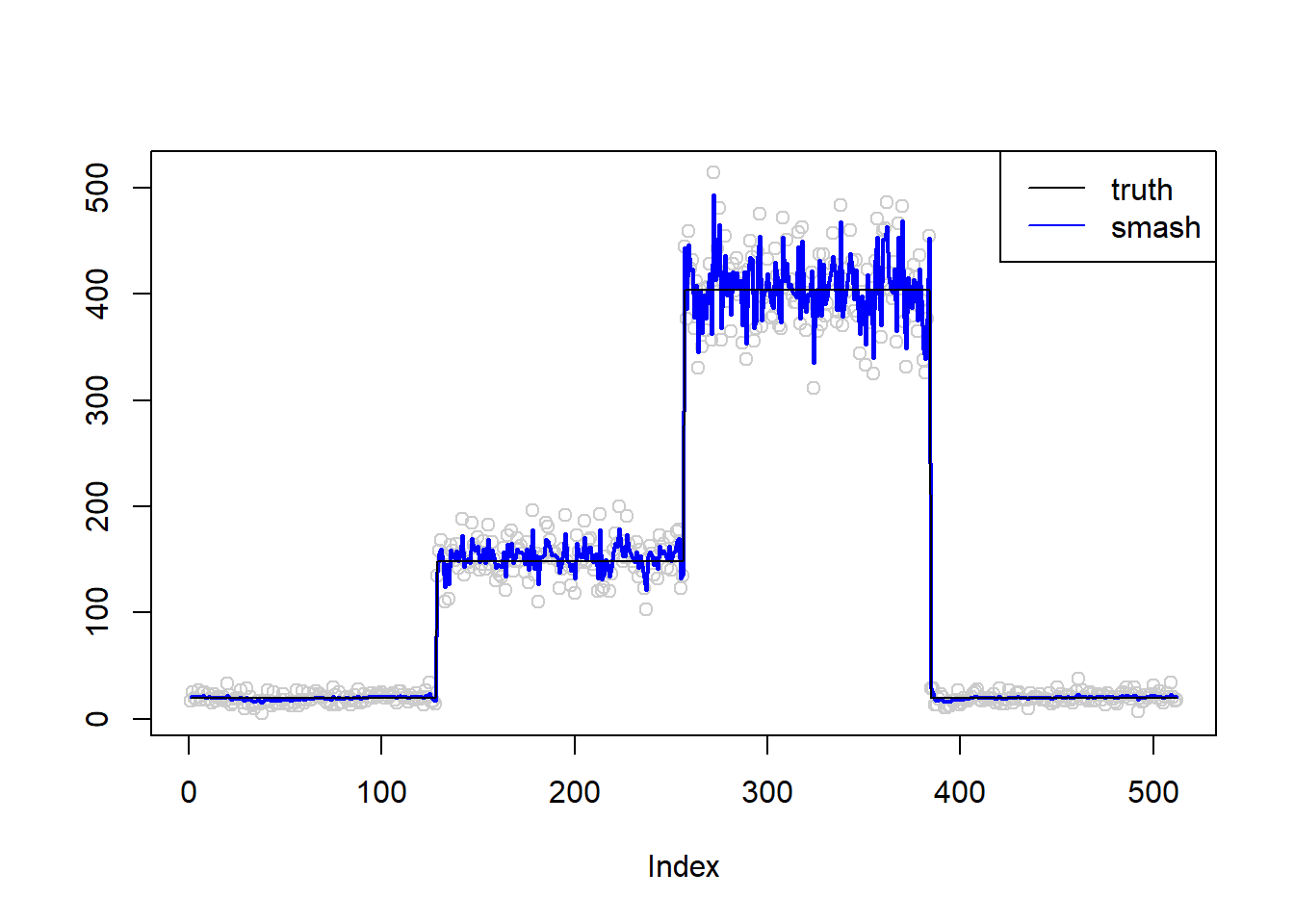
\(\sigma=0.5\)
simu.out=simu_study(m,0.5)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))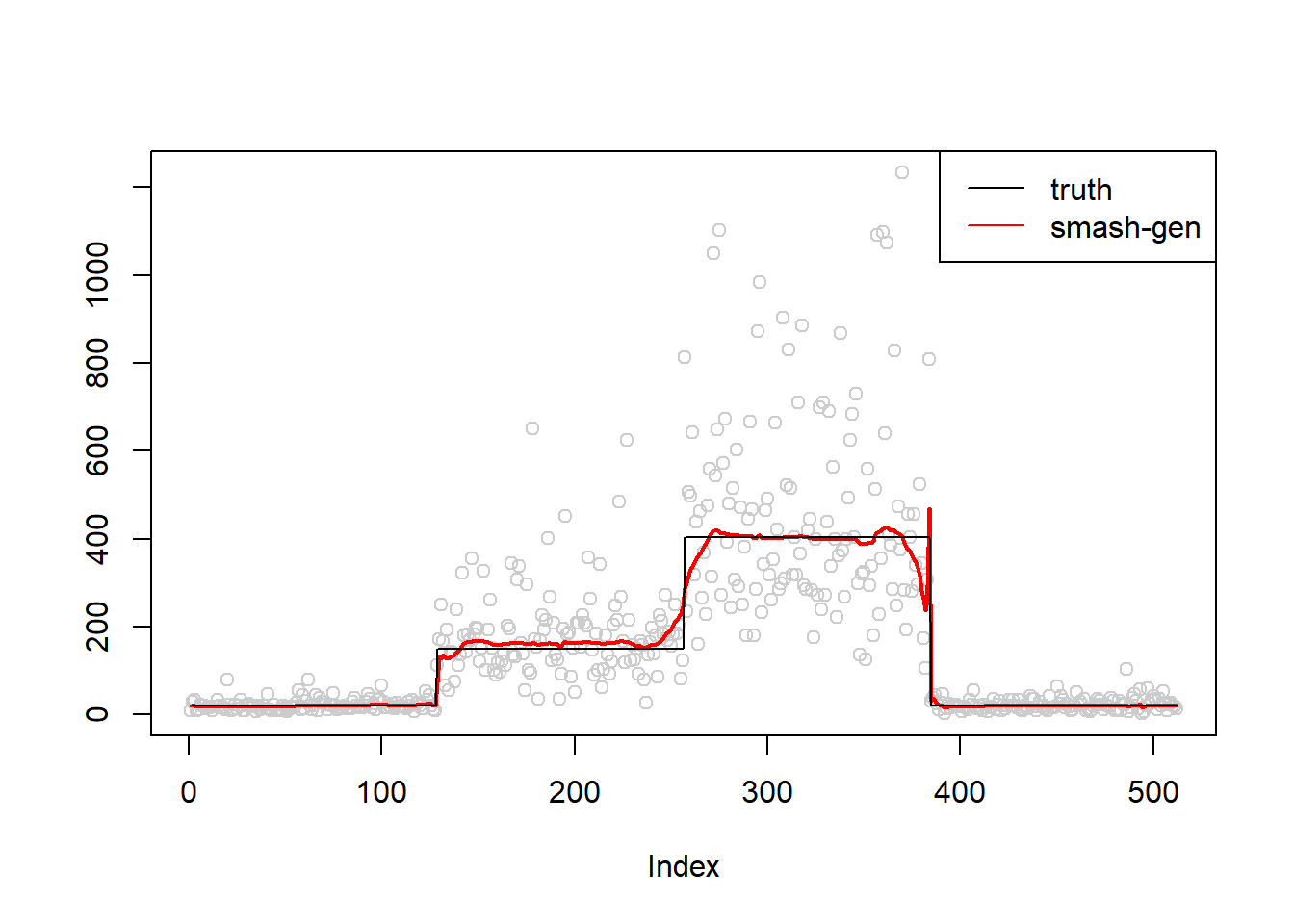
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))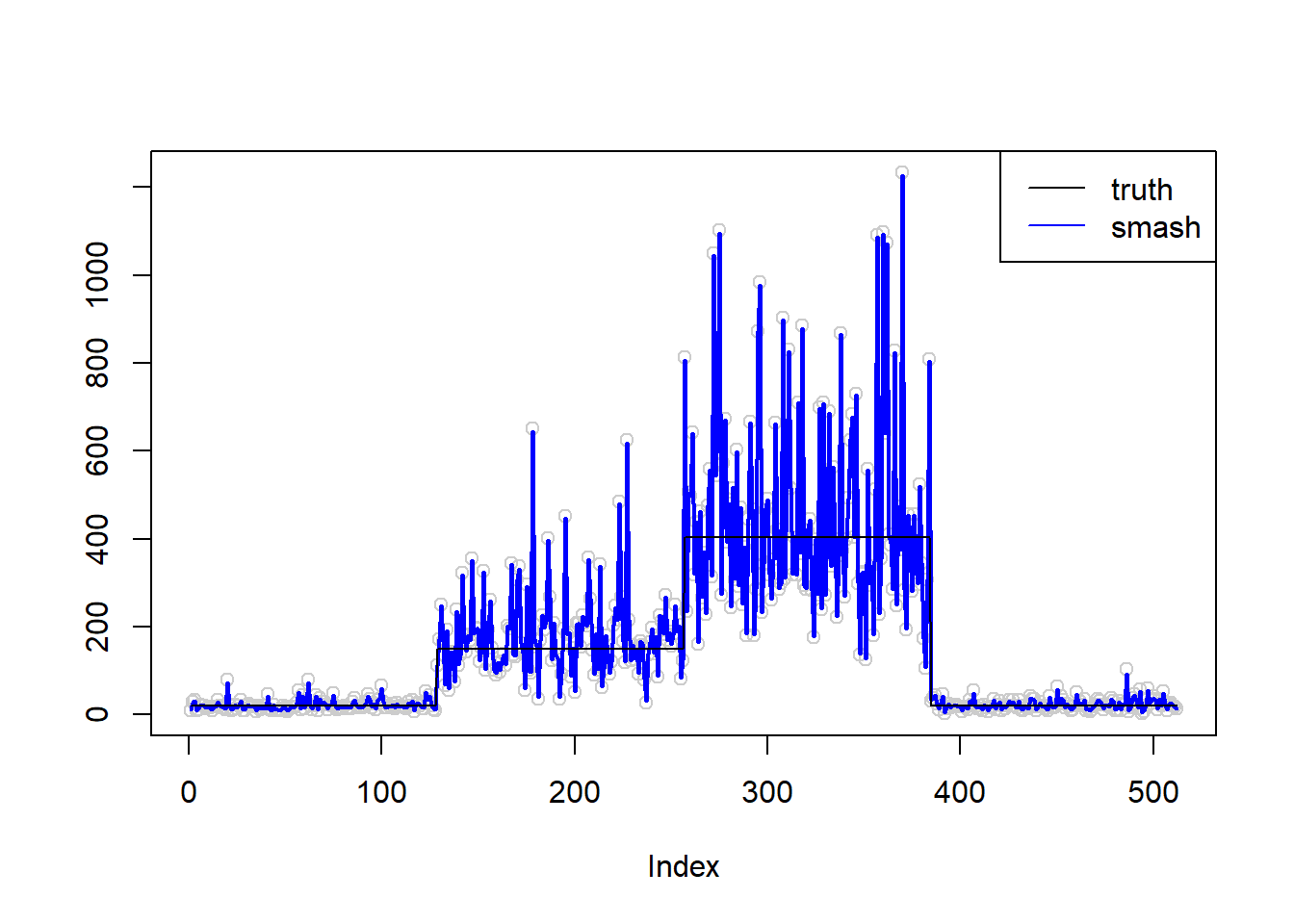
\(\sigma=1\)
simu.out=simu_study(m,1)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topleft",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))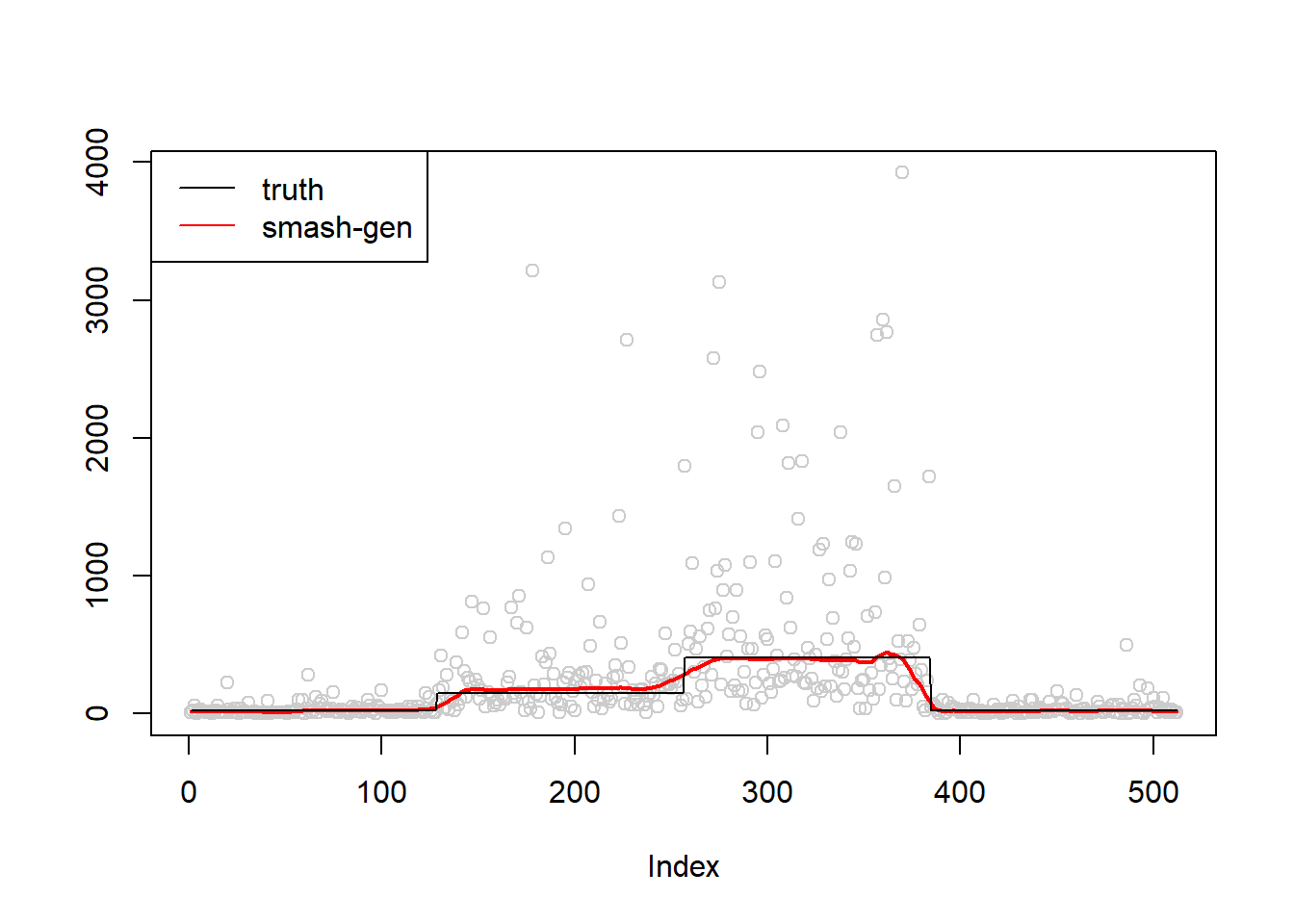
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topleft",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))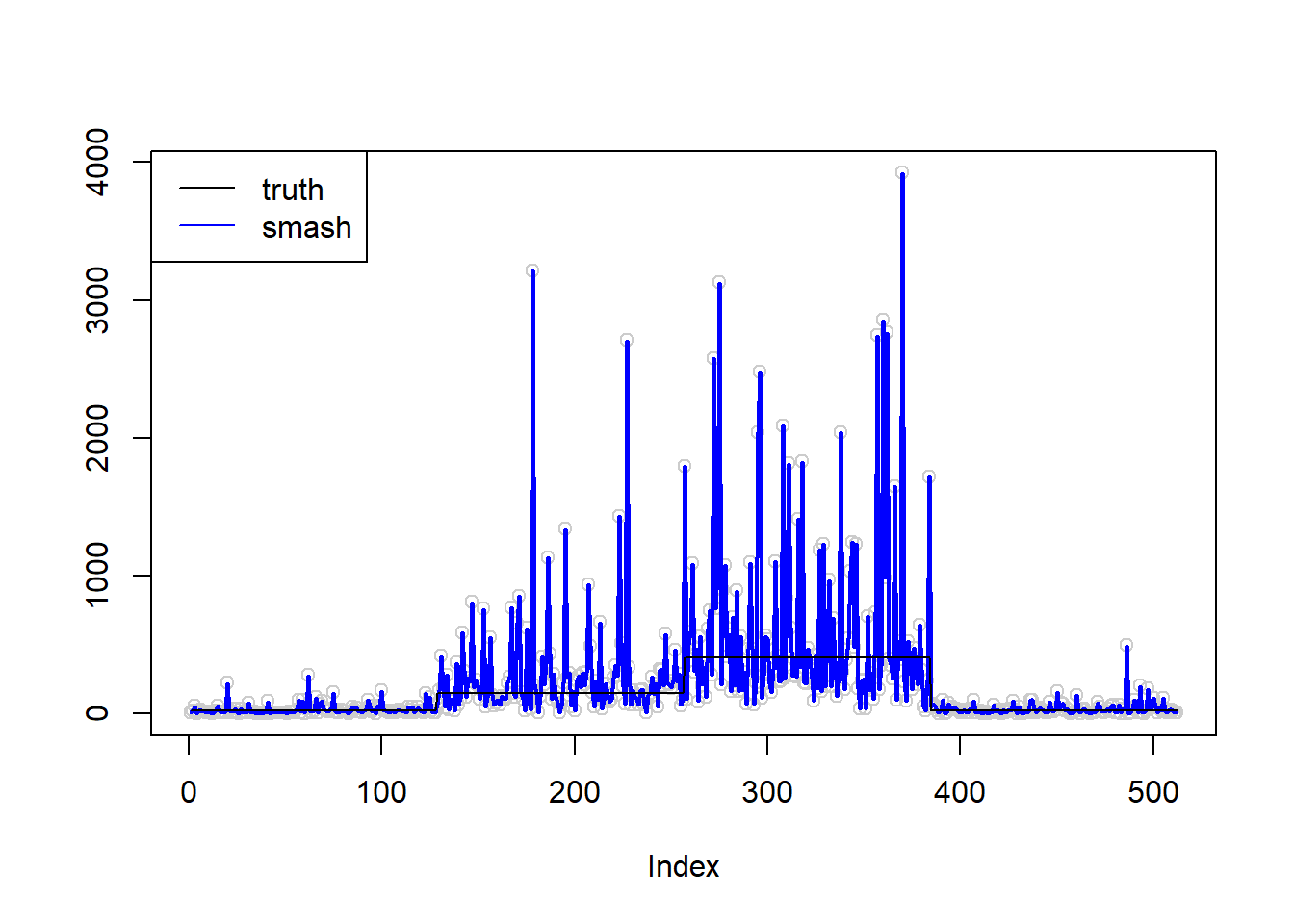
An example that the algorithm does not converge:(there is an ‘extreme’ outlier)
simu.out=simu_study(m,1,seed=2132)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topleft",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))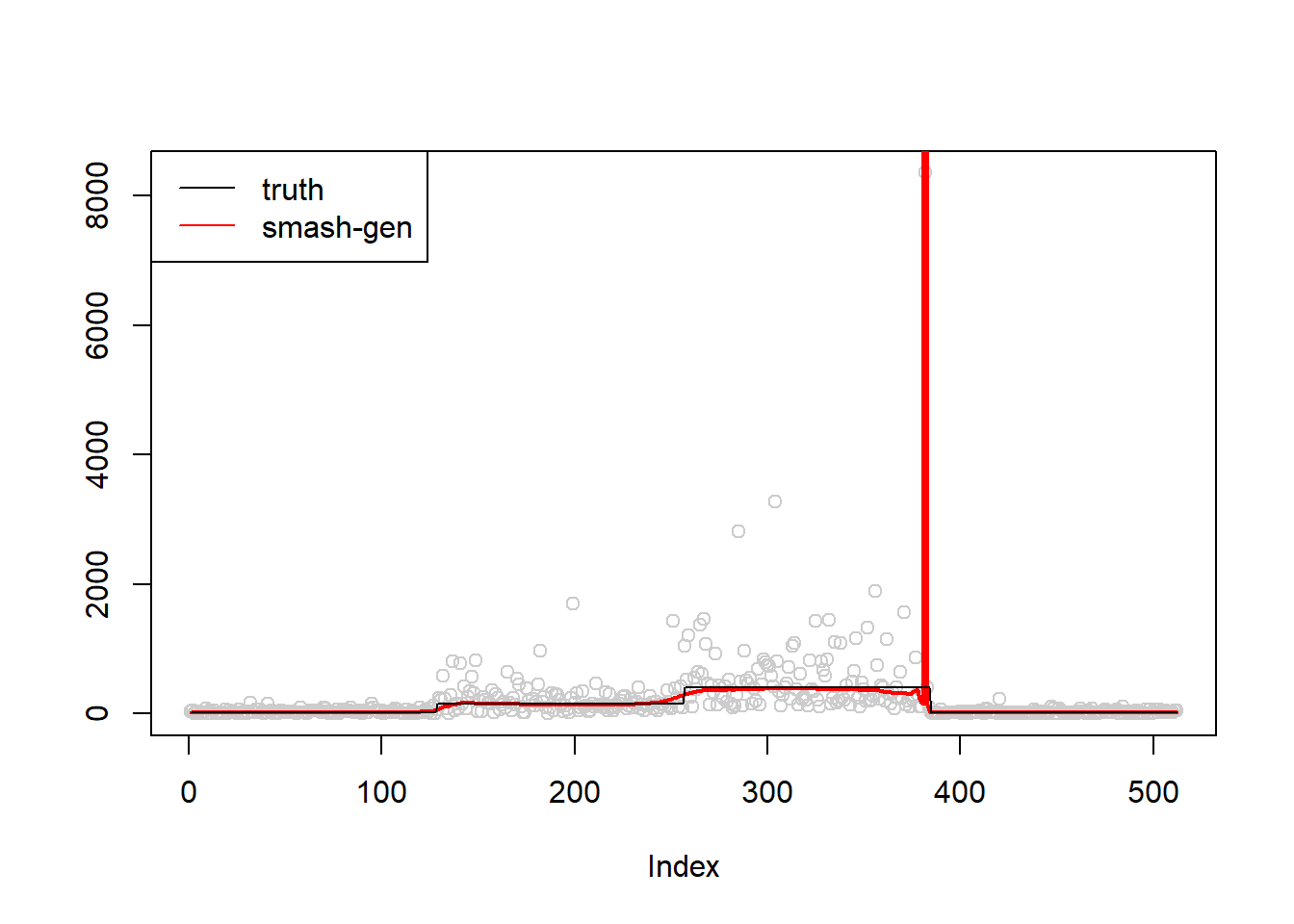
Simulation 3: Polynomial curve Poisson nugget
\(\sigma=0.01\)
m = seq(-1,1,length.out = 256)
m = m^3-2*m+1
simu.out=simu_study(m,0.01)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))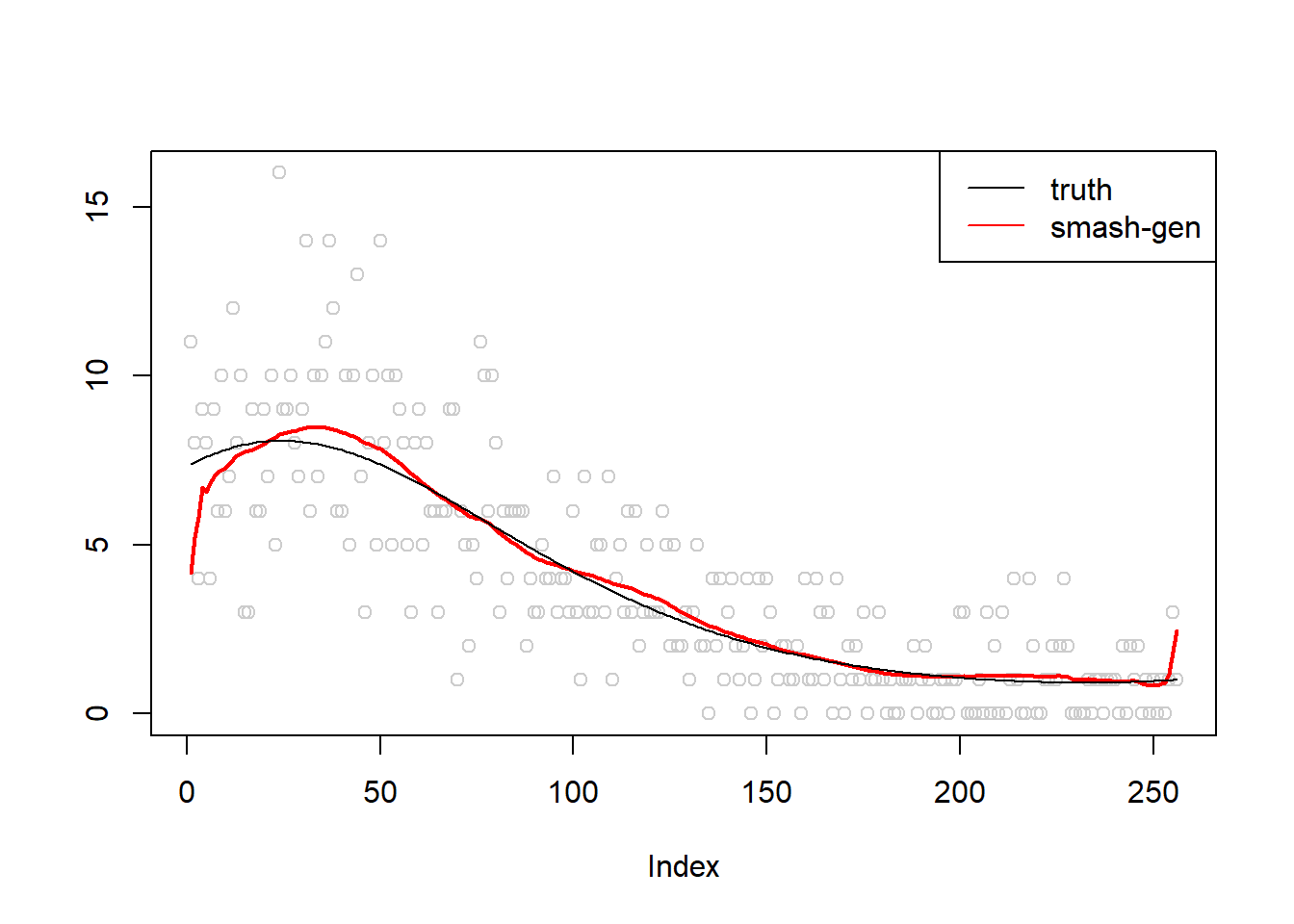
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))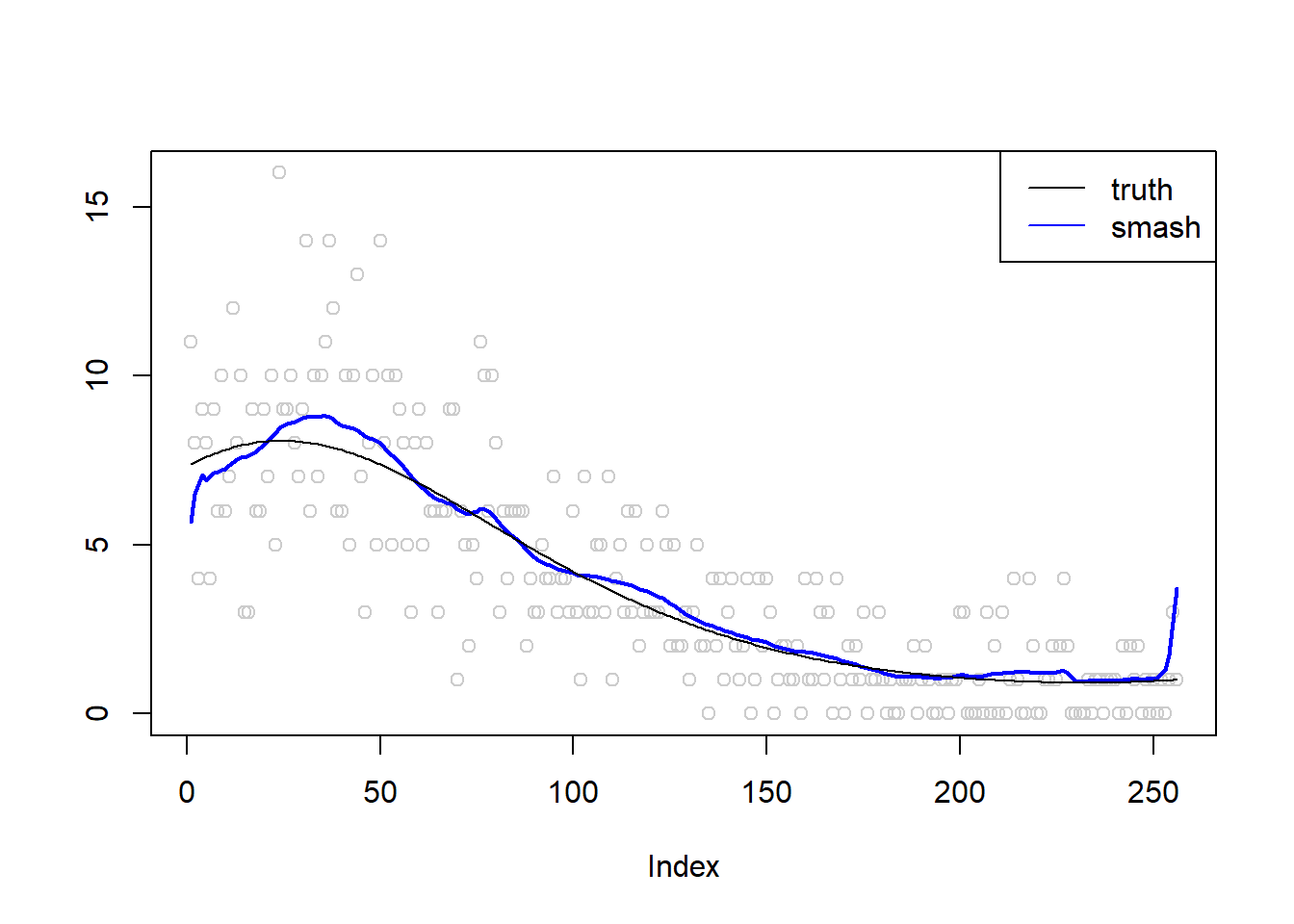
\(\sigma=0.1\)
m = seq(-1,1,length.out = 256)
m = m^3-2*m+1
simu.out=simu_study(m,0.1)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))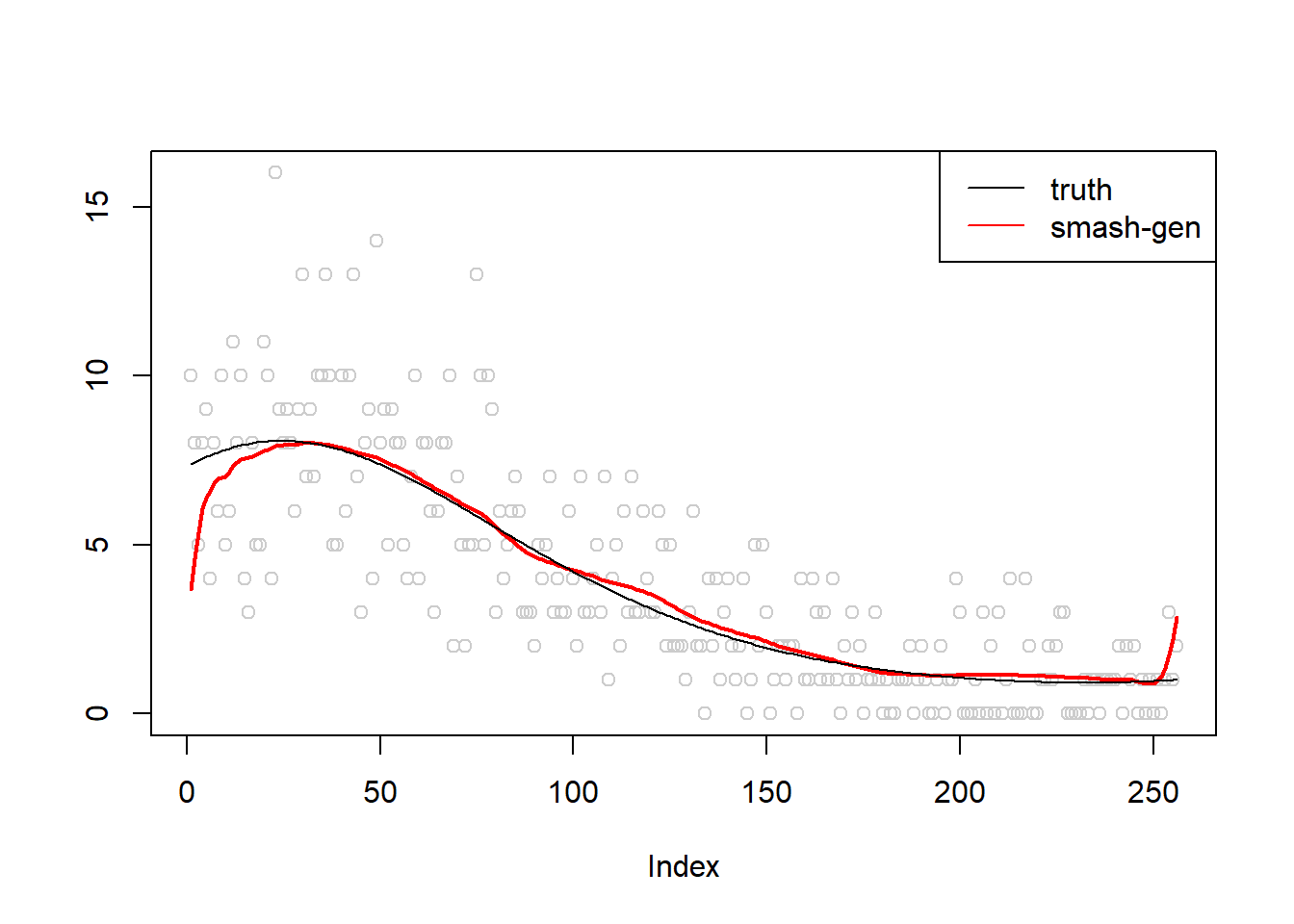
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))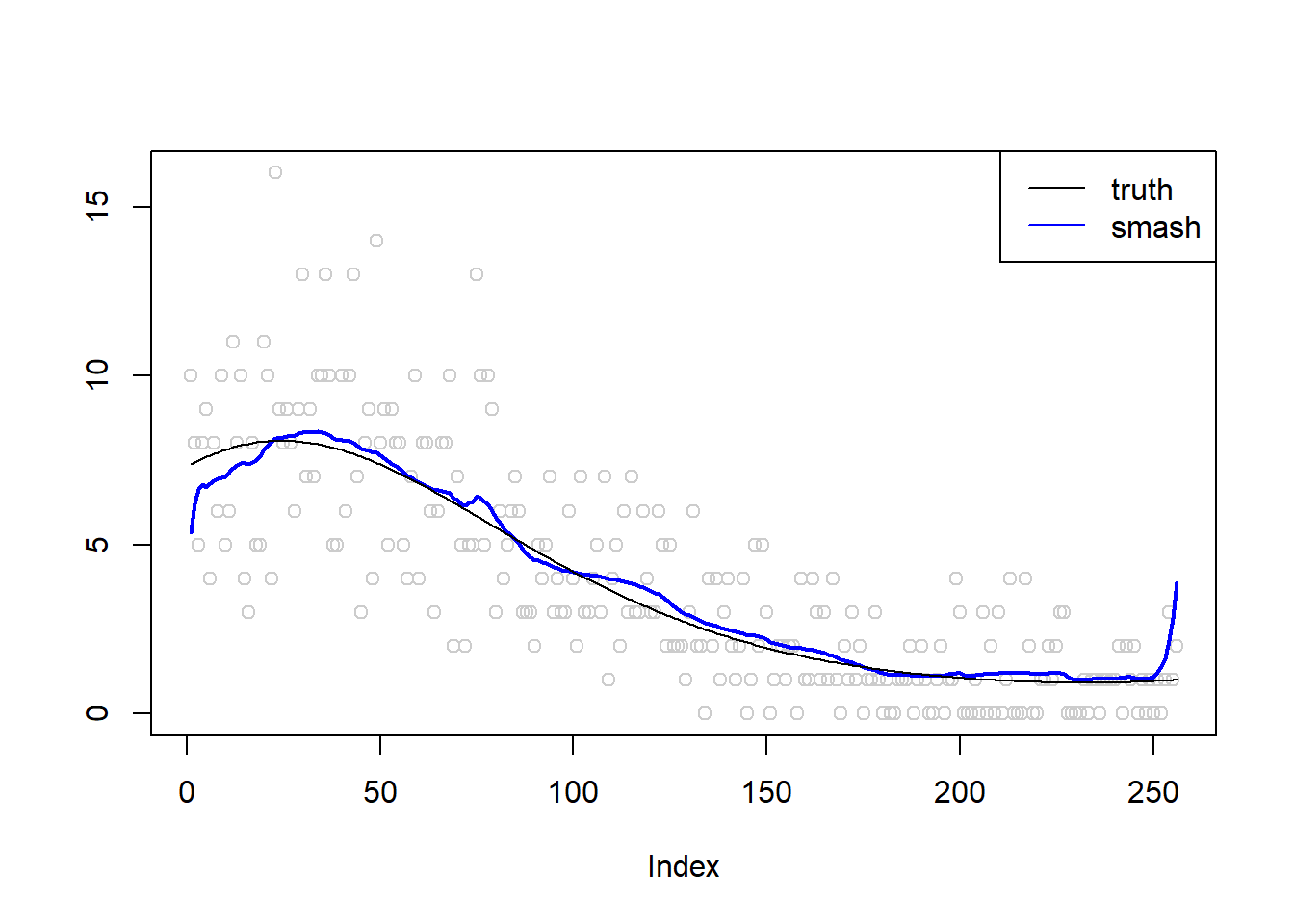
\(\sigma=0.5\)
m = seq(-1,1,length.out = 256)
m = m^3-2*m+1
simu.out=simu_study(m,0.5)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))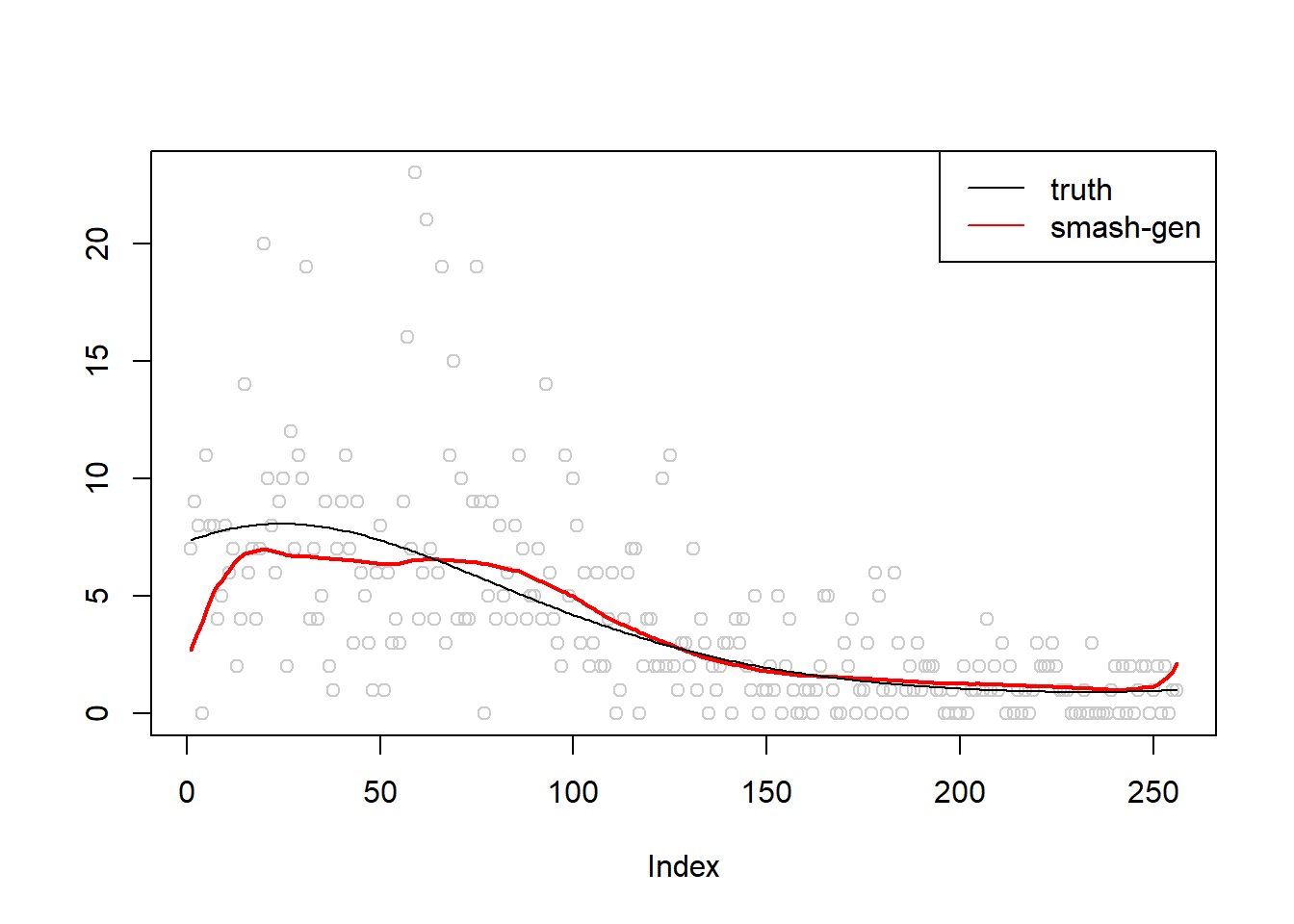
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))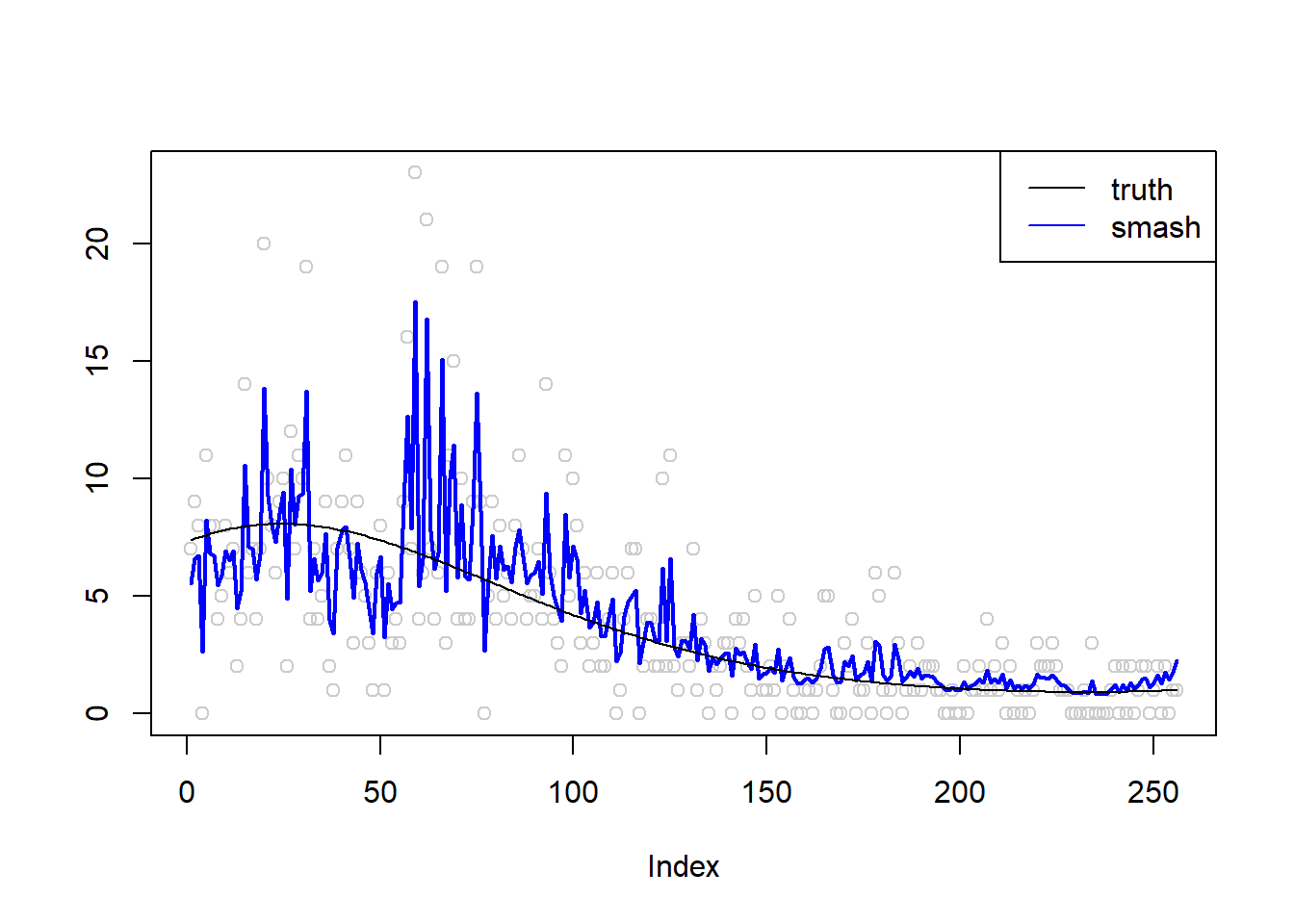
\(\sigma=1\)
m = seq(-1,1,length.out = 256)
m = m^3-2*m+1
simu.out=simu_study(m,1)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))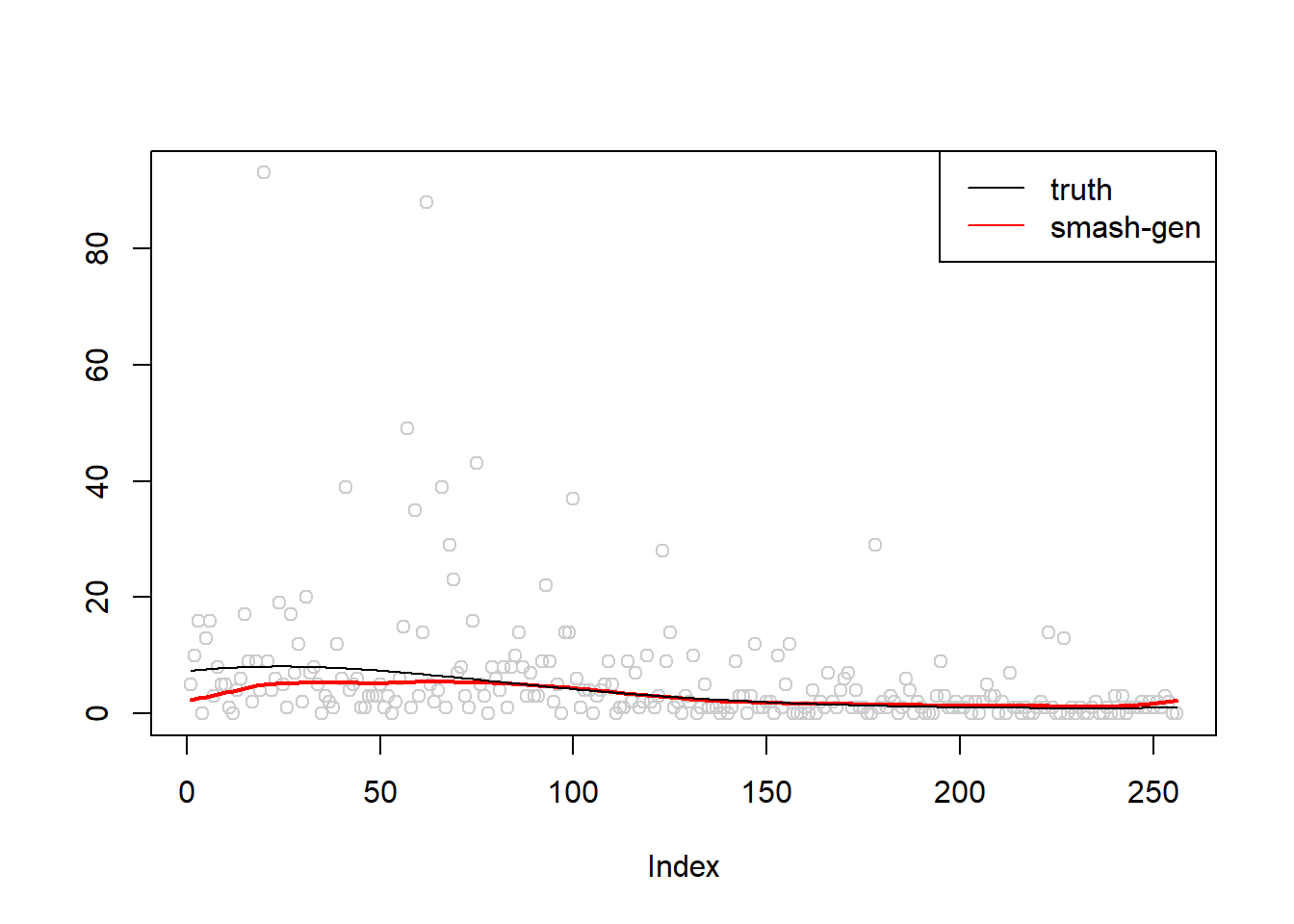
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))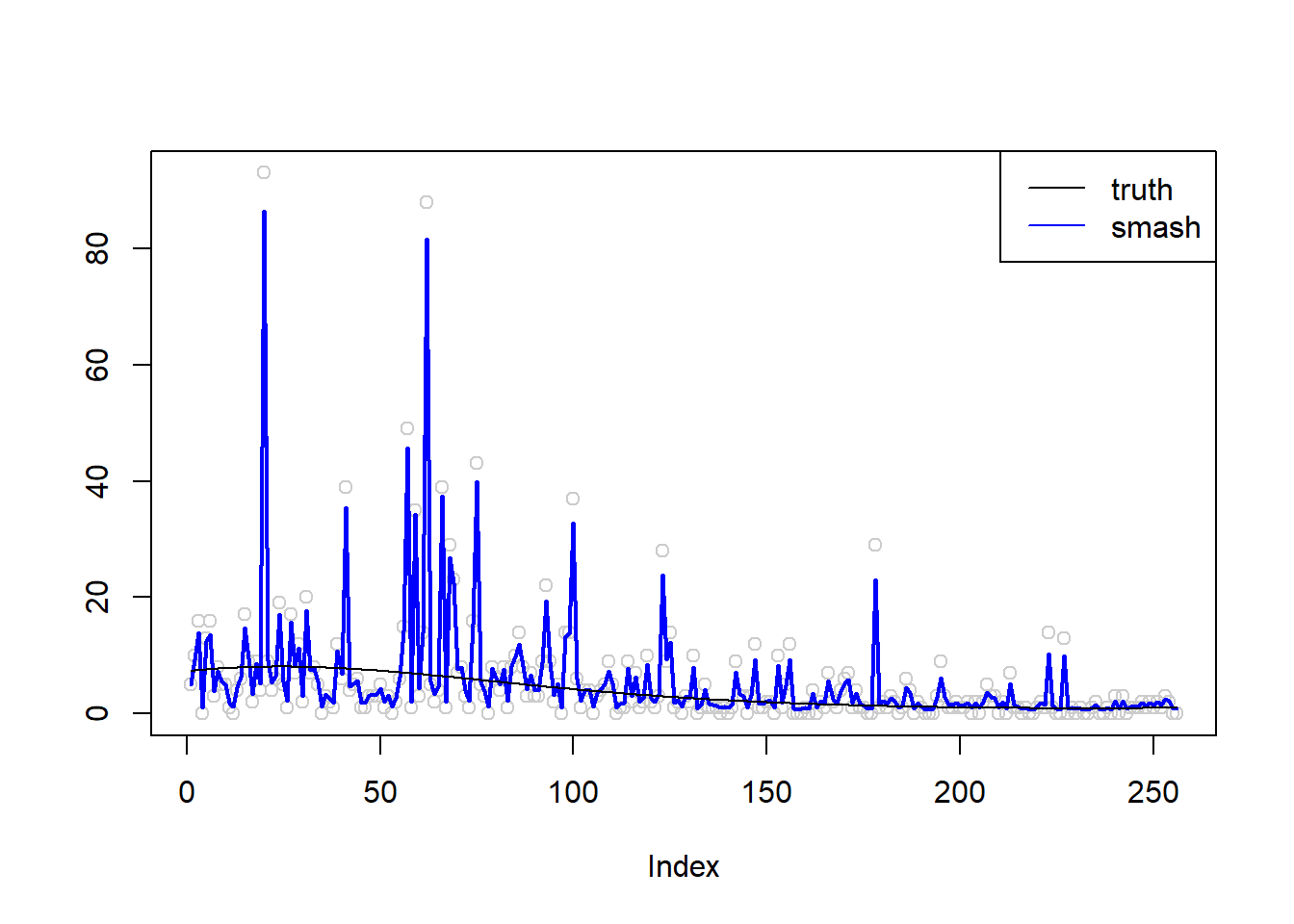
Simulation 4: Sin curve Poisson nugget
\(\sigma=0.01\)
m = seq(-pi,pi,length.out = 256)
m = 2*(sin(m)+1)
simu.out=simu_study(m,0.01)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))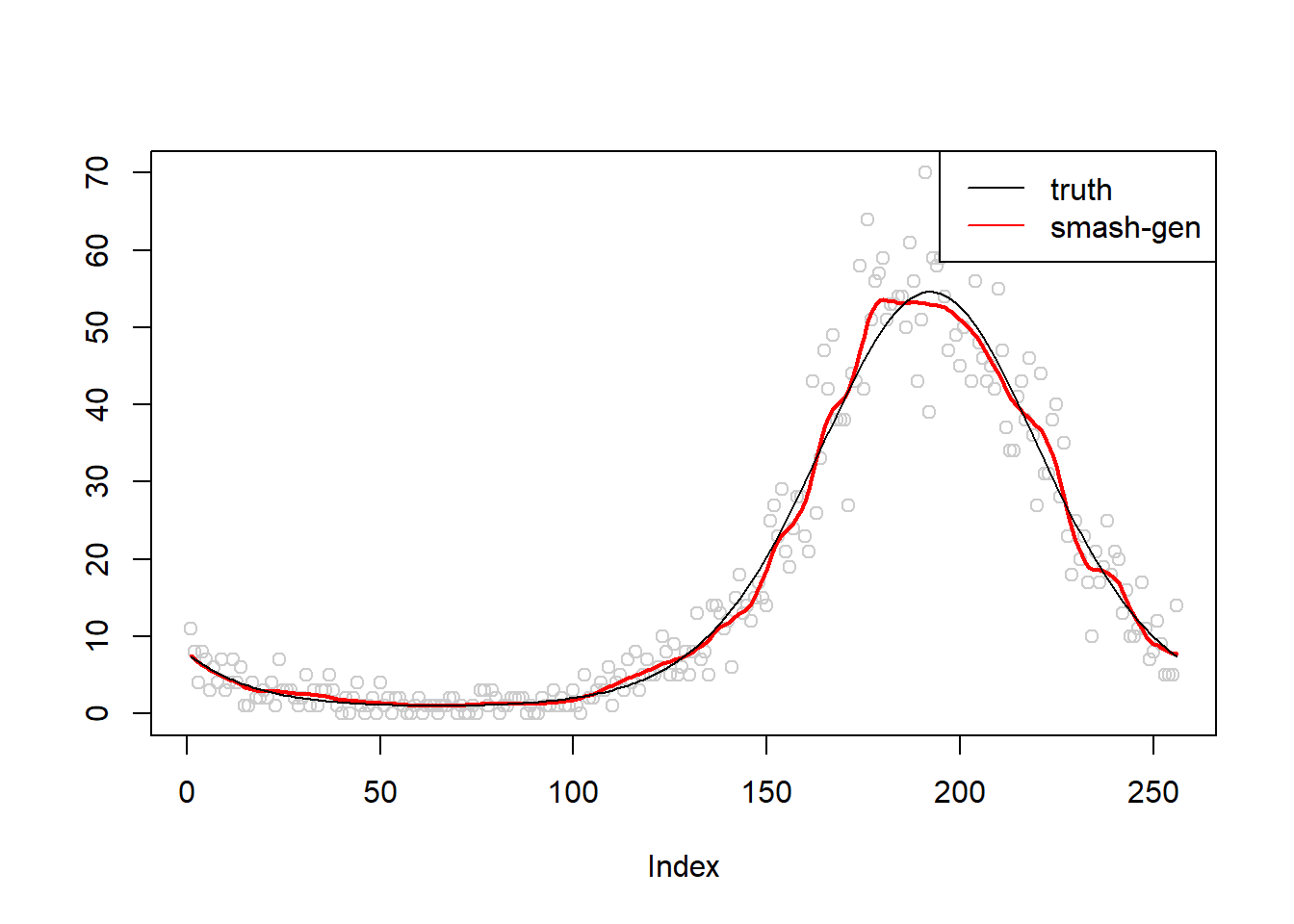
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))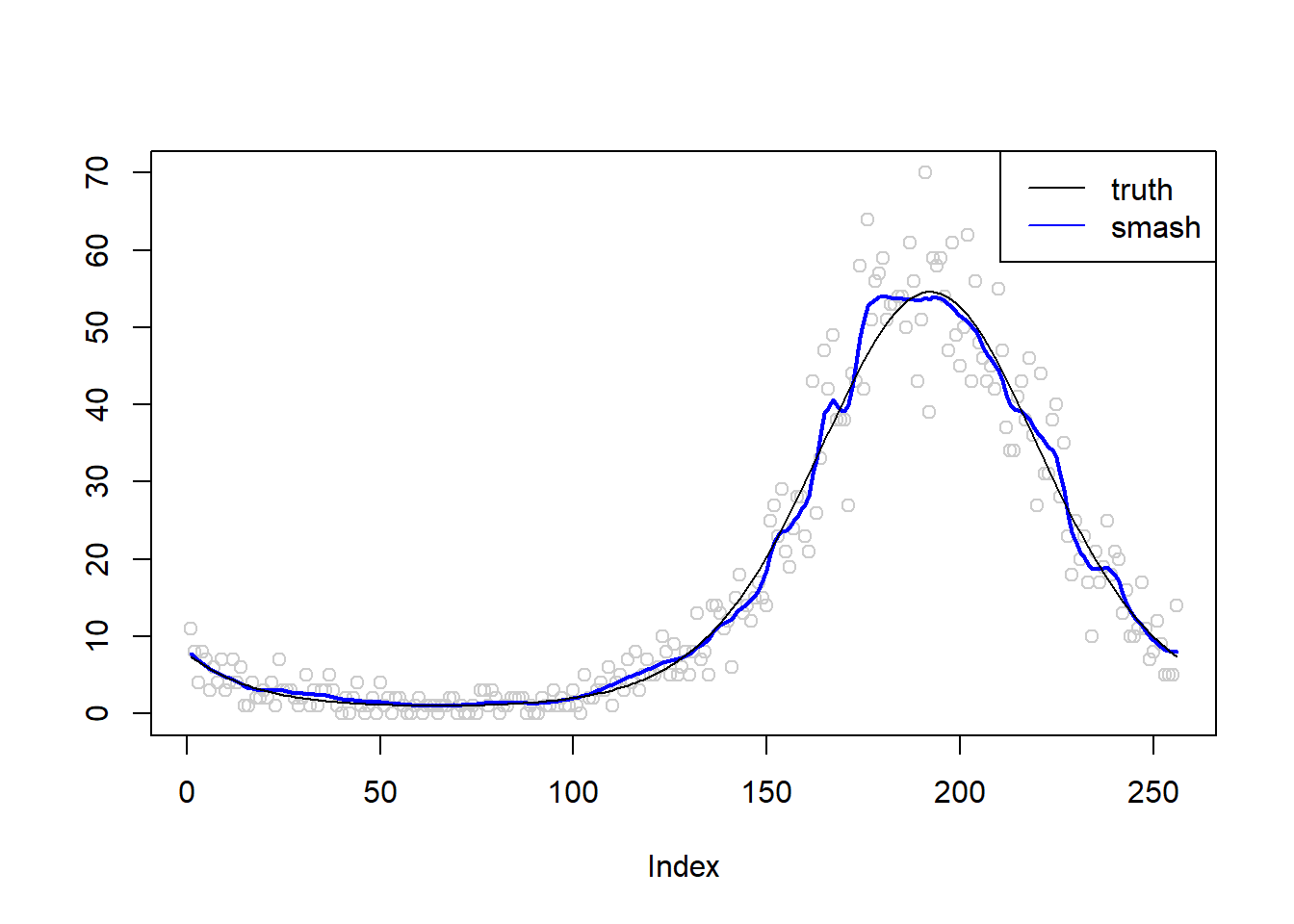
\(\sigma=0.1\)
simu.out=simu_study(m,0.1)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))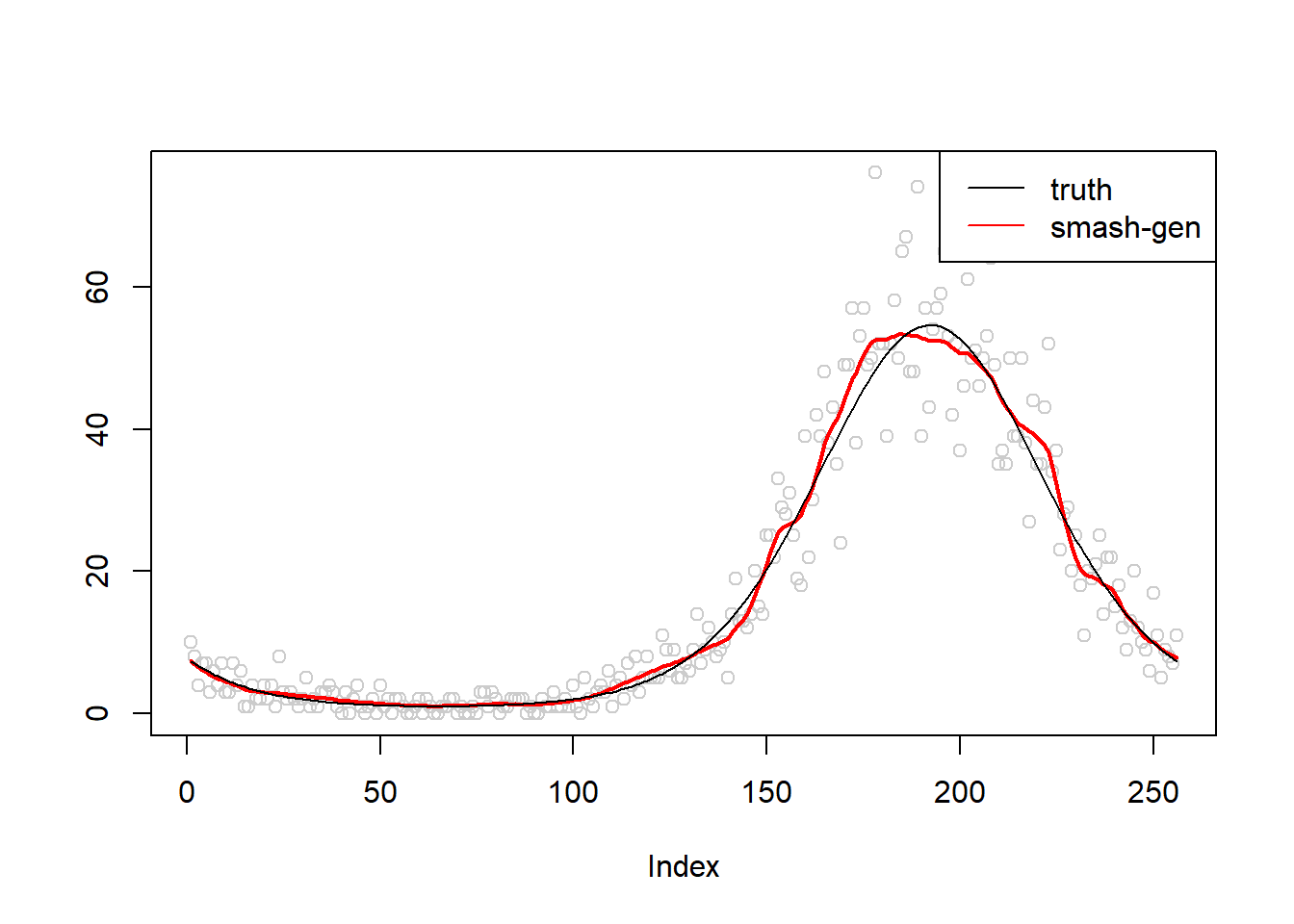
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))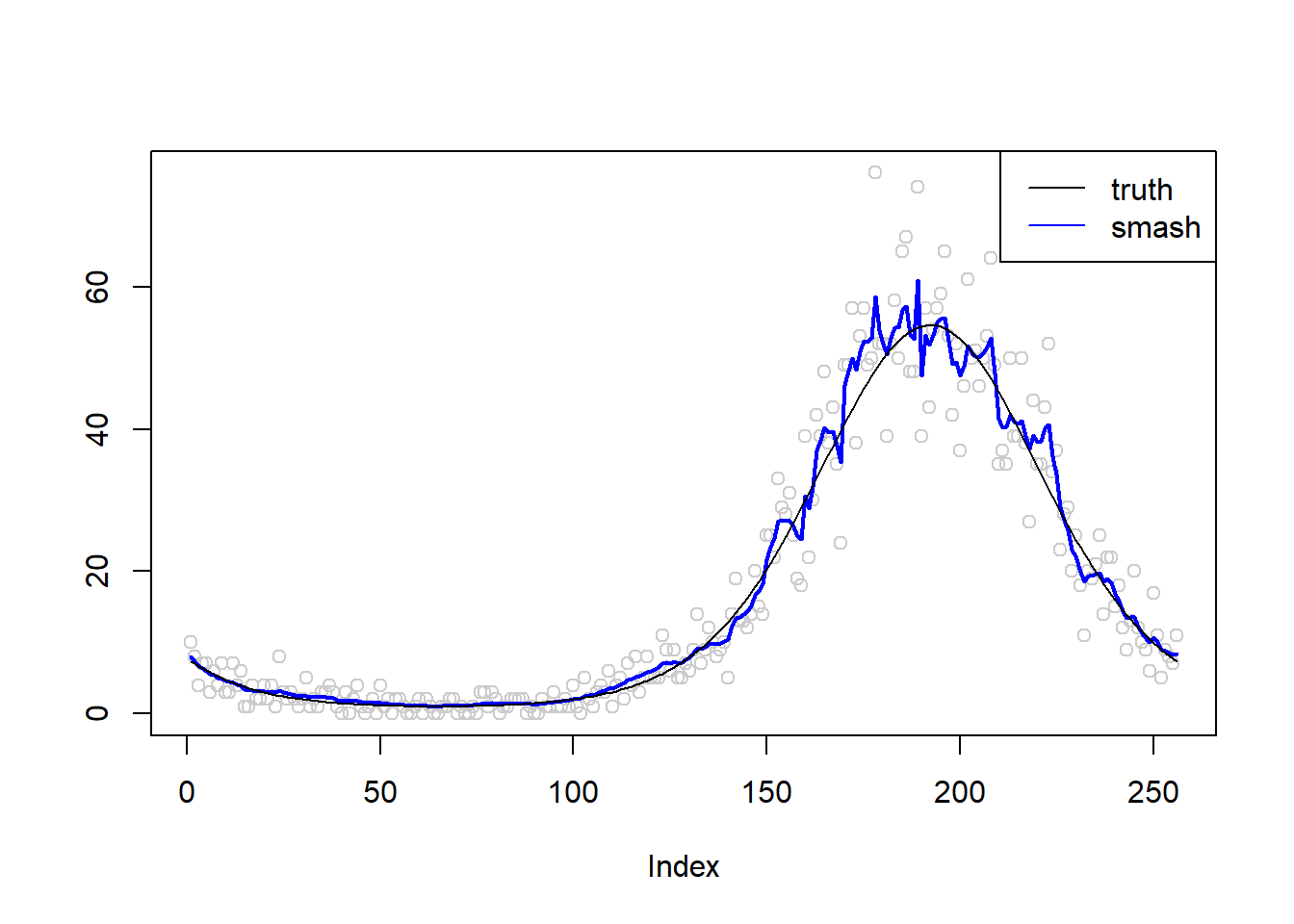
\(\sigma=0.5\)
simu.out=simu_study(m,0.5)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))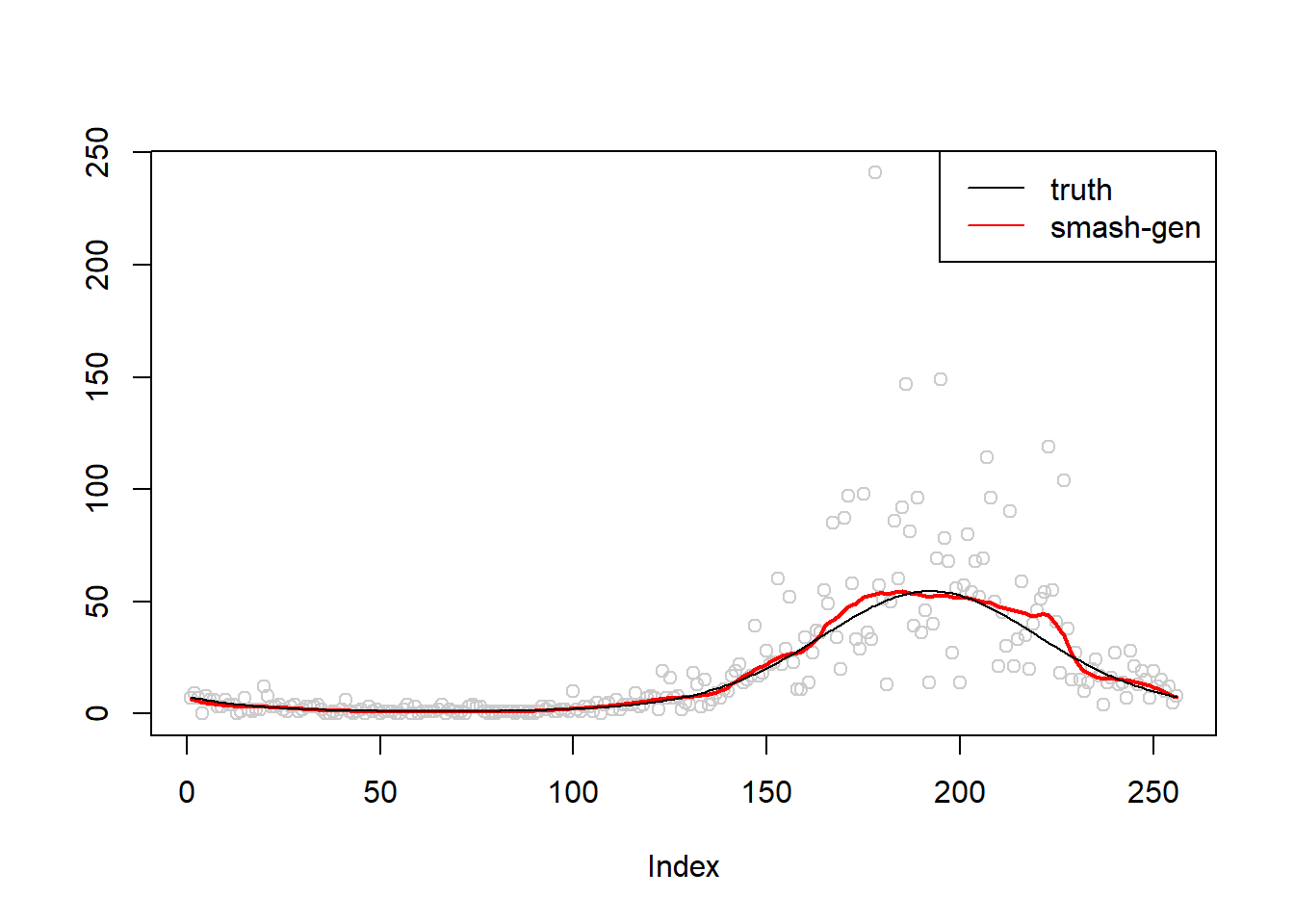
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))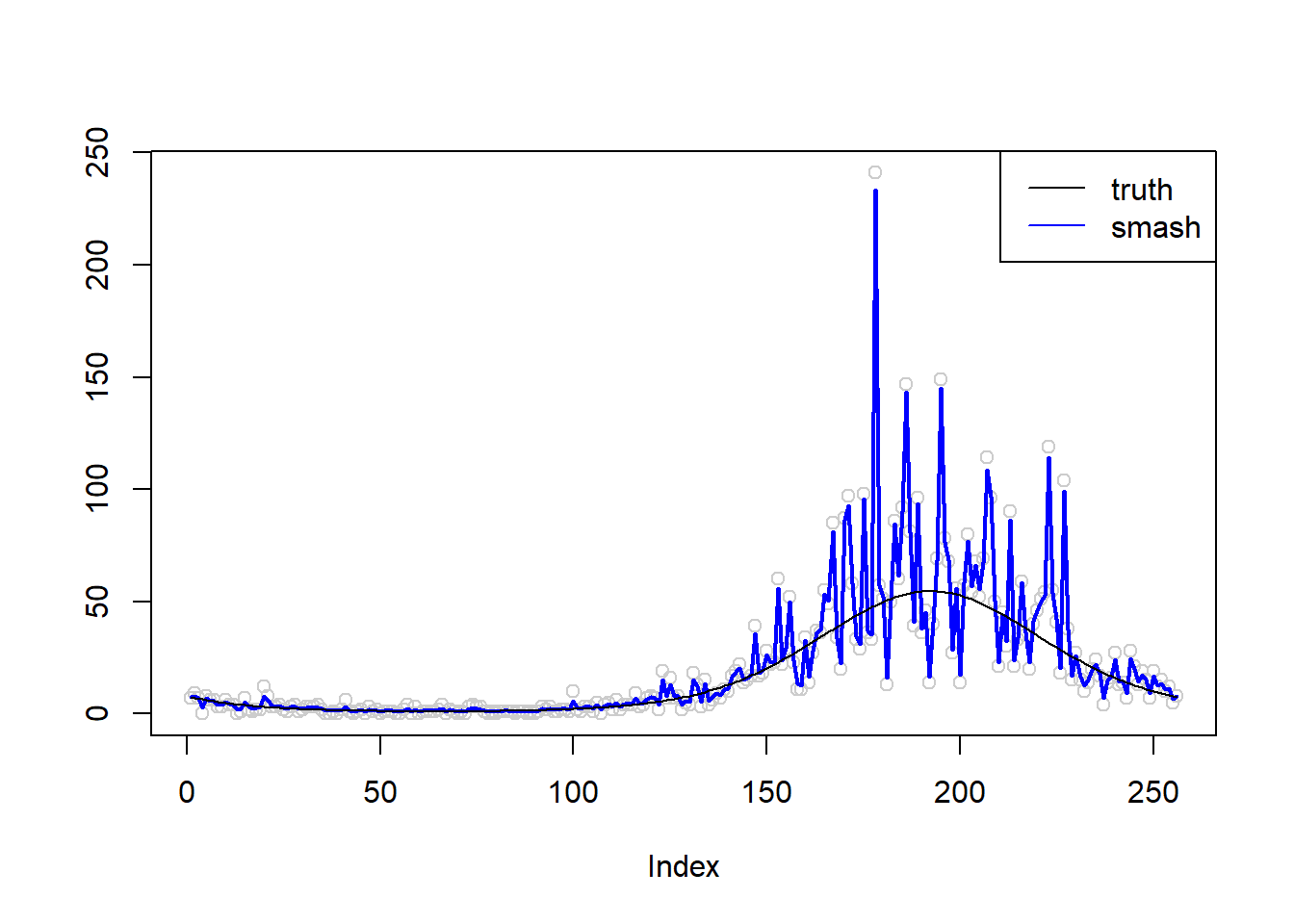
\(\sigma=1\)
simu.out=simu_study(m,1)
#par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.gen.out, col = "red", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth","smash-gen"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black","red", "blue"))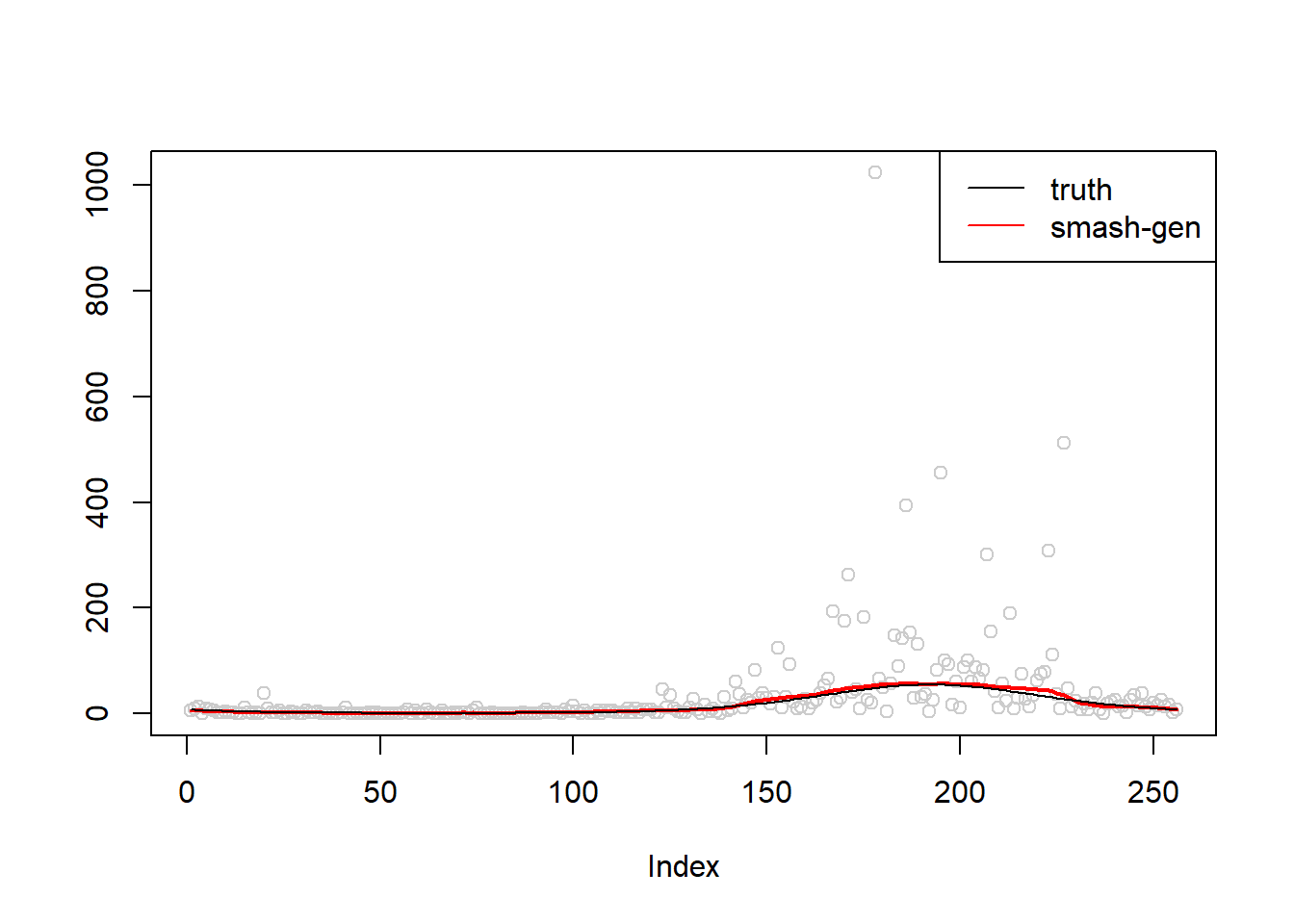
plot(simu.out$x,col = "gray80" ,ylab = '')
lines(simu.out$smash.out, col = "blue", lwd = 2)
lines(exp(m))
legend("topright",
c("truth", "smash"),
lty=c(1,1),
lwd=c(1,1),
cex = 1,
col=c("black", "blue"))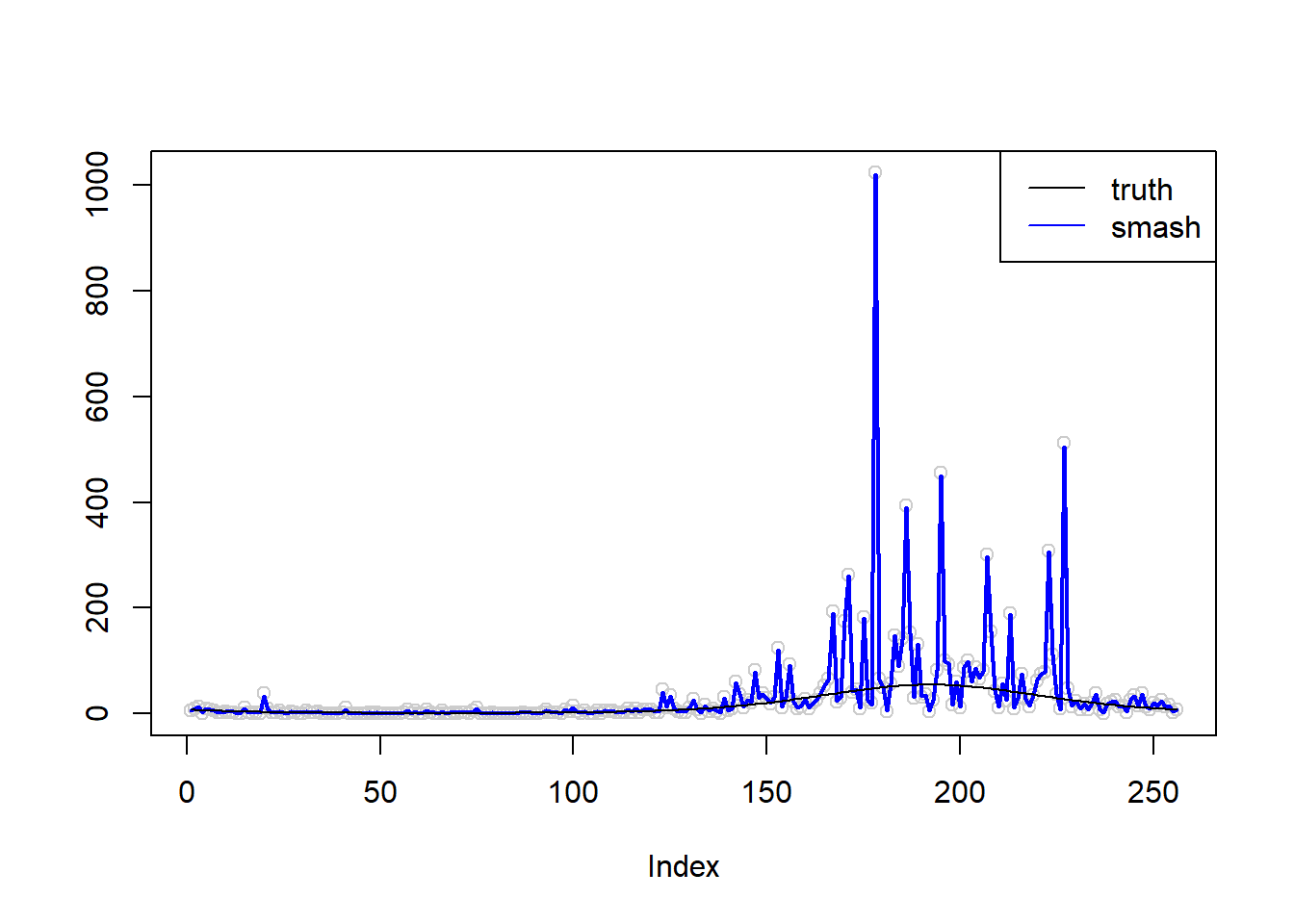
Summary
When there are extreme outiers(see step trend \(\sigma=1\)), the smash-gen algorithm does not converge. While for most of the cases, it converges and gives smooether estiamte than smash.
Session information
sessionInfo()R version 3.4.0 (2017-04-21)
Platform: x86_64-w64-mingw32/x64 (64-bit)
Running under: Windows 10 x64 (build 16299)
Matrix products: default
locale:
[1] LC_COLLATE=English_United States.1252
[2] LC_CTYPE=English_United States.1252
[3] LC_MONETARY=English_United States.1252
[4] LC_NUMERIC=C
[5] LC_TIME=English_United States.1252
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] smashr_1.1-1
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] Rcpp_0.12.16 knitr_1.20 whisker_0.3-2
[4] magrittr_1.5 workflowr_1.0.1 REBayes_1.3
[7] MASS_7.3-47 pscl_1.4.9 doParallel_1.0.11
[10] SQUAREM_2017.10-1 lattice_0.20-35 foreach_1.4.3
[13] ashr_2.2-7 stringr_1.3.0 caTools_1.17.1
[16] tools_3.4.0 parallel_3.4.0 grid_3.4.0
[19] data.table_1.10.4-3 R.oo_1.21.0 git2r_0.21.0
[22] iterators_1.0.8 htmltools_0.3.5 assertthat_0.2.0
[25] yaml_2.1.19 rprojroot_1.3-2 digest_0.6.13
[28] Matrix_1.2-9 bitops_1.0-6 codetools_0.2-15
[31] R.utils_2.6.0 evaluate_0.10 rmarkdown_1.8
[34] wavethresh_4.6.8 stringi_1.1.6 compiler_3.4.0
[37] Rmosek_8.0.69 backports_1.0.5 R.methodsS3_1.7.1
[40] truncnorm_1.0-7 This reproducible R Markdown analysis was created with workflowr 1.0.1